Inversor para coche: Todo lo que debe saber antes de enchufarlo
Índice
Cuando está de viaje y necesita un modo de alimentar su ordenador portátil, cargar su teléfono o incluso prepararse una taza de café, un inversor para coche se convierte en algo más que un práctico artilugio: cambia las reglas del juego. Tanto si acampas en la naturaleza como si trabajas a distancia desde tu vehículo o te preparas para emergencias, contar con un inversor fiable para el coche puede marcar la diferencia. Pero antes de enchufar uno, es importante saber cómo funciona, qué puede soportar la batería de tu coche y cómo elegir el tamaño y el tipo adecuados. En esta guía te explicamos todo lo que necesitas saber sobre los inversores de coche, cómo evitar los errores más comunes, qué dispositivos son seguros y cómo evitar que se agote la batería. Vamos a sumergirnos en las respuestas del mundo real que todo conductor necesita antes de invertir en un inversor de batería de coche, especialmente si está pensando en un potente inversor de 2000 vatios.
¿Qué es un inversor de corriente para coche y cómo funciona?
Si alguna vez ha necesitado cargar su portátil, encender un ventilador o hacer funcionar un pequeño electrodoméstico durante un viaje por carretera, es probable que alguien le haya mencionado la posibilidad de adquirir un inversor para su coche. Pero, ¿qué es exactamente y cómo funciona?
En esencia, un inversor de corriente para coche es un dispositivo que convierte la corriente continua (CC) de la batería de 12 voltios del coche en corriente alterna (CA), que es lo que necesitan la mayoría de los aparatos electrónicos domésticos. Básicamente, tiende un puente entre el sistema de alimentación del vehículo y los aparatos cotidianos de los que dependes. Sin él, sería imposible enchufar los dispositivos alimentados por CA directamente al vehículo.
¿Qué hace un inversor por un coche?
Un inversor de batería de coche tiene una finalidad principal: le permite utilizar enchufes de pared estándar en su vehículo. Piense en él como una minicentral eléctrica en su coche. Cuando conectas el inversor al encendedor o directamente a la batería del coche, convierte los 12 V de corriente continua en corriente alterna de 110 ó 120 V, según donde vivas. Algunos inversores de coche de gama alta ofrecen incluso puertos USB, pantallas LCD y varias tomas de corriente para cargar dispositivos simultáneamente.
La magia reside en los circuitos internos del inversor. Utiliza componentes electrónicos para invertir rápidamente la polaridad de la electricidad, imitando básicamente las formas de onda de CA a las que están acostumbrados sus aparatos. Esta conversión permite alimentar portátiles, ventiladores portátiles, videoconsolas o incluso una pequeña batidora directamente desde el vehículo.
Cómo los inversores de baterías de coche suministran energía doméstica en carretera
No todos los adaptadores de corriente para coche son iguales. La forma de conectar el inversor es importante. Los inversores más pequeños, normalmente de menos de 150 vatios, pueden conectarse directamente a la toma del encendedor del coche. Son ideales para cargadores de teléfonos, tabletas y portátiles pequeños.
Pero cuando se trate de cargas más pesadas, como un frigorífico portátil o un microondas de 700 W, tendrá que conectar el inversor directamente a la batería del coche con pinzas de cocodrilo o cableado. Aquí es donde entra en juego un inversor de 2000 vatios. Estos modelos más potentes están diseñados para tareas que consumen más energía, pero también exigen más al sistema eléctrico del vehículo. Si opta por esta opción, es esencial que conozca los límites de la batería y el alternador.
Tipos de inversores para coche: Onda sinusoidal pura frente a onda sinusoidal modificada
Al comprar un inversor para el coche, a menudo encontrará dos tipos: de onda sinusoidal pura y de onda sinusoidal modificada. He aquí el desglose:
- Los inversores de onda sinusoidal pura suministran una electricidad muy parecida a la de la red. Son ideales para aparatos electrónicos delicados, como dispositivos médicos, ordenadores portátiles nuevos y todo lo que tenga un motor que necesite una alimentación limpia y constante. Suelen ser más caros, pero ofrecen un rendimiento más suave y estable.
- Los inversores de onda sinusoidal modificada, en cambio, son más asequibles y suficientes para la mayoría de usos básicos, como cargadores de teléfonos, luces o herramientas eléctricas. Sin embargo, pueden provocar zumbidos en los equipos de audio o reducir la eficiencia de algunos electrodomésticos.
Conocer la diferencia le ayudará a tomar la decisión correcta, especialmente cuando dependa de que el inversor de la batería de su coche funcione de forma fiable sobre el terreno.

Elegir el inversor adecuado para su vehículo
Encontrar el inversor adecuado para el coche no es sólo cuestión de potencia, sino de conocer sus necesidades de energía, las limitaciones de su vehículo y su seguridad. No todos los inversores para coche son iguales, y una elección equivocada puede provocar rápidamente la muerte de la batería, el sobrecalentamiento de los cables o la fritura de los componentes electrónicos.
Veamos cómo elegir un inversor que se adapte a tu estilo de vida, tu equipo y las posibilidades de tu coche.
Factores a tener en cuenta antes de comprar un inversor para el coche
Antes de añadir a su cesta un inversor para el coche, hay varios factores clave que debe evaluar:
- Requisitos de potencia: ¿qué piensas utilizar realmente? Un cargador de móvil consume una fracción de la energía que consume una cafetera o un hervidor eléctrico. Comprueba siempre el vataje de tus dispositivos.
- Potencia continua frente a potencia pico: los inversores están clasificados tanto para potencia continua como para potencia pico. Un inversor de batería de coche puede indicar "2000W pico / 1500W continuos". Eso significa que puede manejar 2000 vatios brevemente, pero sólo 1500 vatios durante un tiempo.
- Tamaño y estado de la batería: si la batería de su vehículo es vieja o pequeña, es posible que tenga problemas para soportar inversores de mayor tamaño, sobre todo cuando el motor no está en marcha.
- Tipo de inversor - Decida entre onda sinusoidal pura y onda sinusoidal modificada en función de lo que vaya a alimentar.
- Método de instalación: ¿lo conectará a un puerto de 12 V o lo cableará a la batería? Su configuración determina tanto la comodidad como la seguridad.
Elegir el inversor de batería de coche adecuado no es sólo una cuestión de especificaciones, sino de adaptar su caso de uso real a la solución adecuada.
¿Un inversor de 2000 vatios es demasiado para mi vehículo?
Un inversor de 2000 vatios parece impresionante, y lo es, pero no es una solución válida para todos. Que sea "demasiado" depende del sistema eléctrico de tu vehículo y de cómo pienses utilizar el inversor.
Vamos a desglosarlo.
Un inversor de 2000 vatios puede extraer hasta 166 amperios de una batería de 12 V. La mayoría de las tomas de mechero tienen fusibles de 10 a 15 amperios. Esto significa que necesitarás una conexión directa a la batería, idealmente con cableado de alta resistencia y fusibles adecuados. Si el alternador y la batería no están a la altura, hacer funcionar un inversor de 2000 W durante demasiado tiempo podría sobrecargarlos o incluso dañarlos.
Dicho esto, si conduce un vehículo más grande, como un camión o un todoterreno, y sólo piensa utilizar el inversor mientras el motor está en marcha, un inversor de 2000 vatios para coche puede ser una opción sólida. Es muy popular entre los campistas y los conductores de furgonetas por una buena razón: puede con todo, desde microondas hasta herramientas eléctricas.
Así que no, no es necesariamente "demasiado". Pero tienes que ser realista sobre lo que tu coche puede soportar, sobre todo si no vas a actualizar la batería o el alternador.
Opciones de alimentación del adaptador para coche: Conexión directa al encendedor o a la batería
Opciones de alimentación del adaptador para coche: Conexión directa al encendedor o a la batería
En lo que respecta a los adaptadores de corriente para coche, hay dos formas principales de conectar el inversor: a través de la toma del encendedor o directamente a la batería. Cada una tiene sus pros, sus contras y sus limitaciones de potencia.
Enchufe para mechero
- Ventajas: Rápido, fácil, sin necesidad de herramientas. Ideal para inversores pequeños (menos de 150 W).
- Contras: Corriente limitada (normalmente 10-15 amperios), por lo que no puedes alimentar aparatos grandes. Riesgo de fundir un fusible si lo aprietas demasiado.
Conexión directa a la batería
- Ventajas: Permite utilizar inversores de coche de gran potencia, hasta 2000 W o más. Fuente de alimentación más estable.
- Contras: Requiere más configuración: cables adecuados, fusibles y, posiblemente, un relé o interruptor. Más arriesgado si no se hace correctamente.
Si sólo quieres alimentar un teléfono, un ventilador o un pequeño ordenador portátil, puedes utilizar el encendedor. Pero si quieres usar una batidora, una mininevera o un hervidor eléctrico, lo más seguro es usar la batería directamente.
Recuerde: cuanto mayor sea el inversor para coche, más potencia demandará y más crítico será el método de conexión.
Cómo calcular el tamaño del inversor que necesita
La elección del inversor adecuado para el coche empieza con una pregunta sencilla: ¿Qué necesita alimentar y durante cuánto tiempo?
Paso 1: Sume los vatios
Comprueba la potencia nominal de cada aparato que vayas a utilizar: televisor, portátil, máquina de CPAP, calefactor pequeño, etc. Si los utilizas al mismo tiempo, debes sumar su potencia total. Si el portátil consume 100 W y el televisor 150 W, necesitarás al menos un inversor de batería de coche de 300 W, más un margen de seguridad.
Paso 2: Factor de potencia máxima
Algunos aparatos, sobre todo los que tienen motor, como los frigoríficos o las herramientas eléctricas, necesitan más potencia para arrancar que para funcionar. Es lo que se denomina pico de potencia. Asegúrate de que tu inversor puede soportarlo.
Paso 3: Adaptar a la capacidad de la batería
Una batería de coche pequeña no da para mucho. Una batería de 100Ah (amperios-hora) proporciona unos 1200 vatios-hora a 12V. Si utilizas un aparato de 300 W, en teoría tienes cuatro horas de autonomía. En la realidad, querrás mantener el uso de la batería por debajo de 50% para evitar daños.
Paso 4: Tenga en cuenta sus hábitos de uso
¿El motor del coche estará en marcha mientras el inversor esté encendido? ¿Piensa alimentar objetos durante la noche? Estos hábitos de uso determinan si necesita una unidad básica de 300 W o un potente inversor de 2000 vatios.
Consejo final:
Utilice esta sencilla fórmula para calcular el consumo de corriente continua:
Vatios ÷ Voltios = Amperios
Así, 600 vatios ÷ 12 voltios = 50 amperios. Eso es mucha corriente, más de la que puede soportar tu encendedor.
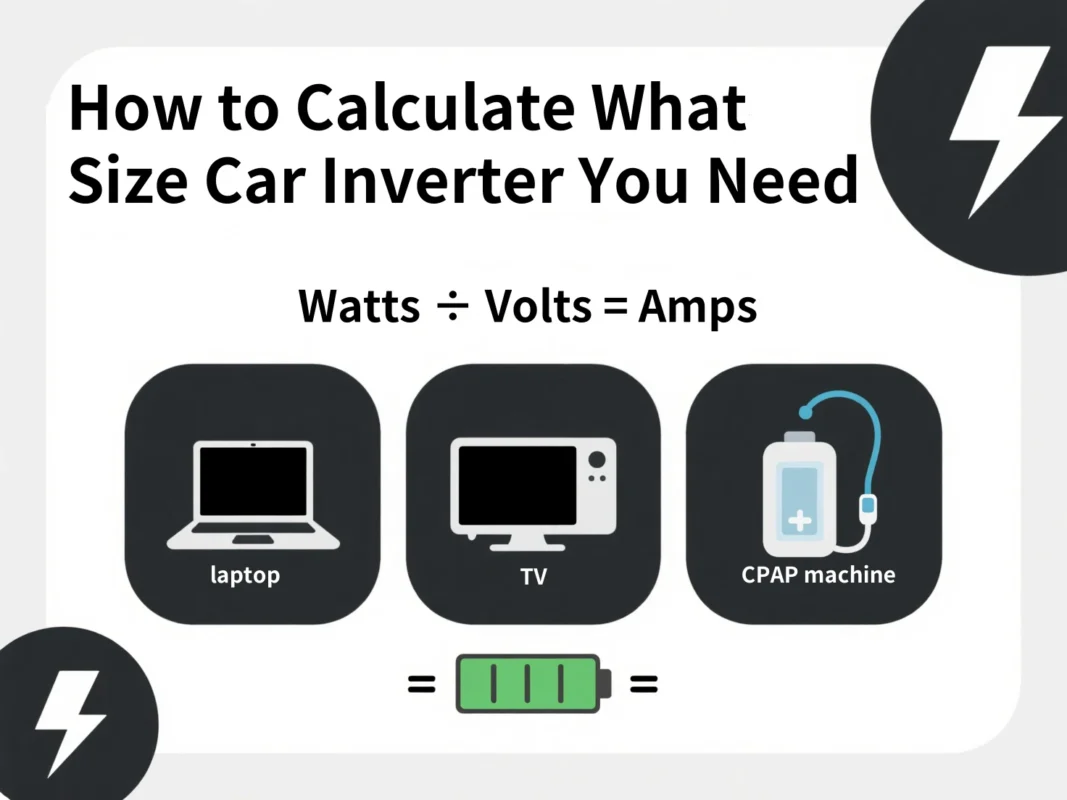
¿Qué se puede alimentar con un inversor de automóvil?
Cuando se trata de utilizar un inversor para el coche, una de las primeras preguntas que se hacen los conductores es: ¿Qué puedo enchufar exactamente a este trasto? ¿La respuesta corta? Muchas cosas, siempre que conozca las limitaciones del inversor y la capacidad de la batería de su coche.
Tanto si acampa sin conexión a la red eléctrica como si trabaja a distancia desde su vehículo o simplemente necesita energía de reserva en caso de emergencia, los inversores para coche le abren las puertas a un amplio abanico de posibilidades. Pero no todo lo que tiene enchufe es válido.
Vamos a desglosarlo por opciones seguras, casos especiales como los frigoríficos, y los dispositivos que definitivamente debe evitar.
Dispositivos comunes que puede utilizar con seguridad
Con el inversor para coche adecuado, puede alimentar de forma segura muchos aparatos domésticos y de viaje comunes. Estas son algunas categorías de dispositivos que funcionan bien con la mayoría de los inversores de batería para coche, especialmente los de 150-1000 vatios:
- Portátiles y tabletas: un cargador de portátil suele consumir entre 60 y 100 W. Perfecto para profesionales móviles.
- Smartphones y pequeños dispositivos electrónicos: utiliza el adaptador de corriente del coche para cargar teléfonos, lectores electrónicos, GoPros o dispositivos de juego portátiles.
- Ventiladores o luces portátiles: las lámparas LED o los ventiladores de 12 V funcionan muy bien con un inversor de menor potencia.
- Máquinas CPAP - Para las personas con apnea del sueño, un inversor de corriente para coche puede mantener en funcionamiento una CPAP durante la noche si se dimensiona correctamente.
- Televisores y monitores: los televisores de pantalla plana de menos de 32″ suelen tener menos de 200 W, lo que los convierte en una opción segura para los inversores de tamaño medio.
- Pequeños electrodomésticos de cocina - Cosas como batidoras, sandwicheras o incluso un pequeño microondas pueden funcionar con un inversor de coche de 2000 vatios, siempre que la batería y el alternador de tu coche estén preparados para la tarea.
Recuerde que no se trata sólo de lo que hace funcionar, sino de cuánto tiempo lo hace. Incluso los pequeños aparatos electrónicos pueden agotar la batería si se dejan encendidos demasiado tiempo con el motor apagado.
¿Se puede utilizar un frigorífico con el inversor del coche?
Esta es una de las preguntas más frecuentes, y con razón. Mantener los alimentos fríos mientras se está de acampada o durante un corte de electricidad puede cambiar las reglas del juego. Entonces, ¿puede un coche hacer funcionar un frigorífico con un inversor? La respuesta es sí, con algunas salvedades importantes.
En primer lugar, necesitará un inversor de batería de coche con una potencia nominal de al menos 1.000 a 1.500 vatios, preferiblemente de onda sinusoidal pura si va a alimentar un aparato sensible o con compresor, como un mini frigorífico o un congelador. Muchos frigoríficos tienen picos de arranque que duplican o triplican temporalmente su consumo normal.
Por ejemplo, un frigorífico compacto puede tener una potencia continua de 150 W, pero una sobretensión de 500 W o más al arrancar. Un inversor de 2000 vatios para el coche te da la potencia necesaria.
En segundo lugar, la capacidad de la batería es importante. Hacer funcionar una nevera durante la noche sin el motor encendido puede agotar rápidamente una batería de 12 V. Usted querrá:
- Doble batería
- Una batería auxiliar de ciclo profundo
- O planea mantener el motor en marcha periódicamente para recargar
En tercer lugar, piense en la eficiencia del inversor. Ni siquiera un inversor de calidad para el coche es 100% eficiente. La pérdida de energía en la conversión de CC a CA es de 10-15%. Si el frigorífico necesita 500 vatios, el sistema puede extraer de la batería entre 550 y 575 vatios.
En resumen: sí, se puede hacer funcionar un frigorífico con un inversor de coche, pero sólo si la instalación tiene el tamaño adecuado y la estrategia de baterías es sólida.
Cosas que no debes enchufar a un inversor
Sólo porque algo tenga un enchufe no significa que sea seguro -o inteligente- conectarlo a su inversor para coche. Algunos dispositivos consumen demasiada corriente, dependen de formas de onda específicas o suponen un riesgo para la seguridad en un entorno móvil.
Esto es lo que hay que evitar:
Calefactores de alto voltaje
Piense en calefactores, secadores de pelo, cafeteras, tostadoras o hornillos. Suelen consumir entre 1.000 y 1.500 W o más de forma continua, lo que puede sobrecargar el inversor de la batería del coche, sobre todo si el alternador no da abasto.
Cargas inductivas con sobretensiones de arranque
Algunas herramientas, como las sierras circulares, los taladros o los compresores de aire, necesitan una gran potencia de arranque, aunque su potencia nominal continua parezca segura. A menos que utilices un inversor para coche de 2000 vatios o más, y tu vehículo esté preparado para la carga, es mejor evitarlos.
Dispositivos médicos sin batería de reserva
Algunos dispositivos médicos sensibles pueden requerir una alimentación ininterrumpida y limpia. Si depende de ellos para su salud y seguridad, no confíe únicamente en un inversor de automóvil, a menos que se trate de un modelo de onda sinusoidal pura con una batería de reserva robusta.
Electrodomésticos con controles digitales
Aparatos como lavadoras, frigoríficos grandes o electrodomésticos con pantallas digitales y compresores pueden comportarse de forma errática o apagarse por completo con un inversor de onda sinusoidal modificada. Por eso los expertos suelen recomendar inversores de onda sinusoidal pura para este tipo de aplicaciones.
En general, si no estás seguro de enchufar algo, lee la etiqueta. Si consume más de 400 vatios, merece la pena comprobar si el sistema de alimentación del adaptador del coche y el inversor pueden soportarlo.
¿Cuánto tiempo puede funcionar la batería de un coche con un inversor?
Al utilizar un inversor para el coche, una de las preguntas más prácticas a las que se enfrentará es: ¿Cuánto tiempo puedo hacer funcionar mis dispositivos antes de que se agote la batería? Tanto si se trata de hacer funcionar un portátil durante un largo viaje por carretera como de alimentar un mini frigorífico durante la noche, la capacidad de la batería del coche y el consumo de energía de los dispositivos marcan la diferencia.
Por desgracia, no hay una respuesta única. Depende del tamaño del inversor de la batería del coche, de la capacidad de la batería, de la potencia del dispositivo que utilices y del tiempo que pienses utilizarlo.
Veamos los factores clave que influyen en el tiempo de funcionamiento y qué puedes hacer para evitar quedarte tirado con la batería descargada.
¿Descargan los inversores las baterías de los coches?
Sí, pueden hacerlo, y lo harán si no tienes cuidado.
Cada vez que utilice un inversor para coche sin el motor en marcha, estará extrayendo energía directamente de la batería de su coche. Cuanto mayor sea la potencia, más rápido se agotará. Esto es especialmente cierto en el caso de los inversores para coche que utilizan grandes electrodomésticos o varios dispositivos a la vez.
Un error común que comete la gente es asumir que sólo porque un inversor está conectado a través de un adaptador de corriente del coche (como el encendedor de cigarrillos), es automáticamente seguro. En realidad, si la carga supera la generación de energía en reposo del coche, la batería se agota. Si lo dejas en marcha el tiempo suficiente, necesitarás un puente de arranque.
Incluso con el motor en marcha, el alternador tiene límites. Por ejemplo, un alternador estándar puede producir entre 80 y 120 amperios. Si el inversor y los dispositivos demandan más que eso, el sistema seguirá tirando de la batería y acabará agotándola.
Así que sí, los inversores de batería de coche pueden agotar su batería. Pero con un uso inteligente y un poco de planificación, puedes evitarlo por completo.
¿Cuánto dura una batería de 12 V con un inversor?
Aquí es donde entran en juego los números. El tiempo de ejecución depende de dos cosas:
- Capacidad de la batería (medida en amperios-hora o Ah)
- Carga del inversor y los dispositivos conectados (vatios)
Supongamos que tiene una batería de coche estándar de 12 V y 70 Ah. Eso significa que, en teoría, puede suministrar 70 amperios durante una hora, o 7 amperios durante 10 horas. Pero utilizar un inversor para el coche cambia un poco las matemáticas debido a las pérdidas por conversión de energía (normalmente 10-15%).
Hagamos un ejemplo rápido:
- Batería: 12 V, 70 Ah → Son 840 vatios-hora (12 V × 70 Ah).
- Consumo del dispositivo: Un portátil que consume 90 vatios
- Eficiencia del inversor: 85%
Por lo tanto, sus vatios-hora reales utilizables = 840Wh × 0,85 = 714Wh
714Wh ÷ 90W = ~7,9 horas de autonomía (si está completamente cargado, sin otras pérdidas)
Supongamos que utilizas un inversor de 2000 vatios para alimentar un pequeño microondas de 800 vatios.
714Wh ÷ 800W = menos de una hora, y te arriesgas a dañar la batería descargándola tan bajo.
Si utilizas un aparato como un mini frigorífico que consume 100 W de forma continua, una batería de 12 V totalmente cargada puede durar entre 6 y 7 horas como máximo. Pero las descargas profundas frecuentes acortan la vida útil de la batería.
Así que, aunque puedes utilizar el inversor de batería de tu coche para alimentar dispositivos durante unas horas, sé precavido. No es una fuente de energía ilimitada.
Cómo evitar que la batería se descargue al utilizar un inversor
Nadie quiere despertarse en un camping o terminar una sesión de trabajo a distancia para descubrir que se ha agotado la batería. Por suerte, hay formas inteligentes de evitarlo.
Hacer funcionar el motor con cargas elevadas
Si está alimentando algo de más de 150 vatios, es mejor mantener el motor en marcha. De ese modo, el alternador puede ayudar a suministrar corriente al inversor para coche y ralentizar el agotamiento de la batería.
Utilice una batería auxiliar de ciclo profundo
Muchos autocaravanistas y viajeros sin conexión a la red instalan una batería de ciclo profundo separada específicamente para los inversores de potencia de sus coches. Estas baterías están diseñadas para descargarse y recargarse repetidamente sin sufrir daños.
Utiliza un monitor de batería
Existen monitores de batería compactos que te permiten controlar el nivel de carga en tiempo real. Si utilizas un adaptador para el coche, un medidor de voltaje básico puede indicarte si el nivel es demasiado bajo.
Configurar una desconexión automática por baja tensión (LVD)
Algunos inversores incorporan funciones LVD, que desconectan automáticamente el inversor si la batería desciende por debajo de un umbral de seguridad (normalmente entre 10,5 y 11 V). Esto ayuda a proteger la batería de daños permanentes.
Go Solar
Combinar el inversor para coche con un sistema compacto de paneles solares puede proporcionarle una forma renovable de recargar durante el día, especialmente si acampa o viaja durante largos periodos.
En resumen, la gestión inteligente lo es todo. Un inversor de batería de coche es una herramienta poderosa, pero sólo si la utilizas sabiamente. No confíe en conjeturas. Controle su uso, conozca los límites de su batería y planifique en consecuencia.
Seguridad, riesgos y desventajas de los inversores de coche
¿Son seguros los inversores de coche?
Sí, si se utiliza correctamente. Un inversor de coche de alta calidad incluye protecciones incorporadas como:
- Protección contra sobrecargas
- Desconexión por sobrecalentamiento
- Alarmas de baja tensión
- Prevención de cortocircuitos
Elija marcas de confianza y siga las directrices de instalación.
¿Cuáles son las desventajas de un inversor de automóvil?
A pesar de su utilidad, los inversores para coche tienen inconvenientes:
- Agotar la batería rápidamente
- Puede sobrecalentarse si no se ventila correctamente
- Puede que no admita aparatos de gran potencia
- Puede interferir con la radio o la electrónica sensible
También ocupan espacio y requieren una instalación cuidadosa.
Errores de instalación que podrían dañar su vehículo
Estos son los errores más comunes que hay que evitar:
- Utilización de cableado demasiado pequeño
- Saltarse un fusible o un disyuntor
- Sobrecarga del inversor
- Funcionamiento del inversor sin ventilación
Una mala instalación puede provocar circuitos quemados, baterías descargadas o incluso riesgos de incendio.
¿Merecen la pena los inversores de coche?
Cuando un inversor de automóvil cambia las reglas del juego
Si acampa, viaja por trabajo o se prepara para emergencias, un inversor para el coche es imprescindible. Puede alimentar tu trabajo desde el coche, mantener en funcionamiento tus dispositivos médicos o permitirte preparar café sobre la marcha.
Para los amantes de las furgonetas y las autocaravanas, un inversor de 2000 vatios es casi imprescindible.
Cuándo es mejor evitarlo
Si sólo conduce distancias cortas o rara vez utiliza aparatos electrónicos en su coche, puede que el coste y la complejidad no merezcan la pena. Los conductores urbanos habituales quizá no necesiten más que un simple cargador USB.
Alternativas a los inversores para coche
Si no quieres ocuparte de la instalación ni de agotar la batería del vehículo, plantéatelo:
- Centrales eléctricas portátiles
- Baterías USB de gran capacidad
- Cargadores solares
Ofrecen flexibilidad sin intervenir en el sistema eléctrico del vehículo.
Conclusión
Si su estilo de vida implica viajar, acampar o trabajar de forma móvil, un inversor para coche es una inversión inteligente. Sólo tiene que asegurarse de elegir el tamaño adecuado, instalarlo correctamente y utilizarlo de forma responsable. Para cualquiera que necesite energía constante y portátil durante sus desplazamientos, un inversor para coche ofrece una comodidad y fiabilidad inigualables. Si desea comprar un inversor para uso doméstico o comercial puede elegir Afore. Afore es una conocida fabricante de inversores solares. Sus productos incluyen inversores híbridos, inversores de almacenamiento de energíainversores monofásicos e inversores trifásicos, entre otros.

Preguntas frecuentes
1. ¿Qué hace un inversor por un coche?
Un inversor de corriente para coche convierte la corriente continua (CC) de la batería de 12 V del coche en corriente alterna (CA), el mismo tipo de electricidad que se encuentra en los enchufes domésticos. Esto te permite enchufar dispositivos estándar como portátiles, televisores o incluso pequeños electrodomésticos mientras viajas. Sin un inversor de coche, estarías limitado a equipos alimentados por USB o dispositivos que sólo funcionan con la alimentación del adaptador del coche.
2. ¿Qué no debe conectarse a un inversor?
No todos los aparatos son compatibles con el inversor. Evite enchufarlos:
- Elementos calefactores de alta potencia (secadores de pelo, calefactores)
- Equipos médicos, a menos que el inversor sea de onda sinusoidal pura y esté dimensionado para esa carga.
- Cargas inductivas como compresores de aire o algunas herramientas eléctricas, a menos que disponga de un inversor de batería de coche de alta potencia.
Además, no enchufes nada que supere la potencia nominal del inversor, sobre todo si se trata de un inversor para coche de 2000 vatios, que puede parecer muy potente pero tiene sus límites en función de la capacidad de la batería del coche y del método de conexión.
3. ¿Merecen la pena los inversores para coche?
Los inversores para coche son una de las herramientas más útiles y asequibles para viajeros, camioneros, trabajadores remotos y aventureros al aire libre. Tanto si se trata de cargar una cámara en un viaje fotográfico como de hacer funcionar una pequeña nevera en un fin de semana de acampada, un inversor para coche convierte su vehículo en una central eléctrica móvil. Sólo tiene que asegurarse de que el tamaño del inversor se ajusta a sus necesidades y a las capacidades de su coche.
4. ¿Los inversores descargan las baterías de los coches?
Sí, pueden hacerlo, sobre todo si las dejas en marcha con el motor apagado. Una carga pequeña puede tardar varias horas en agotar la batería, mientras que una grande podría hacerlo en menos de una hora. Por eso es importante utilizar los inversores de batería del coche con prudencia, controlar los niveles de voltaje y encender el motor cuando se utilizan dispositivos de alta potencia.
5. ¿Qué puede funcionar con un inversor de coche?
Puede hacer funcionar una sorprendente variedad de dispositivos con un inversor para coche de la potencia adecuada:
- Portátiles, tabletas y teléfonos
- Televisores LED y reproductores de DVD portátiles
- Pequeños electrodomésticos de cocina (tostadoras, cafeteras)
- Ventiladores, iluminación y herramientas eléctricas
- Incluso mini neveras (con la potencia adecuada)
La clave está en saber cuántos vatios consumen tus aparatos y si el inversor de tu coche puede soportar esa carga.
6. ¿Cómo puedo evitar que la batería se descargue con el inversor?
He aquí algunos consejos:
- Mantén el motor en marcha cuando utilices dispositivos de alta potencia
- Utiliza una batería secundaria de ciclo profundo para un uso prolongado
- Instale un interruptor de desconexión de bajo voltaje
- Controla el voltaje de la batería
- Si utiliza un puerto de alimentación para adaptador de coche, limite el uso a dispositivos pequeños.
Estas estrategias ayudan a evitar que las baterías se agoten de forma inesperada y prolongan la vida útil tanto de la batería como del inversor.
7. ¿Puede funcionar un frigorífico con un inversor de coche?
Sí, pero depende del frigorífico y del tamaño del inversor. Un frigorífico estándar de 12 V puede consumir sólo entre 50 y 100 vatios, pero un frigorífico de CA de tipo dormitorio puede consumir más de 200 vatios y aumentar más durante el arranque. Un inversor de coche de 2.000 vatios suele ser suficiente, pero debe conectarse directamente a la batería, no a través de la toma del encendedor. Compruebe siempre la potencia nominal de su frigorífico y confirme que su instalación puede soportarla durante el tiempo de funcionamiento deseado.
8. ¿Cuáles son las desventajas de un inversor para coche?
Aunque son increíblemente prácticos, los inversores para coche tienen algunos inconvenientes:
- Pueden agotar la batería si se utilizan sin cuidado.
- Los modelos baratos pueden producir energía de "onda sinusoidal modificada", que no es ideal para la electrónica sensible.
- Los inversores grandes (como un inversor de coche de 2000 vatios) requieren un cableado resistente y, potencialmente, protección con fusibles.
- Los inversores generan calor, por lo que una ventilación inadecuada puede provocar un sobrecalentamiento.
Aun así, con las precauciones adecuadas, las ventajas suelen superar a los inconvenientes.
9. ¿Es seguro utilizar un inversor de 2000 vatios para el coche?
Es seguro si se instala y utiliza correctamente. Un inversor de 2000 vatios consume mucha corriente -hasta 160-180 amperios en carga máxima-, por lo que nunca debe enchufarse al encendedor del coche. Debe conectarse directamente a la batería con cables de calibre grueso y con los fusibles adecuados. Para cargas elevadas, mantenga siempre el motor en marcha y no supere los límites eléctricos del vehículo.
10. ¿Puedo dejar un inversor enchufado todo el tiempo?
Técnicamente, sí, pero no es recomendable. Incluso cuando no se utilizan activamente, los inversores consumen una pequeña cantidad de energía llamada corriente de reposo. Con el tiempo, esto puede agotar la batería, sobre todo si deja el coche aparcado durante días. Si el inversor de la batería del coche tiene un modo de desconexión o de espera incorporado, es más seguro, pero sigue siendo mejor desenchufarlo cuando no se necesita.