Inversores solares comerciales: Empresas más inteligentes

Índice
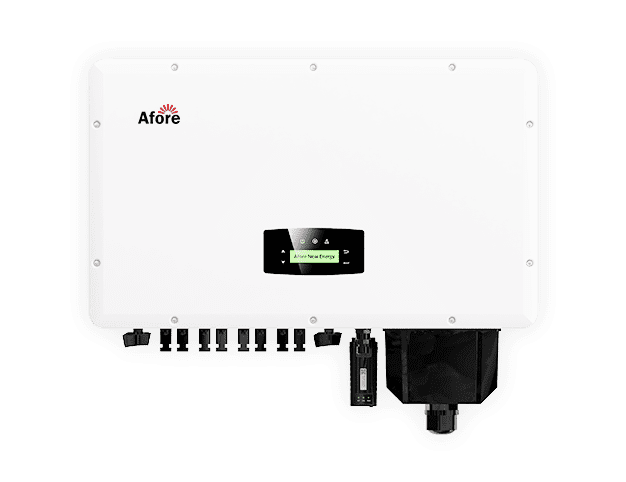
Si ha estado estudiando la energía solar para su empresa, es probable que se haya topado una y otra vez con el término inversores solares comerciales. Y con razón. Estos dispositivos son el corazón de cualquier instalación solar. Convierten la corriente continua (CC) producida por los paneles solares en corriente alterna (CA) que su empresa puede utilizar realmente. Sin ellos, los paneles no son más que silenciosos colectores de luz solar.
Pero, ¿qué diferencia exactamente a un inversor solar comercial de los que se instalan en casa? En pocas palabras, la escala y la capacidad. Los sistemas residenciales están diseñados para cubrir las necesidades energéticas de un hogar, a menudo de menos de 10 kW. En cambio, los inversores solares comerciales están diseñados para gestionar cargas mucho mayores, desde decenas de kilovatios hasta megavatios.
También se fabrican para ofrecer durabilidad, eficiencia y gestión inteligente. Los mejores modelos pueden supervisar cada cadena de paneles, ajustar la potencia mediante el seguimiento del punto de máxima potencia (MPPT) e incluso sincronizarse perfectamente con el almacenamiento en baterías o la red. Ese nivel de sofisticación las hace indispensables para cualquier empresa que intente recortar gastos, reducir la huella de carbono y proyectar una imagen de futuro.
¿Qué es un inversor comercial?
Cuando las empresas exploran la energía solar, uno de los primeros términos técnicos que encuentran son los inversores solares comerciales. Pero, ¿qué significa eso exactamente y por qué es tan importante?
En su forma más simple, un inversor comercial es un tipo especializado de inversor solar que convierte la electricidad de corriente continua (CC) generada por los paneles solares en corriente alterna (CA), que alimenta sus luces, ordenadores, sistemas de climatización y maquinaria. Mientras que los inversores residenciales están diseñados para sistemas de pequeña escala -normalmente de 3 a 10 kilovatios-, los inversores solares comerciales están diseñados para gestionar una capacidad mucho mayor, desde 20 kilovatios en el tejado de una pequeña oficina hasta varios megavatios para grandes almacenes, hospitales o instalaciones industriales.
Diferencias entre un inversor comercial y un inversor residencial
- Escala y capacidad: Un inversor residencial puede gestionar una docena de paneles, pero un inversor comercial puede coordinar cientos o incluso miles, suministrando energía constante para apoyar operaciones empresariales complejas.
- Durabilidad: Dado que se espera que los sistemas comerciales funcionen de forma continua, los inversores están fabricados con componentes robustos que pueden soportar altas cargas eléctricas, temperaturas extremas y largas horas de funcionamiento.
- Funciones inteligentes: Los inversores solares comerciales modernos incluyen monitorización en tiempo real, diagnóstico remoto y seguimiento avanzado del punto de máxima potencia (MPPT), lo que garantiza que cada panel contribuya con la máxima eficiencia.
Tipos de inversores comerciales
No existe un único "inversor comercial". Las empresas pueden elegir entre varias categorías en función de sus necesidades:
- Inversores de cadenas: Varias cadenas de paneles se conectan a cada inversor, ideal para tejados de tamaño medio con luz solar constante.
- Inversores centrales: La opción más potente, capaz de gestionar miles de paneles a la vez. Suelen utilizarse en huertas solares o grandes complejos comerciales.
- Inversores híbridos: Combinan las capacidades de la energía solar y la batería, cambiando automáticamente entre las fuentes para proporcionar energía estable durante los cortes o los periodos de precios máximos.
- Microinversores: Menos comunes en sistemas a gran escala, pero útiles cuando los tejados tienen sombras o diferentes ángulos de inclinación, ya que optimizan la producción a nivel de panel.
Por qué es importante un inversor comercial
Sin el inversor adecuado, sus paneles solares no pueden suministrar electricidad utilizable. Un inversor mal dimensionado o de baja calidad puede atascar su sistema, reducir la eficiencia e incluso acortar la vida útil de su inversión. Por otro lado, la elección del inversor solar comercial correcto garantiza:
- Máxima eficiencia de conversión (hasta 98,5% en los modelos superiores).
- Tiempo de actividad fiable para operaciones de misión crítica.
- Flexibilidad para ampliar el sistema a medida que aumenta la demanda de energía.
- Un camino más fácil para alcanzar los objetivos de sostenibilidad al tiempo que se reducen los costes energéticos.

Elegir el mejor sistema solar para uso comercial
Instalar energía solar ya no es sólo una cuestión ecológica, sino una inversión inteligente a largo plazo. Pero con tantas opciones disponibles, ¿cómo saber qué combinación de paneles e inversores solares comerciales es la adecuada para su empresa? La respuesta está en conocer los tipos de inversores, sopesar los criterios de selección más importantes y adaptar el diseño del sistema a las necesidades energéticas específicas de su empresa.
Criterios clave de selección
No todos los inversores solares comerciales son iguales. Cuando reduzca sus opciones, tenga en cuenta estos factores:
- Eficacia
Un pequeño aumento de la eficiencia de conversión -por ejemplo, de 97% a 98,5%- puede ahorrar miles de dólares a lo largo de la vida útil de un sistema.
- Escalabilidad
Piense dónde estará su empresa dentro de cinco o diez años. Puede el sistema inversor crecer a la par que sus necesidades energéticas?
- Fiabilidad
El tiempo de inactividad puede ser perjudicial. Busque inversores con un historial probado y garantías sólidas, preferiblemente de fabricantes con una red de asistencia mundial.
- Supervisión y funciones inteligentes
Las plataformas de supervisión avanzadas le permiten comprobar el rendimiento en tiempo real, solucionar problemas a distancia y detectar pequeños problemas antes de que se conviertan en costosas averías.
- Garantía y servicio
Dado que la mayoría de los inversores duran entre 10 y 15 años, una garantía sólida no es negociable.
- Coste vs. Valor
No caiga en la trampa de elegir el modelo más barato por adelantado. La oferta más barata suele conllevar costes ocultos en pérdidas de eficiencia, tiempos de inactividad o sustitución prematura.
¿Cuál es el mejor sistema solar para uso comercial?
El "mejor" sistema no es un único producto, sino el que se adapta a las necesidades actuales y futuras de su organización.
- Para empresas medianas como oficinas, comercios o escuelas, los inversores monofásicos combinados con paneles solares comerciales de 350-400 W suelen ofrecer una excelente relación calidad-precio.
- Para grandes instalaciones como almacenes, fábricas u hospitales, los inversores centrales suelen ser la opción más eficiente y rentable.
- Para las empresas que necesitan resiliencia energética, especialmente las situadas en regiones con redes inestables, los inversores híbridos combinados con almacenamiento constituyen una potente salvaguarda contra los cortes y la volatilidad de los precios.
En última instancia, el mejor sistema solar es el que equilibra eficiencia, escalabilidad y rentabilidad de la inversión a largo plazo. Un proyecto bien diseñado no solo reducirá los costes de electricidad, sino que también reforzará su perfil de sostenibilidad, algo cada vez más valioso en el mercado actual.
Vida útil de los inversores de conexión a red: Expectativas y rendimiento real
Una de las primeras preguntas que se hacen los empresarios es: "¿Cuánto durarán realmente mis inversores solares comerciales?".
Categorías típicas de la vida útil
- Inversores monofásicos y centrales: 10-15 años de media.
- Inversores híbridos: 10-12 años, dependiendo de los ciclos de la batería.
- Microinversores: A menudo hasta 20-25 años, casi igualando la vida útil de los propios paneles solares.
Datos reales y garantía frente a rendimiento real
Aquí está el truco: aunque las garantías suelen prometer 5 años o más, los informes de campo muestran que muchos inversores fallan antes, a veces alrededor de los 6-7 años. Esto no significa que los fabricantes sean deshonestos; los inversores están expuestos al calor, el polvo, la humedad y las altas cargas eléctricas, que inevitablemente les pasan factura.
Aun así, con los cuidados adecuados, las empresas pueden esperar al menos una década de buen rendimiento antes de que sea necesaria su sustitución.
¿Cuál es la vida útil típica de un inversor de conexión a red?
La respuesta es sencilla: 10-15 años para la mayoría de los inversores solares comerciales. Los microinversores, sin embargo, pueden durar dos décadas o más. Este plazo significa que, en cualquier estrategia solar a largo plazo, las empresas deberían presupuestar la sustitución de un inversor durante los 25-30 años de vida útil de los paneles.

Comprender el comportamiento del inversor: Batería vs. Red
Otra preocupación común surge cuando el sistema parece comportarse de forma extraña.
¿Por qué mi inversor funciona con batería aunque haya corriente?
Esto puede resultar confuso, pero la respuesta suele ser sencilla. Los inversores pueden pasar al modo de batería aunque haya energía de la red debido a:
- Tensión de red baja (por debajo del rango de funcionamiento seguro).
- Subidas de tensión que podrían dañar los equipos.
- Frecuencia de red inestable.
- Ciclos de gestión de la batería, en los que el sistema mantiene el equilibrio de carga.
Por lo tanto, no se asuste si observa este comportamiento: a menudo es una señal de que su inversor de conexión a red está haciendo su trabajo de proteger los componentes electrónicos sensibles.
Funcionalidad del inversor híbrido
Los inversores híbridos son especialmente inteligentes a la hora de gestionar estas transiciones. Actúan como directores de orquesta, equilibrando a la perfección la entrada de energía solar, el suministro de red y las reservas de batería. Esto garantiza que su empresa disfrute de una energía constante y fiable, incluso cuando la red falla.
¿Merece la pena la energía solar comercial? Beneficios económicos y estratégicos
Para muchos empresarios, la gran pregunta no es cómo funciona la energía solar, sino si resulta rentable. La respuesta es clara: invertir en un sistema solar comercial, con inversores solares comerciales fiables, no es sólo una cuestión de responsabilidad medioambiental, sino de economía inteligente y estrategia a largo plazo. Veamos por qué.
Justificación financiera
El primer beneficio que la mayoría de las empresas tienen en cuenta es el ahorro de costes. Las facturas de electricidad comercial pueden ser uno de los mayores gastos de explotación, especialmente para fabricantes, almacenes e instalaciones con equipos que consumen mucha energía. Al generar su propia energía, se reduce la dependencia de la red y se reducen inmediatamente los gastos mensuales.
Las principales ventajas financieras son:
- Menores costes de explotación: Con los inversores solares comerciales que convierten la energía solar en energía de CA utilizable, las empresas pueden compensar una parte significativa de sus necesidades de electricidad.
- Incentivos y créditos fiscales: Muchas regiones ofrecen generosos descuentos, planes de amortización acelerada y créditos fiscales a la inversión que reducen el coste inicial de un proyecto solar.
- Retorno de la inversión predecible: Un sistema solar bien diseñado suele amortizarse en 7-10 años, tras lo cual la electricidad pasa a ser prácticamente gratuita.
- Protéjase contra el aumento de los costes energéticos: Las tarifas de los servicios públicos rara vez bajan. Asegurar una fuente de energía estable y renovable protege su cuenta de resultados frente a subidas de precios impredecibles.
En otras palabras, aunque la inversión inicial pueda parecer elevada, las cifras cobran sentido cuando se amplían. Las empresas no solo compran equipos, sino décadas de ahorro energético.
Ventajas medioambientales y estratégicas
Los beneficios de la energía solar van mucho más allá del balance. Los consumidores, los inversores e incluso los empleados de hoy en día se preocupan por la sostenibilidad. La instalación de inversores solares comerciales posiciona a su empresa como líder en responsabilidad corporativa.
Las ventajas estratégicas incluyen:
- Reputación de marca más sólida: El compromiso público con las energías renovables puede diferenciar a su empresa en mercados competitivos.
- Cumplimiento de la normativa: Muchas industrias se enfrentan a una presión cada vez mayor para cumplir las normas medioambientales. La energía solar ayuda a cumplir o superar esos requisitos.
- Independencia energética: La combinación de paneles solares inversor solar híbrido y el almacenamiento garantizan la continuidad de las operaciones críticas incluso durante los cortes de la red.
- Atractivo para empleados y clientes: La gente prefiere trabajar y apoyar a empresas que contribuyen activamente a un futuro más ecológico.
Puede que estos beneficios no financieros no se reflejen en la factura mensual de la luz, pero pueden tener un profundo impacto en el crecimiento, la resistencia y la percepción pública.
¿Merece la pena la energía solar comercial?
En pocas palabras: sí. Desde un punto de vista financiero y estratégico, la energía solar comercial es una de las mejoras de infraestructura más valiosas que puede hacer una empresa.
Un sistema basado en inversores solares comerciales de alta calidad no sólo reduce drásticamente los costes de electricidad, sino que también ofrece valor de reputación, ventajas de cumplimiento normativo y estabilidad a largo plazo. Tanto si dirige una pequeña oficina como una instalación multinacional, la decisión de optar por la energía solar ya no se trata solo de "ser ecológico", sino de seguir siendo competitivo y estar preparado para el futuro.
Entonces, ¿merece la pena la energía solar comercial? Desde luego que sí. La combinación de ahorro de costes, sostenibilidad y posicionamiento estratégico la convierte en una de las inversiones más inteligentes que puede hacer cualquier empresa moderna.

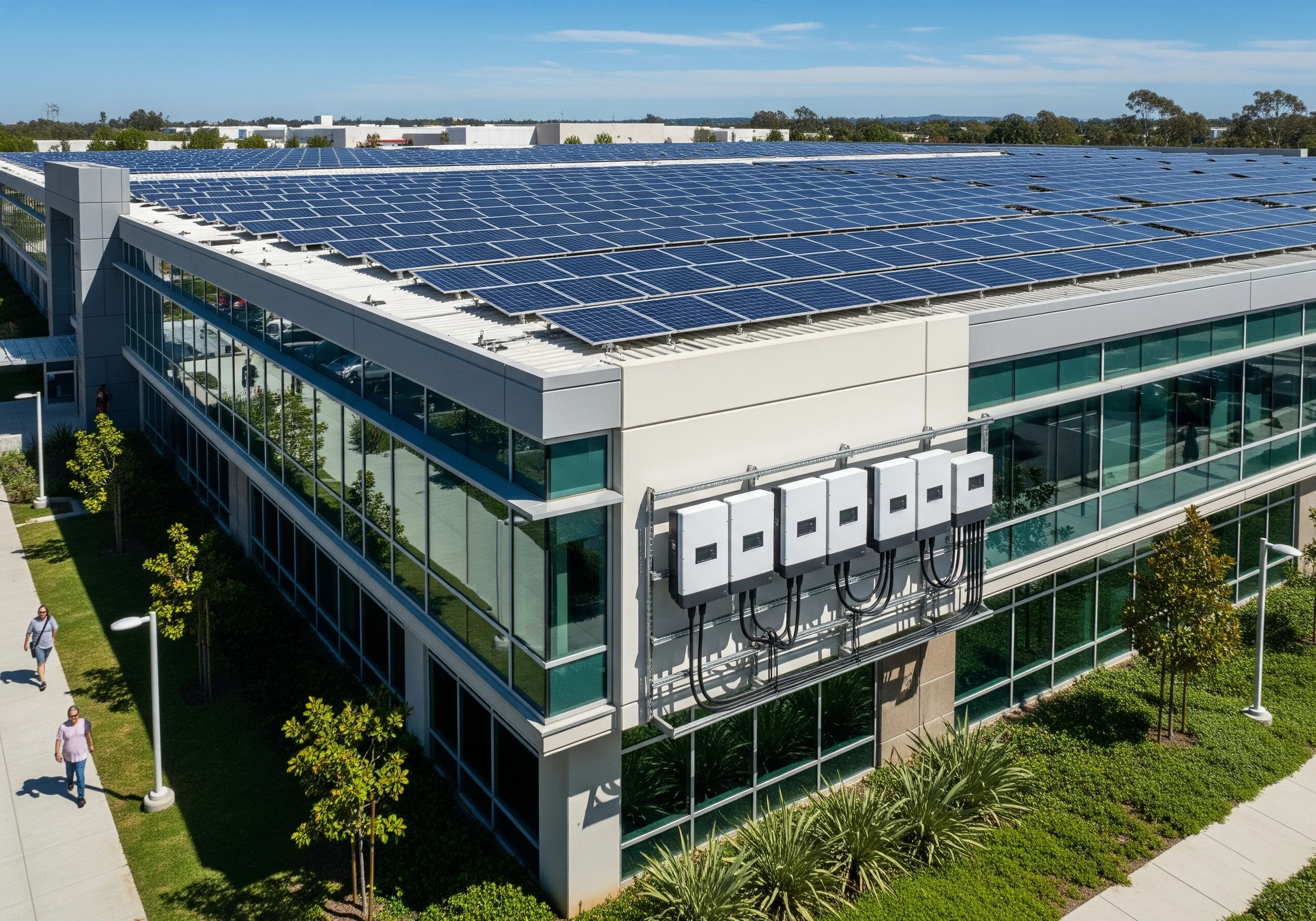
Métricas de los paneles solares comerciales
Cuando las empresas planifican un proyecto solar, a menudo se centran mucho en los inversores solares comerciales, y con razón, ya que los inversores determinan la eficacia con la que la energía solar se convierte en energía utilizable. Pero el rendimiento de su sistema solar también depende de los propios paneles. Comprender la potencia, el tamaño y las dimensiones típicas de los paneles solares comerciales garantiza que el inversor y los paneles funcionen perfectamente juntos para ofrecer la máxima eficiencia.
Potencia típica por panel solar comercial
La mayoría de los paneles solares comerciales modernos oscilan entre 350 y 400 vatios, aunque los nuevos módulos de alto rendimiento pueden alcanzar los 500-600 vatios. Estos paneles se construyen con células más grandes y materiales más avanzados que los paneles residenciales estándar, lo que los hace ideales para tejados y sistemas montados en el suelo donde es crucial maximizar la densidad de energía.
- Paneles de gama media (350-400 W): Comunes para escuelas, oficinas y edificios comerciales.
- Paneles de alta potencia (450-500 W): Adecuados para almacenes o plantas de fabricación con gran espacio en el tejado.
- Paneles de uso general (500-600 W): Normalmente emparejados con inversores solares comerciales centrales en grandes instalaciones, como centros de distribución o huertos solares.
Elegir la potencia adecuada es importante porque afecta tanto a la producción de energía como al diseño del sistema. Por ejemplo, si se combinan paneles de gran potencia con un inversor solar de tamaño insuficiente, puede producirse un recorte de la energía, con la consiguiente pérdida de rendimiento potencial. Por otro lado, los inversores demasiado grandes añaden costes innecesarios. Lograr el equilibrio adecuado entre la potencia de los paneles y la capacidad del inversor es clave para un sistema comercial de alto rendimiento.
Tamaño y dimensiones del panel
Los paneles solares comerciales son físicamente más grandes que los residenciales, tanto para dar cabida a una mayor potencia como para reducir el número de paneles necesarios para un tamaño de sistema determinado.
- Dimensiones estándar: Alrededor de 6,5 pies de alto por 3,25 pies de ancho (aproximadamente 2 metros × 1 metro).
- Peso: Normalmente entre 20 y 25 kg (45-55 libras), dependiendo de los materiales del marco y del grosor del cristal.
- Número de células: La mayoría de los módulos comerciales utilizan 72 ó 96 células solares, frente al formato de 60 células habitual en los paneles residenciales.
¿Por qué son importantes estos parámetros? Los paneles más grandes generan más energía por unidad, pero también requieren sistemas de estanterías más resistentes y un análisis estructural más cuidadoso. Durante el diseño del sistema hay que tener en cuenta la capacidad de carga del tejado, la resistencia al viento y la distancia entre los paneles. En los sistemas instalados en el suelo, el tamaño de los paneles influye en el uso del terreno y en la configuración de los inversores solares comerciales que los conectan.
Las dimensiones también influyen en el transporte y la instalación. Un panel demasiado pesado o difícil de manejar puede ralentizar la instalación y aumentar los costes de mano de obra. Los instaladores profesionales sopesan cuidadosamente estas consideraciones para asegurarse de que tanto los paneles como los inversores están optimizados para ser eficientes y prácticos.
Mantenimiento, supervisión y buenas prácticas
Instalar un sistema solar es sólo el primer paso. Para proteger su inversión y garantizar décadas de rendimiento fiable, las empresas deben comprometerse a realizar un mantenimiento y una supervisión adecuados. Incluso los inversores solares comerciales más avanzados y los paneles de alta eficiencia necesitan cuidados periódicos. Sin ellos, la eficiencia disminuye, los costes de funcionamiento aumentan y la vida útil del sistema puede acortarse.
Por qué es importante el mantenimiento
A diferencia de los paneles, que no tienen piezas móviles y pueden durar entre 25 y 30 años, los inversores son más sensibles. El calor, el polvo, las sobretensiones eléctricas y la humedad pueden degradar su rendimiento con el tiempo. Dado que se espera que la mayoría de los inversores solares comerciales duren entre 10 y 15 años, un cuidado proactivo ayuda a maximizar cada día de uso productivo.
El mantenimiento rutinario reduce el riesgo de fallos inesperados, evita costosos tiempos de inactividad y garantiza que su instalación solar siga proporcionando ahorros predecibles año tras año.
Buenas prácticas para el mantenimiento de inversores y sistemas
- Instalación correcta desde el primer día
La base del éxito a largo plazo es una instalación correcta. Los inversores deben colocarse en zonas sombreadas y bien ventiladas, lejos de fuentes directas de calor. Así se evita el sobrecalentamiento y se prolonga la vida útil de los componentes.
- Inspecciones programadas
Las empresas deben programar inspecciones profesionales al menos una vez al año, idealmente cada seis meses. Los técnicos pueden comprobar si hay cables sueltos, acumulación de polvo, corrosión y signos de desgaste en el interior de la carcasa del inversor.
- Limpieza y ventilación
El polvo y la suciedad son enemigos de la electrónica. Mantener las rejillas de ventilación despejadas y asegurar el flujo de aire alrededor de los inversores solares comerciales es esencial para evitar el sobrecalentamiento.
- Actualizaciones de firmware y software
Muchos inversores modernos vienen con sistemas de monitorización digital. Mantener el firmware actualizado garantiza la compatibilidad con la red, una mayor eficiencia y una mejor detección de fallos.
- Comprobaciones de integración de la batería
En los sistemas con inversores solares híbridos, las pruebas periódicas de los ciclos de gestión de la batería garantizan transiciones fluidas entre la energía solar, la de la batería y la de la red.
El papel de la vigilancia
Las plataformas avanzadas de supervisión son una de las mayores ventajas de los sistemas comerciales actuales. En lugar de esperar a que aparezca un problema en la factura de la luz, los cuadros de mando en tiempo real le permiten:
- Seguimiento del rendimiento del sistema panel por panel.
- Identifique caídas repentinas en la producción que puedan indicar sombreado, fallos en el cableado o problemas en el inversor.
- Reciba alertas al instante, lo que permite una rápida resolución de problemas.
- Generar informes detallados para compartir con las partes interesadas, demostrando el ahorro de energía y el progreso en la reducción de las emisiones de carbono.
Algunos inversores solares comerciales ofrecen incluso análisis predictivos, que le alertan antes de que se produzca un posible fallo. Este enfoque proactivo reduce al mínimo el tiempo de inactividad y protege la productividad.
Planificación de la sustitución
Incluso con las mejores prácticas, ningún inversor dura para siempre. Dado que la vida útil típica de un inversor solar es inferior a la de los paneles, las empresas deben prever un ciclo de sustitución durante la vida útil del sistema. Presupuestarlo garantiza una transición fluida, sin interrupciones en las operaciones.

Conclusión
Pasarse a la energía solar es algo más que una decisión económica: es un paso estratégico hacia la sostenibilidad, la independencia y la resistencia. Al elegir la inversores solares comercialesplanificando su vida útil y manteniéndolas adecuadamente, las empresas pueden obtener décadas de energía limpia y fiable.
La conclusión es clara:
- Invierta en calidad.
- Adapte el tipo de inversor a las necesidades de su empresa.
- Mantener regularmente.
- Planifique a largo plazo.
En la carrera hacia operaciones más ecológicas, los inversores solares comerciales no son sólo un componente de su sistema: son la piedra angular de su futuro energético.
PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
-
¿Cuál es el mejor sistema solar para uso comercial?
El mejor sistema solar para uso comercial depende de sus necesidades energéticas, espacio en el tejado y objetivos a largo plazo. Para la mayoría de las empresas, un sistema conectado a la red con paneles de alta eficiencia y un inversor solar comercial robusto es la opción ideal. Las instalaciones más grandes pueden beneficiarse de los inversores centrales, mientras que las operaciones más pequeñas suelen encontrar más rentables los inversores de cadenas. Si la resiliencia energética es una prioridad, un inversor solar híbrido combinado con baterías proporciona energía de reserva durante los cortes.
-
¿Cuál es la vida útil típica de un inversor solar?
La mayoría de los inversores solares comerciales duran entre 10 y 15 años, en comparación con los paneles solares, que a menudo superan los 25 años. Factores como el calor, el polvo y la carga eléctrica pueden influir en la vida útil. Un mantenimiento regular y una instalación adecuada pueden ayudar a prolongar el rendimiento hasta el extremo superior de ese intervalo. Las empresas deben prever al menos una sustitución del inversor durante la vida útil de su sistema solar.
-
¿Por qué mi inversor funciona con batería aunque haya corriente?
Este problema suele reducirse a cómo está programado el inversor solar. Los inversores híbridos pueden dar prioridad al uso de la batería para reducir la dependencia de la red o para aprovechar la energía almacenada de menor coste durante las horas punta. En otros casos, una mala configuración, sensores defectuosos o problemas de cableado pueden hacer que el inversor cambie a batería innecesariamente. Una inspección profesional y una reprogramación pueden resolver el problema.
-
¿Qué es un inversor comercial?
Un inversor comercial es el corazón de un sistema solar diseñado para empresas. Convierte la corriente continua (CC) producida por los paneles solares en corriente alterna (CA), que alimenta los equipos de oficina, la iluminación y la maquinaria. A diferencia de los inversores residenciales, los modelos comerciales se construyen para gestionar una mayor capacidad, integrar herramientas de supervisión avanzadas y ampliarse para grandes instalaciones u operaciones en múltiples emplazamientos.
-
¿Merece la pena la energía solar comercial?
Sí. Un sistema solar bien diseñado, basado en inversores solares comerciales de alta calidad, ofrece beneficios tanto financieros como estratégicos. Las empresas ahorran considerablemente en costes energéticos, pueden optar a incentivos fiscales y se protegen contra el aumento de las tarifas de los servicios públicos. Más allá del dinero, la energía solar mejora las credenciales de sostenibilidad, la reputación de la marca y el cumplimiento de la normativa medioambiental.
-
¿Cuántos vatios por panel solar comercial?
La mayoría de los paneles solares comerciales producen entre 350 y 500 vatios, y los últimos paneles de alto rendimiento alcanzan los 600 vatios. La potencia exacta depende del fabricante, la tecnología celular y el tamaño del panel. Los paneles de mayor potencia reducen el número de paneles necesarios, lo que simplifica la instalación y se combina eficazmente con inversores solares comerciales de gran capacidad.
-
¿Necesitan los inversores solares comerciales un mantenimiento regular?
Por supuesto. Aunque los paneles requieren relativamente poco mantenimiento, los inversores solares comerciales requieren inspecciones periódicas. La eliminación del polvo, las actualizaciones de software y las comprobaciones de los componentes hacen que funcionen con la máxima eficiencia. Un mantenimiento profesional programado puede evitar averías inesperadas y prolongar la vida útil del inversor.
-
¿Qué pasa si falla mi inversor?
Si falla un inversor solar, sus paneles no pueden suministrar electricidad utilizable a su empresa. Esto significa tiempo de inactividad y pérdidas potenciales. La mayoría de los fallos pueden diagnosticarse rápidamente mediante sistemas de monitorización. Afortunadamente, muchos inversores están respaldados por garantías y los ciclos de sustitución planificados garantizan una continuidad sin problemas.
-
¿Cómo elegir entre inversores monofásicos, centrales e híbridos?
- Los inversores monofásicos funcionan mejor en sistemas de tamaño medio con luz solar constante.
- Los inversores centrales son ideales para instalaciones a gran escala, como almacenes o huertos solares.
- Los inversores híbridos son ideales para empresas que necesitan baterías de reserva o independencia energética.
Su elección depende de las condiciones del lugar, el tamaño del sistema y si desea energía de reserva. Un instalador profesional diseñará el sistema en función de sus necesidades específicas. -
¿Puedo controlar mi instalación solar en tiempo real?
Sí. Los inversores solares comerciales modernos vienen con herramientas de supervisión avanzadas que le permiten realizar un seguimiento del rendimiento panel por panel. Estos paneles identifican ineficiencias, le alertan de fallos de funcionamiento y proporcionan datos para informes financieros y medioambientales. La supervisión es una de las formas más eficaces de proteger la rentabilidad de su inversión.
-
¿Afectan los inversores solares al rendimiento de la inversión?
Por supuesto. La eficiencia y fiabilidad de su inversor solar influyen directamente en la cantidad de energía que cosecha y, por tanto, en la rapidez con la que recupera la inversión. Un inversor de alta calidad garantiza que se desperdicie el mínimo de energía en la conversión, lo que mejora la rentabilidad de la inversión a lo largo de la vida útil del sistema.