Guide ultime de dépannage des onduleurs solaires : Solutions d'experts pour les problèmes courants

Table des matières
L'énergie solaire est devenue un élément essentiel de la vie moderne et durable, et au cœur de chaque système d'énergie solaire se trouve l'onduleur solaire. Ce dispositif essentiel convertit le courant continu (CC) généré par les panneaux solaires en courant alternatif (CA) qui alimente les habitations et les entreprises. Cependant, même les onduleurs solaires les plus fiables peuvent rencontrer des problèmes qui affectent la production d'énergie et l'efficacité du système. Comprendre les problèmes courants, savoir comment effectuer un dépannage de base de l'onduleur solaire et reconnaître quand l'aide d'un professionnel est nécessaire permet d'économiser du temps, de l'argent et du stress. Dans ce guide complet, nous vous guiderons à travers toutes les étapes, des simples réinitialisations aux diagnostics avancés, en vous fournissant des conseils pratiques pour assurer le bon fonctionnement de votre système solaire tout en maximisant la production d'énergie.
Comprendre les onduleurs solaires et leur rôle dans votre système énergétique
Qu'est-ce qu'un onduleur solaire ?
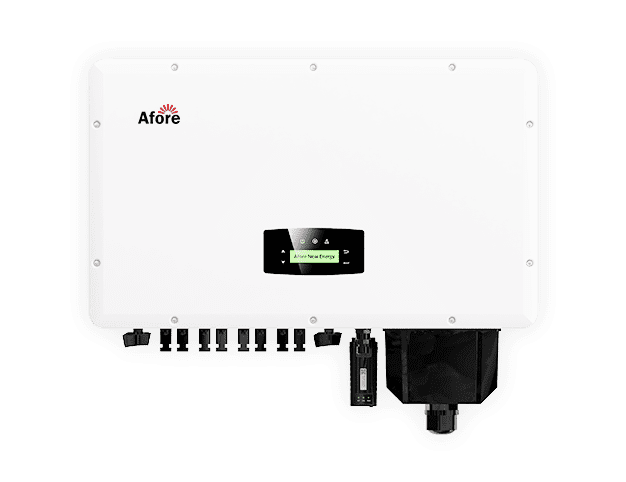
A onduleur solaire est le cœur d'un système d'énergie solaire. Il convertit le courant continu (CC) produit par les panneaux solaires en courant alternatif (CA) qui alimente votre maison ou votre entreprise. Sans onduleur solaire, l'énergie générée par vos panneaux solaires resterait inutilisable pour les appareils électriques courants.
Importance des onduleurs dans les systèmes d'énergie solaire
Les onduleurs solaires sont essentiels car ils ne se contentent pas de convertir l'énergie, ils la régulent et l'optimisent. Ils surveillent les performances du système, détectent les pannes et communiquent parfois avec des plateformes de surveillance pour s'assurer que tout fonctionne efficacement. Un onduleur défectueux peut réduire considérablement votre production d'énergie.
Types de convertisseurs solaires
Il existe plusieurs types d'onduleurs solaires, chacun présentant des caractéristiques distinctes :
- Onduleurs de branche : Connectés à une série de panneaux, ils sont idéaux pour les installations résidentielles standard.
- Micro-onduleurs : Installés sur chaque panneau, ils améliorent les performances dans les configurations de toits ombragés ou complexes.
- Onduleurs hybrides : Combinent les capacités de stockage de l'énergie solaire et de la batterie, et conviennent pour l'indépendance énergétique.

Problèmes courants des onduleurs solaires et leurs solutions
Posséder un système d'énergie solaire est un investissement judicieux, mais comme toute technologie, les onduleurs solaires peuvent rencontrer des problèmes qui affectent leurs performances. Il est essentiel de comprendre les problèmes les plus courants et de savoir comment les résoudre pour maintenir un rendement énergétique optimal et prolonger la durée de vie de votre système. Dans cette section, nous allons analyser les problèmes les plus fréquents des onduleurs et fournir des solutions pratiques que vous pouvez appliquer immédiatement.
1. Pas de sortie d'alimentation CA ou CC
L'un des problèmes les plus alarmants auxquels sont confrontés les propriétaires est l'absence totale de sortie d'un onduleur solaire. Plusieurs raisons peuvent être à l'origine de ce problème : un disjoncteur déclenché, un fusible grillé, des câbles déconnectés ou même des défauts internes de l'onduleur. Commencez par vérifier les déconnexions CA et CC et assurez-vous que le système est correctement connecté. Inspectez le câblage visible pour vérifier que les connexions ne sont pas desserrées ou endommagées. Si tout semble intact, une réinitialisation contrôlée de l'onduleur peut souvent rétablir le fonctionnement. Une surveillance et une maintenance régulières permettent d'éviter ces interruptions soudaines de l'alimentation.
2. Surchauffe de l'onduleur
La surchauffe est un autre problème courant. Les onduleurs génèrent de la chaleur pendant leur fonctionnement, et des températures excessives peuvent déclencher des arrêts automatiques, voire des dommages permanents. Des facteurs tels qu'une mauvaise ventilation, des évents obstrués, des températures ambiantes élevées ou des environnements poussiéreux peuvent exacerber le problème. Pour éviter la surchauffe, veillez à ce que votre onduleur soit installé dans un endroit bien ventilé, à l'abri de la lumière directe du soleil. Nettoyez régulièrement les évents et les surfaces environnantes pour maintenir la circulation de l'air, et envisagez l'installation d'un petit ventilateur ou d'un dispositif d'ombrage si nécessaire. Ces mesures préventives peuvent considérablement prolonger la durée de vie de votre onduleur.
3. Codes d'erreur et messages d'erreur
Les onduleurs solaires modernes affichent souvent des codes d'erreur ou des messages de défaut lorsque quelque chose ne va pas. Ces codes sont conçus pour aider à diagnostiquer les problèmes, mais ils peuvent être déroutants si l'on n'est pas correctement guidé. Les erreurs les plus courantes sont la surtension, la sous-tension, la déconnexion du réseau ou les échecs de communication. L'interprétation précise de ces messages est la première étape du dépannage d'un onduleur solaire. Souvent, pour résoudre le problème, il faut vérifier les connexions de câblage, les paramètres du système ou effectuer une réinitialisation sécurisée. Si les codes d'erreur persistent malgré le dépannage, il est recommandé de contacter un technicien professionnel.
4. Production d'énergie faible ou nulle
Il arrive qu'un onduleur semble opérationnel, mais que votre système solaire produise moins d'énergie que prévu. Les causes peuvent aller de l'ombrage des panneaux, de l'accumulation de saletés ou d'une mauvaise orientation à une mauvaise configuration de l'onduleur ou à des inefficacités internes. Commencez par inspecter visuellement vos panneaux pour vérifier qu'ils ne sont pas ombragés ou sales, puis vérifiez que les paramètres de votre onduleur correspondent aux spécifications de votre système. L'utilisation d'outils de surveillance ou de multimètres peut aider à détecter les incohérences de tension. L'identification en temps utile de ces problèmes permet à votre système de fonctionner de manière optimale et d'éviter les pertes d'énergie inutiles.
5. Arrêts intermittents
Les arrêts intermittents des onduleurs peuvent être particulièrement frustrants parce qu'ils se produisent sporadiquement. L'instabilité du réseau, la fluctuation des conditions environnementales ou l'usure des composants internes en sont les causes. Pour résoudre le problème, surveillez le moment des arrêts et vérifiez les journaux d'erreurs ou les alertes du système. L'ajustement des paramètres de l'onduleur, la stabilisation des connexions au réseau et la garantie d'une ventilation adéquate peuvent souvent réduire ces occurrences. Toutefois, des arrêts persistants peuvent signaler la nécessité d'une évaluation professionnelle afin d'éviter des dommages à long terme.
6. Défauts de communication
De nombreux onduleurs modernes communiquent avec des plateformes de surveillance pour fournir des données de performance. Lorsque la communication échoue, cela peut vous empêcher de suivre la production d'énergie et de détecter les défaillances potentielles. Les causes peuvent être des problèmes de réseau, des câbles lâches, des microprogrammes obsolètes ou des problèmes de routeur. Commencez par inspecter toutes les connexions, assurez-vous que l'onduleur est correctement mis en réseau et vérifiez les mises à jour logicielles. Le rétablissement de la communication permet non seulement de restaurer la fonctionnalité de surveillance, mais aussi de procéder à un dépannage proactif de l'onduleur solaire.
7. Questions relatives à la charge de la batterie (pour les systèmes hybrides)
Pour les systèmes avec stockage intégré, les problèmes d'onduleur peuvent se manifester par des problèmes de charge. Les causes les plus courantes sont la dégradation des batteries, un câblage incorrect ou une mauvaise configuration des paramètres de l'onduleur. Inspectez votre parc de batteries pour détecter les signes d'usure ou de déséquilibre, vérifiez les connexions et assurez-vous que les protocoles de charge de l'onduleur correspondent aux spécifications de votre système. La résolution rapide de ces problèmes permet d'éviter les pertes d'énergie, de prolonger la durée de vie des batteries et de maintenir l'efficacité globale du système.

Comment réinitialiser un onduleur solaire
Même les onduleurs solaires les plus fiables peuvent occasionnellement rencontrer des problèmes, des codes d'erreur ou des pannes temporaires. L'une des solutions les plus simples et les plus efficaces pour résoudre les problèmes mineurs consiste à effectuer une réinitialisation. Comprendre comment réinitialiser votre onduleur en toute sécurité est une partie essentielle du dépannage d'un onduleur solaire, et le faire correctement permet de gagner du temps, d'éviter d'autres dommages et de restaurer les performances optimales du système.
Procédure de réinitialisation pas à pas
L'exécution d'une réinitialisation peut varier légèrement en fonction de votre système, mais le processus général suit une séquence sûre et standardisée :
- Couper le courant alternatif - Cela permet d'isoler l'onduleur du réseau électrique principal et d'éviter tout risque électrique potentiel pendant la réinitialisation.
- Coupez la déconnexion DC ou le disjoncteur - La déconnexion de l'entrée DC de vos panneaux solaires permet à l'onduleur de se décharger complètement et de réinitialiser les composants internes.
- Attendez 5 à 10 minutes - Cette pause garantit que tous les condensateurs internes et l'énergie résiduelle sont déchargés en toute sécurité, ce qui permet à l'onduleur de se réinitialiser complètement.
- Activez d'abord la déconnexion CC - La reconnexion des panneaux solaires rétablit progressivement la puissance d'entrée de l'onduleur.
- Enclencher la déconnexion AC - La reconnexion au réseau achève le processus de réinitialisation, permettant à l'onduleur de reprendre son fonctionnement normal.
- Observez l'écran de l'onduleur - Vérifiez la présence d'indicateurs d'état normaux ou de codes d'erreur. Si l'onduleur s'allume sans afficher de défauts, la réinitialisation est réussie.
Cette méthode est largement recommandée pour traiter les défauts mineurs tels que les erreurs de communication temporaires, les avertissements de faible puissance ou certains messages de défaut. Il s'agit d'une première étape essentielle dans le dépannage des onduleurs solaires avant de passer à des diagnostics plus avancés.
Quand effectuer une réinitialisation
Tous les problèmes liés à l'onduleur ne nécessitent pas une réinitialisation. Effectuez une réinitialisation dans les cas suivants
- L'onduleur affiche une erreur ou un avertissement temporaire qui n'indique pas un dommage permanent.
- La production d'énergie semble plus faible que prévu en raison d'un problème de système.
- Vous avez vérifié les connexions électriques, les facteurs environnementaux et d'autres étapes de dépannage de base sans succès.
Évitez les réinitialisations fréquentes, car des échecs répétés peuvent indiquer des problèmes sous-jacents nécessitant l'intervention d'un professionnel. Considérez la réinitialisation comme un outil de diagnostic plutôt que comme une solution permanente.
Précautions à prendre lors de la réinitialisation
La sécurité est essentielle lors de la manipulation d'équipements électriques. Respectez les précautions suivantes pour éviter les accidents :
- Porter des gants et des lunettes de protection - Même les composants à basse tension peuvent provoquer des blessures s'ils sont mal manipulés.
- Évitez les environnements humides ou mouillés - L'eau et l'électricité sont une combinaison dangereuse, assurez-vous donc que votre espace de travail est sec.
- Suivez les directives du système - Respectez toujours le manuel de votre onduleur et les consignes de sécurité pour déconnecter et reconnecter l'alimentation.
- Ne contournez jamais les mécanismes de sécurité - Ne tentez pas de prendre des raccourcis, par exemple en rebranchant l'alimentation trop rapidement ou en sautant des étapes de déconnexion, car cela pourrait endommager l'onduleur.
En respectant ces mesures de sécurité, la réinitialisation peut être un élément simple et sûr de votre kit de dépannage d'onduleur solaire.
Les avantages d'une bonne réinitialisation
Une réinitialisation correctement effectuée peut :
- Rétablir le fonctionnement normal de l'onduleur sans réparations coûteuses.
- Effacez les codes d'erreur temporaires et améliorez la production d'énergie.
- Aider à déterminer si les problèmes sont mineurs ou s'ils nécessitent l'intervention d'un professionnel.
La réinitialisation de votre onduleur solaire est souvent la méthode la plus rapide et la plus simple pour résoudre des problèmes mineurs, mais elle doit toujours être associée à des inspections visuelles, à une surveillance et à une maintenance préventive pour obtenir les meilleurs résultats à long terme.
Test et diagnostic des performances de l'onduleur
Même lorsqu'un onduleur solaire semble fonctionner normalement, des défauts subtils peuvent avoir un impact sur la production d'énergie et l'efficacité du système. Des tests réguliers et un diagnostic précis sont des éléments essentiels du dépannage des onduleurs solaires, qui aident les propriétaires et les techniciens à détecter les problèmes à un stade précoce et à maintenir des performances optimales. Cette section fournit des conseils pratiques sur l'évaluation de l'état de l'onduleur, à la fois visuellement et à l'aide d'outils de test.
Indicateurs visuels et sonores
La plupart des onduleurs solaires modernes sont dotés de panneaux d'affichage et de voyants lumineux qui indiquent leur état de fonctionnement. Une attention particulière à ces signaux est une étape fondamentale du dépannage. Les indicateurs visuels les plus courants sont les suivants
- Voyants d'état : Les voyants verts indiquent généralement un fonctionnement normal, tandis que les voyants jaunes ou rouges peuvent signaler des avertissements ou des défauts.
- Codes ou messages d'erreur : Des codes numériques ou alphanumériques peuvent indiquer des problèmes tels qu'une surtension, une sous-tension ou des défauts internes.
- Signaux sonores : Des signaux sonores ou des sons inhabituels peuvent alerter les utilisateurs en cas de surchauffe, d'erreur du système ou de défaillance de la communication.
En observant ces indicateurs, vous pouvez souvent identifier des problèmes mineurs avant qu'ils ne se transforment en pannes majeures. Par exemple, un voyant clignotant peut indiquer un problème de communication temporaire plutôt qu'une défaillance matérielle grave. La documentation de ces relevés permet de suivre les problèmes récurrents et d'informer un service professionnel en cas de besoin.
Utilisation de multimètres et d'outils de contrôle
Pour une évaluation plus précise, utilisez des outils de diagnostic tels que des multimètres et des logiciels de surveillance du système pour tester les performances de l'onduleur. Les étapes clés sont les suivantes :
- Mesurer l'entrée CC des panneaux solaires - Confirmer que la tension et le courant atteignant l'onduleur correspondent aux valeurs attendues. Des écarts importants peuvent indiquer des problèmes de câblage, d'ombrage ou de dégradation des panneaux.
- Vérifier la sortie CA - Assurez-vous que l'onduleur fournit une tension CA constante à votre maison ou au réseau. Des variations peuvent signaler des défauts internes ou une instabilité du réseau.
- Surveiller les tendances de la production d'énergie - La comparaison de la production d'énergie quotidienne et hebdomadaire avec les performances historiques permet d'identifier les baisses d'efficacité et les défauts cachés.
Une surveillance régulière permet non seulement de résoudre les problèmes, mais aussi d'optimiser l'efficacité énergétique, en veillant à ce que votre onduleur solaire fournisse une puissance maximale à votre système.
Services de diagnostic professionnel
Si les tests de base permettent de résoudre de nombreux problèmes courants, certains requièrent des compétences avancées en matière de diagnostic. Les techniciens certifiés en énergie solaire ont accès à des outils et à des logiciels spécialisés qui peuvent :
- Identifier les défauts internes cachés.
- Tester les composants de l'onduleur en conditions de charge.
- Manipuler en toute sécurité des systèmes à haute tension qui peuvent être dangereux pour des personnes non formées.
Faire appel à des services professionnels en cas de besoin garantit un diagnostic sûr et précis et permet d'éviter des dommages coûteux. Combiner votre propre dépannage d'onduleur solaire avec des inspections professionnelles constitue la meilleure stratégie pour assurer la fiabilité à long terme du système.
Les tests : un éclairage préventif
Les tests et diagnostics réguliers ne se limitent pas à la détection des pannes : ils fournissent des informations préventives qui peuvent prolonger la durée de vie de votre onduleur. En identifiant rapidement les écarts de performance mineurs, vous pouvez prendre des mesures correctives telles que le nettoyage des panneaux, l'ajustement du câblage ou la mise à jour des paramètres de l'onduleur avant qu'ils ne se transforment en pannes majeures.

Réparation ou remplacement : Faire le bon choix
La décision de réparer ou de remplacer un onduleur solaire est l'une des plus importantes que puisse prendre le propriétaire d'un système solaire. Si une réparation peut sembler rentable dans un premier temps, des pannes fréquentes ou des composants vieillissants peuvent faire du remplacement une décision plus judicieuse à long terme. Comprendre les facteurs en jeu permet aux propriétaires de faire des choix éclairés, de réduire les pertes d'énergie et de protéger leur investissement.
Évaluation de l'étendue des dommages
La première étape du dépannage d'un onduleur solaire consiste à évaluer avec précision l'étendue du problème. Les problèmes mineurs tels que des fusibles grillés, des câbles mal fixés ou des problèmes logiciels temporaires sont souvent facilement réparables. En revanche, des codes d'erreur persistants, des arrêts répétés, une surchauffe ou des défaillances de composants internes indiquent des problèmes plus profonds qui peuvent nécessiter un remplacement complet. Le fait de documenter soigneusement les messages d'erreur, les tendances en matière de performances et le comportement du système permet de déterminer clairement si une réparation est suffisante ou si un remplacement est nécessaire.
Analyse coûts-avantages
Lorsqu'il s'agit d'évaluer les réparations par rapport au remplacement, il faut tenir compte à la fois des coûts immédiats et des implications à long terme :
- Réparation : La réparation de pannes mineures est généralement moins coûteuse à court terme. Des réparations simples, telles que le remplacement de fusibles ou la mise à jour de microprogrammes, peuvent rétablir rapidement le fonctionnement du système. Cependant, des réparations répétées peuvent accumuler des coûts et réduire la fiabilité du système au fil du temps.
- Remplacement : L'installation d'un nouvel onduleur a un coût initial plus élevé mais offre des avantages à long terme, notamment une meilleure efficacité, une technologie actualisée et une réduction du risque de pannes futures. Le remplacement peut également éliminer les temps d'arrêt et les problèmes de maintenance, maximisant ainsi la production d'énergie et le rendement financier.
En tenant compte de ces facteurs, les propriétaires peuvent prendre une décision financièrement saine qui concilie le coût, les performances du système et la fiabilité.
Considérations relatives à la longévité et à la garantie
La longévité est un autre facteur important dans la décision de réparer ou de remplacer un onduleur solaire. Les anciens onduleurs peuvent être sujets à des pannes récurrentes, même après réparation, alors que les nouveaux onduleurs peuvent prolonger considérablement la durée de vie du système. En outre, la couverture de la garantie doit être prise en compte. La réparation d'un onduleur défectueux sous garantie peut être couverte par le fabricant, alors que des réparations répétées sur des systèmes hors garantie peuvent ne pas être rentables. Dans certains cas, le remplacement assure une protection continue de la garantie et une tranquillité d'esprit.
Prendre une décision éclairée
Faire le bon choix :
- Documenter les problèmes du système - Suivre les baisses de performance, les codes d'erreur et l'historique des réparations.
- Consulter un professionnel - Des techniciens expérimentés peuvent fournir une évaluation objective pour déterminer s'il est préférable de réparer ou de remplacer le produit.
- Tenir compte des pertes d'énergie - Tenir compte de la réduction potentielle de la production d'énergie si l'on répare régulièrement l'onduleur au lieu de le remplacer.
- Évaluer la fiabilité à long terme - Un nouvel onduleur peut offrir un meilleur rendement, des fonctions modernes et des besoins de maintenance réduits.
En fin de compte, une décision bien informée donne la priorité à la sécurité, à l'efficacité énergétique et au bon sens financier. En prenant le temps d'évaluer soigneusement votre onduleur solaire, vous vous assurez que votre système solaire continuera à fonctionner à son plein potentiel pendant de nombreuses années.
Conseils de maintenance préventive pour la longévité des onduleurs
Un onduleur solaire bien entretenu est essentiel pour une production d'énergie constante et une efficacité à long terme du système. Si le dépannage de l'onduleur solaire permet de résoudre les problèmes existants, la maintenance proactive permet de prévenir les problèmes potentiels avant qu'ils n'affectent les performances. La mise en œuvre de quelques pratiques simples peut considérablement prolonger la durée de vie de votre onduleur et protéger votre investissement dans l'énergie solaire.
Nettoyage et inspection réguliers
La poussière, la saleté et les débris peuvent s'accumuler sur votre onduleur au fil du temps, obstruant le flux d'air et provoquant une surchauffe. Des inspections visuelles régulières permettent d'identifier les premiers signes d'usure ou d'endommagement, tels que :
- Connexions de câblage lâches ou corrodées
- Signes d'infiltration d'eau ou de dommages dus à l'humidité
- Accumulation de poussière autour des évents ou des ventilateurs de refroidissement
Nettoyer le boîtier de l'onduleur et s'assurer que les évents ne sont pas obstrués améliore la circulation de l'air et réduit le risque d'arrêts thermiques. Une inspection régulière, idéalement tous les trois à six mois, permet également de détecter les problèmes mineurs avant qu'ils ne se transforment en défaillances majeures, ce qui en fait une étape cruciale du dépannage des onduleurs solaires.
Mises à jour des microprogrammes et surveillance du système
Les onduleurs modernes s'appuient souvent sur un micrologiciel pour optimiser les performances et communiquer avec les systèmes de surveillance. La mise à jour du logiciel de votre onduleur garantit qu'il fonctionne efficacement et qu'il peut réagir avec précision aux conditions du réseau ou aux défaillances du système. En outre :
- Suivre régulièrement les tendances de la production d'énergie
- Vérifier les baisses de performance inhabituelles
- Comparez les résultats obtenus à la production attendue pour votre système
En surveillant activement les performances et en appliquant les mises à jour du micrologiciel, vous pouvez détecter rapidement les petits écarts, maintenir une efficacité maximale et éviter des réparations ou des remplacements coûteux.
Considérations environnementales
L'environnement d'installation joue un rôle important dans la longévité de l'onduleur. La chaleur extrême, l'humidité et la lumière directe du soleil peuvent solliciter les composants internes et entraîner une défaillance prématurée. Pour atténuer ces risques :
- Installez l'onduleur dans un endroit ombragé et bien ventilé.
- Éviter les zones sujettes à l'accumulation d'eau ou aux inondations
- Veiller à ce que la température ambiante reste dans la fourchette recommandée par le fabricant.
Un emplacement approprié et la protection de l'environnement réduisent les contraintes exercées sur l'onduleur et minimisent la fréquence des interventions de dépannage, ce qui contribue à une fiabilité à long terme.
Avantages de la maintenance préventive
La mise en œuvre d'un entretien de routine permet non seulement d'éviter les pannes, mais aussi d'améliorer la production d'énergie. Les propriétaires qui entretiennent activement leurs onduleurs solaires en font l'expérience :
- Moins d'arrêts inattendus ou de codes d'erreur
- Durée de vie prolongée du système
- Optimisation de l'efficacité énergétique et réduction des coûts d'exploitation
Les soins préventifs complètent le dépannage des onduleurs solaires en réduisant la probabilité d'apparition des problèmes, ce qui permet à votre système de fournir en permanence une énergie fiable et durable.

Questions fréquemment posées
-
Quel est le problème le plus courant avec les onduleurs solaires ?
Les problèmes les plus fréquents sont la surchauffe, la perte de puissance, les codes d'erreur, les défaillances de communication et les arrêts intermittents. Ces problèmes sont souvent dus à des facteurs environnementaux, à des défauts de câblage ou à l'usure des composants. Une détection précoce par le biais d'une surveillance et d'inspections visuelles permet d'éviter que des problèmes mineurs ne se transforment en pannes majeures.
-
Comment réinitialiser un onduleur solaire ?
Une réinitialisation permet souvent de résoudre des problèmes mineurs. Commencez par couper le courant alternatif, puis coupez le courant continu ou le disjoncteur. Attendez 5 à 10 minutes pour permettre à l'onduleur de se décharger. Rebranchez d'abord l'entrée CC, puis l'entrée CA. Observez l'affichage pour vérifier que le fonctionnement est normal. Respectez toujours les consignes de sécurité et évitez les réinitialisations répétées sans traiter la cause sous-jacente.
-
Comment savoir si un onduleur solaire est défectueux ?
Les signes d'un onduleur défaillant sont des codes d'erreur persistants, l'absence de sortie CA ou CC, des arrêts fréquents, des bruits inhabituels et une surchauffe. Une faible production d'énergie malgré un ensoleillement optimal et des panneaux fonctionnant correctement peut également indiquer des défaillances internes. Une surveillance constante et un diagnostic professionnel permettent de confirmer si l'onduleur doit être réparé ou remplacé.
-
Comment résoudre un problème d'onduleur ?
Commencez par le dépannage de base de l'onduleur solaire : vérifiez le câblage, les connexions, la ventilation et les paramètres du système. Observez les codes d'erreur ou les voyants d'avertissement, effectuez une réinitialisation sûre si nécessaire et utilisez des multimètres pour tester la tension et le courant. Si les problèmes persistent, consultez un technicien certifié pour un diagnostic avancé afin d'éviter tout dommage supplémentaire.
-
Comment tester le fonctionnement d'un onduleur ?
Vous pouvez tester le fonctionnement de l'onduleur en mesurant l'entrée CC des panneaux solaires et la sortie CA de votre maison à l'aide d'un multimètre. En outre, surveillez l'affichage de l'onduleur pour détecter les voyants d'état, les codes d'erreur ou toute activité inhabituelle. La comparaison entre les performances réelles et la production d'énergie attendue permet de savoir si l'onduleur fonctionne correctement.
-
Est-il plus économique de réparer ou de remplacer un onduleur ?
Les pannes mineures sont généralement moins coûteuses à réparer, comme les fusibles grillés, les câbles mal fixés ou les mises à jour logicielles. Toutefois, en cas de pannes répétées, d'endommagement des composants internes ou de vieillissement des onduleurs, le remplacement peut s'avérer une solution plus rentable à long terme. Tenez compte des pertes d'énergie, de la fiabilité du système et des implications de la garantie avant de prendre votre décision.
-
Puis-je effectuer moi-même la maintenance de l'onduleur ?
Les tâches de maintenance de base, telles que le nettoyage de l'onduleur, l'inspection des connexions et le contrôle des performances, peuvent être effectuées en toute sécurité par les particuliers. Les tests électriques complexes ou les réparations internes doivent être confiés à des professionnels qualifiés afin de garantir la sécurité et de préserver la couverture de la garantie.
-
À quelle fréquence dois-je entretenir mon onduleur solaire ?
Il est recommandé de procéder à une inspection visuelle tous les trois à six mois et à un entretien professionnel tous les un à deux ans. Des contrôles réguliers permettent de détecter les premiers signes d'usure, d'éviter les surchauffes et de maintenir une production d'énergie optimale. La tenue d'un journal d'entretien peut également permettre de suivre les problèmes récurrents pour le dépannage de l'onduleur solaire.
-
Qu'est-ce qui annule la garantie de mon onduleur ?
La couverture de la garantie peut être annulée en cas de réparation non autorisée, d'altération, de dégâts des eaux, de surcharge électrique ou de négligence. Respectez toujours les consignes de sécurité du fabricant, effectuez l'entretien avec soin et faites appel à des professionnels pour les réparations dépassant le cadre d'une inspection de base.
-
Comment puis-je améliorer l'efficacité de mon onduleur ?
L'efficacité peut être améliorée par un entretien régulier, le nettoyage des panneaux et des évents de l'onduleur, une bonne ventilation, la mise à jour du micrologiciel et le suivi des tendances de la production d'énergie. Une configuration correcte du système, y compris l'orientation correcte des panneaux et le réglage de la tension, maximise également les performances de l'onduleur et réduit la nécessité de dépannages fréquents.