Vantaggi principali e guida agli inverter ibridi solari per la vostra casa

Indice dei contenuti
Se stai cercando modi per massimizzare l’efficienza e l’affidabilità del tuo impianto solare, gli inverter ibridi solari sono una soluzione rivoluzionaria che vale la pena approfondire. Che tu sia un proprietario di casa, un appassionato di energia solare o stia valutando il tuo prossimo aggiornamento energetico, questa guida ti fornirà tutte le informazioni necessarie sugli inverter ibridi solari, il loro funzionamento, i vantaggi, gli svantaggi e perché potrebbero essere la soluzione perfetta per il tuo impianto solare.
In questo articolo dettagliato forniremo anche informazioni essenziali sugli inverter solari in generale, assicurandoci che tu comprenda il loro ruolo cruciale nel tuo ecosistema energetico. Cominciamo!
Cos’è un inverter ibrido per impianti solari?
Definizione e ruolo in un sistema di energia solare
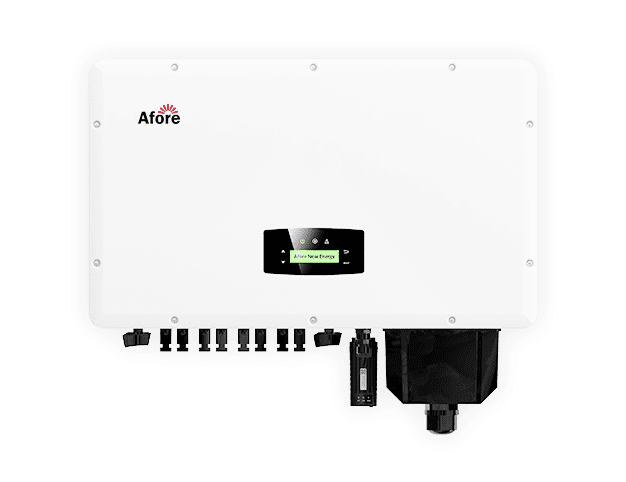
Un inverter ibrido solare è un dispositivo innovativo progettato per gestire il flusso di energia proveniente da più fonti, principalmente dai pannelli solari, dalla rete elettrica e dai sistemi di accumulo energetico come le batterie. Immaginatelo come il cervello che coordina quando prelevare energia dai pannelli solari, quando caricare o scaricare la batteria e quando prelevare elettricità dalla rete.
A differenza di un inverter solare tradizionale che si limita a convertire l’elettricità in corrente continua prodotta dai pannelli solari in corrente alternata utilizzabile per la vostra casa, un inverter ibrido aggiunge la funzionalità fondamentale di integrare perfettamente l’accumulo in batteria. Ciò significa che potete immagazzinare l’energia solare in eccesso generata durante il giorno e utilizzarla in seguito, ad esempio durante la notte o in caso di interruzioni di corrente.
La capacità dell’inverter ibrido di passare dall’energia solare a quella della batteria e della rete lo rende un componente indispensabile nei moderni sistemi di energia solare che mirano ad aumentare l’autoconsumo e l’indipendenza energetica.
In che cosa si differenzia dagli altri inverter solari
Per comprendere cosa rende unici gli inverter ibridi solari, è utile confrontarli con altri tipi di inverter comuni:
- Inverter solari collegati alla rete: questi collegano il vostro impianto solare direttamente alla rete, reimmettendo l’energia in eccesso e prelevando energia quando quella solare non è sufficiente. Tuttavia, non sono in grado di fornire energia di riserva in caso di interruzioni di corrente.
- Inverter off-grid: questi inverter funzionano indipendentemente dalla rete e si basano interamente su batterie e pannelli solari. Sebbene garantiscano la piena autonomia, richiedono una notevole capacità di accumulo delle batterie e possono essere costosi da mantenere.
- Microinverter: collegati ai singoli pannelli solari, i microinverter ottimizzano la conversione energetica pannello per pannello, migliorando le prestazioni del sistema, ma solitamente a un costo e una complessità maggiori.
Gli inverter ibridi solari combinano i vantaggi degli inverter collegati alla rete e di quelli non collegati alla rete, offrendo interazione con la rete e backup a batteria, motivo per cui stanno rapidamente guadagnando popolarità.

Vantaggi principali degli inverter ibridi solari
Indipendenza energetica e alimentazione di riserva
Uno dei vantaggi più interessanti degli inverter ibridi solari risiede nella loro capacità di offrire una vera indipendenza energetica. A differenza degli inverter solari convenzionali che si limitano a convertire la luce solare in energia elettrica utilizzabile, gli inverter ibridi consentono ai proprietari di case di immagazzinare l’energia in eccesso nelle batterie e di accedervi quando necessario. Questa capacità significa che non si dipende solo dalla rete elettrica o dai pannelli solari, ma si dispone di un backup affidabile pronto per i momenti in cui il sole non splende o manca la corrente.
Immaginate un tipico scenario di blackout. Con un inverter solare standard, il vostro impianto si spegne, lasciandovi al buio nonostante abbiate dei pannelli solari sul tetto. Ma un inverter ibrido passa senza soluzione di continuità all’alimentazione a batteria, mantenendo le luci, gli elettrodomestici e i dispositivi critici in funzione senza interruzioni. Questa funzione di backup è preziosa nelle zone soggette a interruzioni di corrente o dove l’affidabilità della rete è incerta. Inoltre, con l’aumento dei costi dell’elettricità e l’imprevedibilità delle condizioni meteorologiche, disporre di energia solare immagazzinata può garantire tranquillità e vera indipendenza.
Utilizzando l’energia solare non solo nel momento in cui è disponibile, ma ogni volta che ne avete bisogno, gli inverter ibridi vi consentono di ridurre la dipendenza dalla rete elettrica tradizionale. Nel tempo, ciò si traduce in bollette mensili più basse, un maggiore controllo sul consumo energetico e un passo verso una vita sostenibile e autosufficiente.
Autoconsumo e trasferimento del carico
Un altro importante vantaggio offerto dagli inverter ibridi solari è la possibilità di massimizzare l’autoconsumo dell’energia solare. In parole povere, autoconsumo significa utilizzare la maggior parte dell’energia solare che si produce autonomamente, invece di reimmettere l’energia in eccesso nella rete elettrica. Perché è importante? Perché molte aziende elettriche offrono tariffe di immissione in rete basse, il che significa che si viene pagati molto meno per l’energia elettrica esportata rispetto a quanto si paga per acquistarla da loro.
Gli inverter ibridi risolvono questo problema immagazzinando in modo intelligente l’energia solare in eccesso nelle batterie durante il giorno e rilasciandola quando la vostra famiglia ne ha più bisogno, ad esempio la sera o la mattina presto. Questo processo è noto come spostamento del carico. Lo spostamento del carico consente di evitare di prelevare energia elettrica costosa dalla rete durante le ore di punta, riducendo efficacemente i costi dell’elettricità.
Con il crescente interesse per la gestione energetica intelligente delle abitazioni, gli inverter ibridi sono spesso dotati di software che monitorano i modelli di consumo e regolano l’utilizzo della batteria di conseguenza. Questo approccio personalizzato consente di ridurre significativamente la dipendenza dalla rete elettrica senza modificare le routine o le abitudini quotidiane.
Inoltre, immagazzinando e utilizzando la propria energia solare, si contribuisce alla stabilità della rete e si riducono le emissioni complessive di carbonio, rafforzando il proprio ruolo in un futuro energetico più pulito e resiliente.
Monitoraggio semplificato e adeguamento alle esigenze future
Gli inverter ibridi solari non sono solo potenti, ma anche intelligenti. Una delle loro caratteristiche distintive è il sistema di monitoraggio integrato, che fornisce dati in tempo reale sulla produzione di energia solare, lo stato delle batterie e il consumo energetico, il tutto in un unico posto. Questo livello di approfondimento rende la gestione del vostro impianto solare semplicissima, sia che siate utenti esperti di tecnologia o principianti.
Grazie a un’app o a un portale web di facile utilizzo, puoi monitorare la quantità di energia solare prodotta dal tuo impianto, la quantità di energia immagazzinata o scaricata dalle batterie e la quantità di elettricità prelevata o immessa nella rete. Questa trasparenza ti aiuta a identificare tempestivamente le inefficienze, a risolvere i problemi prima che diventino gravi e a ottimizzare quotidianamente le prestazioni del tuo impianto.
Per quanto riguarda la sicurezza futura, gli inverter ibridi sono progettati per essere scalabili e flessibili. Se decidete di ampliare il vostro impianto solare, aggiungere altre batterie o persino integrare la ricarica dei veicoli elettrici, il vostro inverter ibrido può adattarsi a questi aggiornamenti senza una revisione completa del sistema. Questa adattabilità protegge il vostro investimento iniziale e garantisce che il vostro impianto solare possa crescere di pari passo con le vostre esigenze e i progressi tecnologici.
In un panorama energetico in rapida evoluzione, avere un inverter ibrido significa non solo acquistare un’apparecchiatura, ma investire in una soluzione energetica intelligente a lungo termine in grado di evolversi insieme a voi.
Svantaggi degli inverter solari ibridi
Costo iniziale più elevato e più componenti
Sebbene gli inverter ibridi solari offrano una grande versatilità, hanno un costo maggiore rispetto agli inverter solari standard. L’integrazione aggiuntiva della batteria e le funzionalità di backup aumentano sia i costi iniziali che la complessità.
Non si paga solo l’inverter, ma anche l’accumulo in batterie compatibili, il cablaggio e la competenza nell’installazione, il che può rendere l’investimento iniziale più elevato. Tuttavia, molti proprietari di case ritengono che i risparmi a lungo termine e la sicurezza energetica giustifichino questa spesa.
Efficienza ridotta e maggiore complessità
Gli inverter ibridi comportano più fasi di conversione energetica rispetto agli inverter più semplici. Ciò può comportare lievi perdite di efficienza rispetto ai sistemi puramente collegati alla rete. Sebbene i progressi tecnologici abbiano ridotto questo divario, la maggiore complessità nella gestione delle batterie, dell’input solare e dell’energia di rete può rendere più complicata la configurazione e la manutenzione del sistema.
Garantire che il sistema sia dimensionato correttamente e ben mantenuto è fondamentale per evitare perdite inutili e massimizzare le prestazioni.
Compatibilità e limiti di progettazione
Non tutte le batterie e i pannelli solari sono compatibili con ogni modello di inverter ibrido. Alcuni produttori limitano le marche o le capacità delle batterie per garantire prestazioni ottimali e la copertura della garanzia. Ciò significa che è necessario valutare attentamente le opzioni disponibili prima di scegliere un sistema con inverter ibrido.
Inoltre, alcuni inverter ibridi hanno limiti sul numero di pannelli solari che possono gestire, il che potrebbe limitare l’espansione futura a meno che non si aggiorni l’inverter stesso.

Inverter ibridi vs. inverter off-grid e tradizionali
Inverter ibridi vs. inverter collegati alla rete (stringa/micro)
Gli inverter solari tradizionali, come quelli stringa o microinverter, si concentrano esclusivamente sulla conversione dell’energia solare per l’uso immediato o l’esportazione alla rete. Sono più semplici e generalmente meno costosi, ma non dispongono di funzionalità di alimentazione di riserva.
Gli inverter ibridi aggiungono un ulteriore livello di flessibilità integrando l’accumulo in batteria e consentendo di mantenere l’alimentazione durante le interruzioni di corrente. Se non avete bisogno di alimentazione di riserva o accumulo, gli inverter collegati alla rete potrebbero essere più convenienti.
Inverter ibridi vs. inverter off-grid
Gli inverter off-grid funzionano indipendentemente dalla rete elettrica e richiedono banchi di batterie di grandi dimensioni per fornire energia continua. Sono ideali per località remote senza accesso alla rete elettrica, ma possono essere complessi e costosi.
Gli inverter ibridi combinano la flessibilità off-grid con la connettività alla rete elettrica, offrendo il meglio di entrambi i mondi: backup della rete elettrica, accumulo di energia e la possibilità di rivendere l’energia in eccesso alla rete elettrica.
Ibridi vs. Solo batteria/Inverter di ricarica
Alcuni sistemi utilizzano caricabatterie e inverter separati, complicando l’installazione e il funzionamento. Gli inverter ibridi combinano queste funzioni in un’unica unità semplificata, riducendo l’ingombro delle apparecchiature e semplificando la manutenzione.
Aspettativa di vita e manutenzione
Durata tipica degli inverter ibridi
In media, gli inverter ibridi solari durano dai 10 ai 15 anni. Questo dato è paragonabile a quello degli inverter di stringa tradizionali, anche se i microinverter spesso durano più a lungo (fino a 20-25 anni) grazie al loro design distribuito.
La durata dipende in larga misura dalla qualità, dalle condizioni operative e dalla manutenzione.
Allungare la longevità
Per ottenere il massimo dal tuo inverter ibrido solare:
- Assicurati che la ventilazione sia adeguata ed evita il surriscaldamento.
- Controlla regolarmente la disponibilità di aggiornamenti del firmware da parte del produttore.
- Programma ispezioni periodiche per individuare tempestivamente eventuali segni di usura o danni.
- Mantieni il sistema pulito e protetto da fattori ambientali aggressivi.
Gli inverter ibridi sottoposti a una corretta manutenzione possono garantire un funzionamento affidabile oltre la loro durata prevista.
Come capire se il tuo inverter ibrido è difettoso
Il tuo inverter ibrido solare è il cuore del tuo impianto fotovoltaico: gestisce silenziosamente il complesso equilibrio tra i pannelli solari, la rete elettrica e l’accumulatore a batteria. Ma come qualsiasi altro componente critico, può guastarsi. Quando ciò accade, l’intero sistema energetico può funzionare in modo non ottimale o smettere completamente di funzionare. Ecco perché sapere come individuare i segnali di allarme di un inverter ibrido guasto è fondamentale per qualsiasi casa alimentata da energia solare.
Anche gli inverter ibridi di alta qualità possono sviluppare guasti nel tempo, soprattutto se sottoposti a condizioni ambientali difficili o se la manutenzione viene trascurata. Fortunatamente, il tuo inverter ibrido solare di solito ti darà alcuni chiari indizi prima di guastarsi completamente.
1. Improvviso calo della potenza erogata
Uno dei primi e più evidenti segni di un inverter difettoso è un calo inaspettato della produzione di energia. Se i tuoi pannelli solari sono esposti alla stessa quantità di luce solare del solito, ma la tua produzione di energia è diminuita in modo significativo, l’inverter ibrido solare potrebbe non funzionare correttamente.
Non affidatevi alla bolletta elettrica per individuare questo problema, poiché spesso essa registra un ritardo di settimane rispetto al calo effettivo delle prestazioni. Controllate invece regolarmente l’app o il sistema di monitoraggio dell’inverter. Questi strumenti mostrano in genere i dati storici, consentendovi di confrontare le prestazioni odierne con quelle dei giorni precedenti in condizioni simili.
2. Codici di errore e spie luminose
I moderni inverter ibridi solari sono dotati di funzionalità di diagnostica intelligente e autocontrollo. Quando si verifica un problema, solitamente visualizzano un codice di errore o lampeggiano con una spia di avvertimento. Questi indicatori possono apparire sullo schermo LCD dell’unità, tramite indicatori LED o all’interno dell’app dedicata.
Non ignorare questi avvisi. Anche un avviso apparentemente minore, come “sovratensione CC” o “guasto dell’uscita CA”, potrebbe indicare un problema più grave. Consulta il manuale utente per le definizioni dei codici di errore o contatta l’installatore o il team di assistenza del produttore per ricevere aiuto nell’interpretazione.
3. Surriscaldamento o rumori strani
Gli inverter funzionano in genere con un rumore minimo o nullo e entro un intervallo di temperatura sicuro. Se il vostro inverter ibrido emette improvvisamente ronzii, clic o rumori simili, o se risulta insolitamente caldo al tatto, è un segnale di allarme.
Il calore eccessivo può danneggiare i componenti interni e rumori strani possono indicare la presenza di archi elettrici o un condensatore difettoso. Si tratta di gravi problemi di sicurezza che devono essere risolti immediatamente da un tecnico autorizzato.
Una ventilazione adeguata è fondamentale per la longevità di qualsiasi inverter solare, compresi quelli ibridi. Assicuratevi che il vostro inverter sia installato in un’area ombreggiata e ben ventilata, lontano da umidità e luce solare diretta.
4. Comportamento incoerente della batteria
Poiché gli inverter ibridi solari gestiscono l’accumulo della batteria, eventuali irregolarità nelle prestazioni della batteria possono talvolta indicare un problema dell’inverter. Se la batteria non si ricarica completamente durante il giorno o, peggio ancora, si scarica troppo rapidamente durante la notte, il problema potrebbe risiedere nella logica di ricarica dell’inverter o nella sua capacità di regolare la corrente.
Ciò è particolarmente vero se la batteria è relativamente nuova e in buone condizioni. Verifica che le impostazioni della batteria nell’inverter siano configurate correttamente e osserva i modelli di comportamento della batteria utilizzando gli strumenti di monitoraggio.
5. Assenza di alimentazione durante un’interruzione della rete elettrica
Uno dei principali vantaggi di un inverter ibrido solare è la sua capacità di fornire energia di riserva durante le interruzioni di corrente. Se la tua casa rimane senza corrente e il tuo impianto solare non passa alla batteria di riserva come previsto, significa che c’è qualcosa che non va.
Ciò potrebbe essere causato da:
- Un interruttore di trasferimento difettoso all’interno dell’inverter.
- Impostazioni di priorità della batteria configurate in modo errato.
- Un relè interno danneggiato.
Qualunque sia la causa, l’incapacità di fornire energia di riserva compromette uno dei vantaggi principali del tuo sistema ibrido e deve essere risolta immediatamente.
6. Il sistema si spegne in modo intermittente
Se il tuo inverter ibrido solare si spegne e si riavvia frequentemente senza preavviso, è un chiaro segno di instabilità. Ciò può essere causato da:
- Fluttuazioni di tensione dalla rete elettrica
- Messa a terra inadeguata
- Sensori interni difettosi
Sebbene uno o due riavvii possano essere causati da fattori esterni, riavvii costanti sono anomali. Se non controllati, possono portare a un guasto permanente dell’inverter.
Cosa dovresti fare ora
Se noti uno qualsiasi di questi sintomi, non aspettare. Ritardare la riparazione può causare perdita di energia, degrado della batteria o guasti a livello di sistema. Ecco alcuni passaggi da seguire:
- Controlla l’app di monitoraggio o lo schermo dell’inverter per eventuali avvisi.
- Registra i codici di errore e il comportamento del sistema.
- Riavvia il sistema se consigliato dal produttore.
- Contatta un installatore o un tecnico certificato se il problema persiste.
Una manutenzione regolare e un monitoraggio proattivo possono contribuire notevolmente a prolungare la durata del tuo inverter ibrido solare. La maggior parte dei produttori offre anche garanzie che vanno dai 5 ai 10 anni, quindi assicurati di essere coperto e di tenere a portata di mano i relativi documenti.

Migliori pratiche di utilizzo
Posso lasciare acceso il mio inverter solare tutto il tempo?
Sì! Gli inverter ibridi solari sono progettati per funzionare in modo continuo. Funzionano 24 ore su 24, 7 giorni su 7, per ottimizzare l’utilizzo dell’energia e la gestione della batteria.
Assicurati che l’inverter sia installato in un’area ben ventilata, priva di polvere e umidità. Ispezioni periodiche garantiscono il corretto funzionamento del sistema senza surriscaldamento o degrado.
Quando è opportuno utilizzare un inverter ibrido?
Gli inverter ibridi sono particolarmente indicati per:
- Abitazioni situate in zone soggette a interruzioni di corrente o alimentazione instabile.
- Situazioni in cui si desidera massimizzare l’autoconsumo ed evitare di inviare l’energia solare in eccesso alla rete.
- Utenti che intendono aggiungere un sistema di accumulo a batteria ora o in futuro.
- Luoghi con vantaggi limitati o nulli in termini di net metering.
Utilizzo dell’inverter ibrido senza batteria
Un inverter ibrido solare può tecnicamente funzionare senza batteria, con un funzionamento simile a quello di un inverter collegato alla rete. Tuttavia, senza accumulo, si perdono i vantaggi chiave come l’alimentazione di riserva e lo spostamento del carico.
Vale la pena acquistare un inverter ibrido?
Il valore degli inverter ibridi solari dipende dalle circostanze individuali:
- Se si verificano frequenti interruzioni di corrente o l’alimentazione della rete è inaffidabile, le funzionalità di backup sono preziose.
- Se i prezzi dell’elettricità variano in base all’ora o le politiche di net metering sono sfavorevoli, massimizzare l’autoconsumo tramite un inverter ibrido può consentire di risparmiare denaro.
- Rendere il proprio sistema a prova di futuro per lo stoccaggio in batterie aggiunge flessibilità.
Sebbene l’investimento iniziale sia più elevato, molti utenti segnalano risparmi significativi a lungo termine e una maggiore sicurezza energetica. Se questi vantaggi sono in linea con i vostri obiettivi, un inverter ibrido solare è sicuramente da prendere in considerazione.g.
Conclusione
Gli inverter ibridi solari rappresentano un significativo passo avanti nella tecnologia solare, combinando il meglio dei sistemi collegati alla rete e dei sistemi off-grid. Offrono indipendenza energetica, alimentazione di riserva e gestione flessibile dell’energia in un unico dispositivo intelligente.
Per chi è pronto a rendere i propri investimenti nel solare a prova di futuro e massimizzare i risparmi, gli inverter ibridi sono una scelta interessante. Comprendendo i loro vantaggi, svantaggi e requisiti operativi, è possibile prendere una decisione informata che migliora la resilienza energetica e la sostenibilità della propria abitazione.
Se desideri acquistare inverter solari, puoi visitare Afore, un fornitore di inverter solari riconosciuto a livello mondiale.
Domande frequenti
1. Cos’è un inverter ibrido per impianti solari?
Un inverter ibrido è un dispositivo multifunzionale che combina le funzioni di un inverter solare tradizionale con la capacità di gestire l’accumulo in batterie e l’interazione con la rete elettrica.
In termini pratici, consente al vostro impianto solare di:
- Convertire l’energia elettrica in corrente continua prodotta dai pannelli in corrente alternata per l’uso domestico.
- Immagazzinare l’energia in eccesso nelle batterie per un uso successivo.
- Prelevare energia dalla rete quando necessario.
- Fornire energia di riserva in caso di interruzioni di corrente.
Questa funzionalità all-in-one rende gli inverter ibridi particolarmente interessanti per i proprietari di case che desiderano una soluzione solare flessibile, resiliente e pronta per il futuro.
2. Quali sono gli svantaggi degli inverter ibridi?
Sebbene gli inverter ibridi solari offrano flessibilità e capacità di alimentazione di riserva, presentano alcuni compromessi:
- Costi iniziali più elevati: i sistemi ibridi richiedono in genere sia una batteria che un inverter più avanzato, aumentando l’investimento iniziale.
- Efficienza leggermente inferiore: a causa dei molteplici processi di conversione dell’energia (ad esempio, dal solare alla batteria alla casa), possono verificarsi piccole perdite di energia rispetto ai sistemi a uso diretto.
- Dipendenza dalla batteria: se la batteria si guasta o si degrada, ciò può influire sulle prestazioni complessive del sistema ibrido.
- Problemi di compatibilità: non tutti gli inverter ibridi sono universalmente compatibili con ogni marca di batteria o configurazione di pannelli solari, limitando le opzioni di aggiornamento.
Nonostante questi svantaggi, molti proprietari di case ritengono che i risparmi a lungo termine e l’indipendenza energetica superino i costi iniziali.
3. Un inverter ibrido è migliore di un inverter tradizionale?
Dipende dai tuoi obiettivi.
Un inverter solare ibrido è più indicato se:
- Desideri disporre di energia di riserva in caso di interruzioni di corrente.
- Hai intenzione di installare o possiedi già un sistema di accumulo a batteria.
- Vivi in una zona con tariffe elettriche elevate o con limitazioni nella misurazione netta.
Tuttavia, se il tuo unico obiettivo è ridurre le bollette utilizzando l’energia solare senza investire in batterie, un inverter solare tradizionale (collegato alla rete) potrebbe essere più conveniente e più semplice da mantenere.
In sostanza, gli inverter ibridi sono più adatti alle famiglie che desiderano un maggiore controllo sul proprio consumo energetico e vogliono rendere i propri impianti solari a prova di futuro.
4. Qual è la durata di vita prevista di un inverter solare ibrido?
La maggior parte degli inverter ibridi solari è progettata per durare dai 10 ai 15 anni, anche se i modelli di fascia alta possono funzionare bene più a lungo con una corretta manutenzione.
I fattori che influenzano la durata includono:
- Qualità del marchio
- Condizioni ambientali (calore eccessivo, umidità o polvere)
- Pratiche di installazione
- Manutenzione ordinaria
I produttori spesso offrono garanzie che vanno dai 5 ai 10 anni, con opzioni di estensione della copertura. Per garantire una lunga durata, è importante installare l’inverter in un’area ombreggiata e ventilata e seguire gli intervalli di manutenzione raccomandati.
5. Come capire se il tuo inverter ibrido è difettoso?
Ci sono diversi segnali che indicano che il tuo inverter ibrido solare potrebbe non funzionare bene:
- Cali inspiegabili nella produzione di energia solare
- Spegnimenti o riavvii frequenti del sistema
- Messaggi di errore o spie di avvertimento sul display dell’inverter
- Rumori strani (ronzio, brusio o ticchettio)
- Carica/scarica della batteria incostante
- Assenza di alimentazione di riserva durante un’interruzione di corrente
La maggior parte degli inverter ibridi è dotata di app mobili o portali di monitoraggio che facilitano il monitoraggio delle prestazioni del sistema. Se sospetti un problema, consulta un tecnico solare certificato per diagnosticare e risolvere il problema prima di it escalates.
6. Posso lasciare acceso il mio inverter solare tutto il tempo?
Sì, e dovresti farlo. Gli inverter ibridi solari, come tutti i moderni inverter solari, sono progettati per funzionare 24 ore su 24, 7 giorni su 7. Gestiscono continuamente il flusso di energia tra i pannelli, la casa, la batteria e la rete elettrica. Spegnerli inutilmente può interrompere la produzione di energia, influire sulla ricarica della batteria e ridurre l’efficienza del sistema.
Detto questo, è fondamentale mantenere l’inverter adeguatamente ventilato e pulito. Controlli di manutenzione regolari possono garantire che il funzionamento continuo non provochi surriscaldamento o stress dei componenti interni nel tempo.
7. Vale la pena acquistare un inverter ibrido?
Per molti proprietari di case, assolutamente sì. Sebbene un inverter ibrido solare comporti costi iniziali più elevati, i vantaggi a lungo termine possono giustificare l’investimento:
- Sicurezza energetica: non rimarrete al buio durante i blackout.
- Risparmio sulle bollette: utilizzate l’energia solare immagazzinata durante le ore di picco dei prezzi.
- Preparazione al futuro: integrate facilmente le batterie o ampliate il vostro sistema.
- Maggiore indipendenza dalla rete elettrica: aumenta la tua indipendenza energetica.
Il valore di un inverter ibrido aumenta significativamente nelle regioni con:
- Frequenti interruzioni di corrente.
- Fatturazione dell’elettricità in base al tempo di utilizzo.
- Bassa compensazione net metering.
In breve, se pensi a lungo termine, un inverter ibrido è più che conveniente: è strategico.
8. Un inverter solare ibrido può funzionare senza batteria?
Sì, è possibile. Molti inverter ibridi solari moderni sono progettati per funzionare con o senza batteria. Nei sistemi senza accumulo, l’inverter funziona in modo simile a un inverter standard collegato alla rete: immette l’energia solare in eccesso nella rete e preleva energia quando necessario.
Tuttavia, senza una batteria:
- Non avrai energia di riserva durante le interruzioni di corrente
- Perderai il vantaggio di immagazzinare energia per l’uso notturno o nelle ore di picco
- Le capacità di spostamento del carico sono limitate
Ecco perché molti proprietari di case installano prima gli inverter ibridi e poi aggiungono le batterie in un secondo momento, quando il budget o gli incentivi lo consentono.low.
9. Quando è opportuno utilizzare un inverter ibrido?
Un inverter ibrido solare è utile se si verifica una delle seguenti condizioni:
- Desideri un’alimentazione di riserva: sia che tu viva in una zona con un servizio di rete elettrica inaffidabile o che desideri semplicemente stare tranquillo durante i temporali o le emergenze.
- Hai intenzione di installare un sistema di accumulo a batteria ora o in futuro: gli inverter ibridi sono compatibili con varie tecnologie di batterie e ti consentono di espandere il sistema quando sei pronto.
- Siete soggetti a tariffe elettriche basate sul tempo di utilizzo: immagazzinate l’energia solare quando è economica e utilizzatela quando le tariffe raggiungono il picco.
- Avete benefici limitati o nulli dal net metering: conservare l’energia solare per uso personale spesso è più vantaggioso che rivenderla a tariffe basse.
Se la flessibilità, la scalabilità futura e la sicurezza energetica sono priorità, un inverter ibrido non è solo utile, è indispensabile.eal.