Cosa può fare un inverter da 750 Watt? Una guida completa per un uso intelligente dell’energia

Indice dei contenuti
Quando si parla di vita off-grid, di vita in furgone, di viaggi in camper o di configurazioni di emergenza, una delle domande più comuni che ci si pone è: A cosa serve un inverter da 750 watt? Se vi siete chiesti questo, siete nel posto giusto. In questa guida completa, vi illustreremo tutto ciò che c’è da sapere sull’inverter da 750 watt: cosa può alimentare, quanto dura, cosa non collegare e quando è il caso di prendere in considerazione un’opzione più grande.
Sia che stiate confrontando un alimentatore da 750 watt con un inverter da 750 watt, sia che stiate cercando di alimentare la vostra macchina CPAP in un camper, sia che stiate cercando di superare comodamente un blackout, questa guida spiega tutto in termini semplici e umani, senza bisogno di una laurea in ingegneria elettronica.
Capire le basi di un inverter da 750 Watt
Cos’è un inverter da 750 Watt?
Un 750 watt inverter è un dispositivo che converte l’alimentazione in corrente continua (di solito da una batteria da 12 V) in corrente alternata, che viene utilizzata dalla maggior parte dei nostri elettrodomestici e gadget quotidiani. Offre una potenza massima continua di 750 watt, sufficiente per gestire un’ampia gamma di dispositivi di piccole e medie dimensioni.
È bene chiarire che un alimentatore da 750 watt e un inverter da 750 watt non sono la stessa cosa. Un alimentatore si riferisce in genere a un’unità che converte la corrente alternata in corrente continua per i dispositivi elettronici come i computer, mentre un inverter fa il contrario: converte la corrente continua (come quella della batteria dell’auto) in corrente alternata.
Onda sinusoidale pura vs. onda sinusoidale modificata
Esistono due tipi principali di 750w inverter di potenza:
- Inverter a onda sinusoidale pura: Producono forme d’onda pulite e uniformi, ideali per l’elettronica sensibile.
- Inverter a onda sinusoidale modificata: Più convenienti, ma meno compatibili con alcuni dispositivi come le microonde o le apparecchiature mediche.
Pertanto, se si prevede di utilizzare l’inverter con macchine CPAP o computer portatili, scegliere una versione a onda sinusoidale pura.

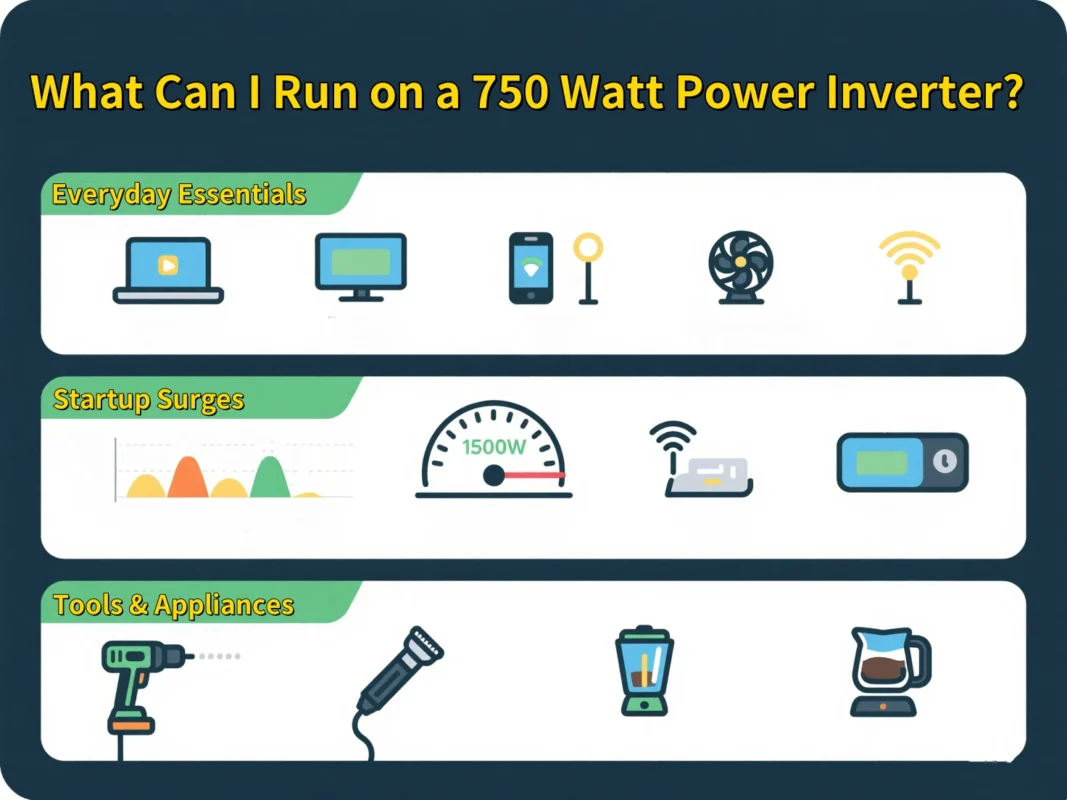
Cosa si può utilizzare con un inverter da 750 Watt?
Un inverter da 750 watt è uno di quei dispositivi che non sono troppo grandi per essere inefficienti, né troppo piccoli per essere limitanti. Se state vivendo una vita da furgone, se vi state preparando per un’interruzione di corrente o se avete semplicemente bisogno di convertire l’alimentazione da CC a CA in movimento, un inverter da 750 watt offre una solida miscela di portabilità e resa pratica. Ma cosa si può utilizzare esattamente?
Scopriamo cosa può gestire realisticamente un inverter da 750 watt, come gestirne saggiamente la potenza e cosa evitare di collegarvi. La comprensione di questi limiti vi aiuterà a utilizzarlo in modo efficiente e sicuro, assicurandovi di ottenere il massimo dalla vostra installazione.
Elementi essenziali di tutti i giorni che possono alimentare
Uno dei maggiori vantaggi dell’utilizzo di un inverter da 750 watt è la sua capacità di far funzionare una serie di dispositivi domestici ed elettronici di piccole e medie dimensioni. Ecco un rapido elenco dei tipi di elettrodomestici e gadget che è possibile utilizzare comodamente senza sovraccaricarlo:
- Laptop e tablet (30-90 watt): Se state lavorando in remoto o se state guardando un film in streaming, un inverter da 750 watt può gestire facilmente uno o due laptop.
- TV LED (fino a 32″) (60-100 watt): Volete seguire la partita o guardare un programma ininterrottamente nel vostro camper? Nessun problema.
- Smartphone e dispositivi USB (5-20 watt): Carica più telefoni o tablet con spazio a disposizione.
- Ventilatori portatili (40-75 watt): Mantengono l’aria in movimento durante i campeggi estivi o le notti calde in caso di interruzione di corrente.
- Sistemi di illuminazione a LED (10-50 watt per luce): Illuminano lo spazio senza intaccare il budget energetico.
- Router e modem Internet (15-30 watt): Rimanere online anche quando la rete elettrica va in tilt.
- Macchine CPAP (30-60 watt): Fondamentale per i soggetti affetti da apnea del sonno: molti utenti di CPAP si affidano agli inverter durante i viaggi o i blackout.
La regola d’oro? Controllare sempre la potenza nominale di ogni dispositivo prima di collegarlo. Solo perché “sembra” poco potente, non significa che non abbia un’elevata sovracorrente all’avvio.
Attenzione all’aumento delle startup
A proposito di picchi, molti dispositivi, in particolare quelli con compressori o motori, assorbono una quantità di energia significativamente maggiore alla prima accensione rispetto al funzionamento costante. Questo picco momentaneo è noto come picco di potenza all’avvio ed è uno dei motivi principali per cui gli inverter si guastano o si danneggiano.
Un inverter da 750 watt gestisce in genere una capacità di picco di circa 1500 watt, ma questo varia a seconda del modello. Ciò significa che è in grado di gestire brevi picchi, purché non durino troppo a lungo o si verifichino contemporaneamente su più dispositivi.
Ad esempio, alcuni televisori a LED o vecchi computer portatili possono raggiungere momentaneamente un picco di 120-150 watt prima di stabilizzarsi. Se ne alimentate diversi contemporaneamente, raggiungerete rapidamente il limite di picco.
Strumenti e piccoli elettrodomestici da utilizzare
Potreste essere sorpresi di scoprire che alcuni utensili leggeri e piccoli elettrodomestici sono a portata di mano:
- Caricabatterie per utensili a batteria (70-150 watt)
- Rasoi elettrici o caricatori di spazzolini da denti (5-20 watt)
- Frullatori o frullatori a bassa potenza (300-500 watt)
- Piccole macchine da caffè (senza piastra) (600-700 watt)
Tutti questi apparecchi sono utilizzabili con un inverter da 750 W, soprattutto se utilizzati uno alla volta. Bisogna solo fare attenzione a non accoppiare più apparecchi a medio carico contemporaneamente: un frullatore e una macchina per il caffè insieme, ad esempio, potrebbero farvi superare il limite.
Ideale per i camper, la vita da furgone e le avventure fuori rete
Un inverter da 750 watt è ideale per camper, roulotte e allestimenti mobili in cui lo spazio e l’efficienza energetica sono importanti. Per i nomadi digitali o gli avventurieri del fine settimana, questa gamma di wattaggio consente di mantenere l’essenziale in funzione, senza portarsi dietro un enorme generatore o scaricare la batteria in un attimo.
Con un alimentatore da 750 watt adeguatamente dimensionato, è possibile allestire un ufficio mobile con un computer portatile, un router Wi-Fi e luci LED, il tutto contemporaneamente. È una quantità di energia sufficiente per uno stile di vita off-grid confortevole, quando le vostre esigenze sono modeste ma essenziali.
Combinare l’uso intelligente con la consapevolezza dell’alimentazione
Sebbene l’elenco di ciò che si può utilizzare con un inverter da 750 W sia impressionante, tutto si riduce alla gestione dell’energia. Non si può semplicemente collegare tutto in una volta e aspettarsi che funzioni perfettamente. Considerate queste buone pratiche:
- Utilizzate un misuratore di watt per monitorare il consumo di energia in tempo reale.
- Scaglionare l’utilizzo in modo che i dispositivi non consumino energia nello stesso momento.
- Evitate i “carichi fantasma”, ossia i dispositivi che assorbono energia anche quando sono spenti.
- Privilegiate le apparecchiature critiche, come i dispositivi medici, rispetto agli elettrodomestici di lusso.
Se si utilizza una batteria, è importante anche calcolare la durata dell’alimentazione. Ad esempio, una batteria da 100Ah a 12 V fornisce circa 1.200 wattora. Il funzionamento continuo di un dispositivo da 600 W si esaurirebbe in sole due ore: la capacità della batteria è importante quanto le dimensioni dell’inverter.
Capendo esattamente cosa è possibile utilizzare con un inverter da 750 watt, sarete in grado di fare scelte più intelligenti e sicure per il vostro fabbisogno energetico. Si tratta di una soluzione potente ed efficiente se utilizzata entro i limiti della sua portata, e che si è guadagnata il suo posto nelle case, nei camper e nei kit di emergenza di tutto il mondo. energy needs. It’s a powerful and efficient solution when used within its range—and one that’s earned its place in homes, campers, and emergency kits around the world.

Quanto dura un inverter da 750 Watt?
Una domanda che spesso ci si pone quando si inizia a utilizzare un inverter da 750 watt è: quanto durerà? La risposta non è univoca, perché la durata dell’inverter dipende da alcuni fattori chiave, in particolare dalle dimensioni della batteria, dal tipo di carico e dall’efficienza del sistema.
Vediamo di capire meglio cosa aspettarsi quando si alimentano i dispositivi con un inverter da 750 watt, sia che si utilizzi una singola batteria da 12 V, sia che si utilizzi un impianto marino a ciclo profondo, sia che si utilizzino banchi di batterie a carica solare.
Le dimensioni della batteria sono importanti, e non si tratta solo di ore/amp.
Quando si dice: “Ho una batteria da 100Ah, quanto durerà il mio inverter?”, non è tutto. L’inverter da 750 watt trae l’energia dalla batteria e la durata dipende dai wattora disponibili, non solo dagli ampere.
Ecco la formula di base:
Capacità della batteria (Ah) × Tensione della batteria (V) = Wattora (Wh)
Quindi, ad esempio, una batteria a ciclo profondo da 100Ah 12V completamente carica fornisce:
100Ah × 12V = 1.200 wattora (Wh)
Ora, se si utilizza un carico continuo di 750 watt:
1.200 Wh ÷ 750 W = 1,6 ore di autonomia (teorica)
Ma c’è un problema: si tratta di una soluzione ideale che non tiene conto della situazione:
- Inefficienza dell’inverter (in genere ~85-90%)
- Limiti di profondità di scarica (in particolare se si utilizzano batterie al piombo-acido)
- Età della batteria e condizioni di temperatura
- Carichi sconnessi o irregolari (come un frullatore o un microonde)
Considerando tutti questi fattori, il vostro alimentatore da 750 watt potrebbe alimentare un carico da 750 W solo per circa 1-1,3 ore con la stessa batteria.
Scenari del mondo reale: cosa aspettarsi
Nella vita reale, è probabile che non si arrivi sempre a 750 watt. Ad esempio, supponiamo che stiate utilizzando un mix di dispositivi:
- Luci a LED (40 watt totali)
- Computer portatile (60 watt)
- Mini frigorifero (50 watt, con brevi picchi a 120 W)
- Router Wi-Fi (15 watt)
Si tratta di circa 165-180 W continui, a seconda del ciclo del compressore del frigorifero.
Ora la batteria da 100Ah a 12 V potrebbe durare:
1.200Wh ÷ 180W ≈ 6,6 ore (realisticamente più vicino a 5-6 ore)
È qui che l’inverter da 750 W brilla: non necessariamente in situazioni di alto consumo, ma in casi di utilizzo moderato e con più dispositivi. È possibile alimentare i dispositivi essenziali per ore senza stressare il sistema o scaricare troppo rapidamente la batteria.
E se si utilizza la batteria dell’auto?
Molti utenti si chiedono se sia possibile collegare l’inverter da 750 watt alla batteria da 12 V del veicolo e partire. Tecnicamente sì, ma solo per brevi periodi e con il motore acceso.
Ecco perché:
- Una tipica batteria per auto è progettata per l’avviamento, non per il deep cycling.
- La maggior parte delle batterie per auto offre circa 50-70Ah e solo una parte di questa quantità è utilizzabile senza danneggiare la batteria.
- Se si utilizza un carico completo di 750 watt, anche per 30-40 minuti, si rischia di non riuscire più ad avviare l’auto.
Quindi, a meno che non si utilizzi una batteria dedicata a ciclo profondo o che il motore sia al minimo per ricaricarsi costantemente, non è il piano più sicuro o efficiente a lungo termine.
Sovratensione e carico continuo: perché influisce sulla durata
Anche se state alimentando solo pochi dispositivi, tenete presente che le sovratensioni all’avvio possono far impennare momentaneamente il consumo dell’inverter. Un piccolo frigorifero può consumare solo 70 watt una volta in funzione, ma l’assorbimento all’avvio può raggiungere brevemente i 300-400 watt.
Questo picco momentaneo non ucciderà l’inverter, ma può influire sulla durata complessiva dell’inverter da 750 watt, perché questi picchi assorbono più corrente dalla batteria.
L’abbinamento dell’inverter a un alimentatore intelligente da 750 watt o a un monitor della batteria può aiutare a tenere sotto controllo l’assorbimento di energia istantaneo e medio, fondamentale per massimizzare il tempo di funzionamento.
È possibile prolungare il tempo di esecuzione?
Assolutamente sì. Ecco alcuni modi per spremere più succo dalla configurazione dell’inverter:
- Utilizzare apparecchi ad alta efficienza (ad esempio, i LED al posto delle incandescenze).
- Aumento della capacità della batteria (collegamento di più batterie da 12 V in parallelo)
- Utilizza batterie al litio, che offrono scariche più profonde e una maggiore energia utilizzabile
- Ricarica tramite pannelli solari per ricaricare durante il giorno ed estendere la disponibilità di energia.
Se state pianificando una vita off-grid, il campeggio o la preparazione alle emergenze, è fondamentale costruire un sistema ben bilanciato che corrisponda alle vostre esigenze. L’inverter da 750 W è spesso il cuore di queste configurazioni e dà il meglio di sé se abbinato a una pianificazione e a una gestione oculate delle batterie.
In breve, il tempo di funzionamento di un inverter da 750 watt dipende da cosa si sta alimentando, dalla capacità della batteria e dall’uso che se ne fa. Per le configurazioni di base con una sola batteria e carichi leggeri, si possono prevedere diverse ore di funzionamento. Se lo si spinge al limite dei 750 watt, il tempo di funzionamento sarà di poco più di un’ora, a meno che non si aggiorni l’alimentatore di conseguenza.
Parliamo poi di ciò che non si dovrebbe collegare all’inverter e del perché questo è più importante di quanto si pensi.
Cosa NON si deve collegare a un inverter da 750 W?
Evitare di collegarsi:
- Frigoriferi
- Compressori d’aria
- Pompe per pozzetti
- Tostapane
- Bollitori elettrici
Questi apparecchi hanno spesso elevati picchi di avvio o assorbimenti continui che superano le capacità di un inverter da 750 watt.
Inoltre, non dimenticate la regola d’oro: se si riscalda o si raffredda, probabilmente assorbe più di 750 watt!
Un inverter da 750 Watt è sufficiente per le vostre esigenze?
Che dimensioni ha l’inverter per far funzionare una casa?
Risposta breve? Non un inverter da 750 watt. Sebbene sia ottimo per piccole attività e per usi di riserva, per gestire un’intera casa sono necessari almeno 3.000 watt. Questo include il funzionamento simultaneo di elementi essenziali come il frigorifero, il microonde e le luci.
Suggeriamo di dimensionare l’inverter in base al wattaggio totale più le spese generali di 20-30%.
Quanto è grande l’inverter di cui ho bisogno per far funzionare l’aria condizionata?
Anche un piccolo condizionatore da finestra può richiedere 1000-1500 W, soprattutto all’avvio. Avreste bisogno di un inverter da almeno 2000 W e di una batteria robusta. Quindi, ancora una volta, un inverter da 750 watt non è sufficiente per le esigenze di raffreddamento.
Quando è opportuno passare da un inverter da 750W?
Se vi ritrovate a calcolare costantemente il wattaggio, a staccare i dispositivi per farne funzionare altri o a dover alimentare qualsiasi cosa con un motore o una bobina di riscaldamento, è arrivato il momento di fare un upgrade.
Considerate un inverter da 1000W o 1500W per:
- Microonde
- Utensili elettrici
- Macchine da caffè
O addirittura fino a 3000W se si intende vivere a lungo fuori dalla rete o se si utilizza molto l’energia solare.
Inverter 750W vs. Generatore: Qual è la scelta giusta?
Generatori come quello da 8000 watt possono alimentare tutta la casa, ma sono ingombranti, rumorosi e consumano molto carburante. Un inverter da 750 watt, invece, offre i seguenti vantaggi:
- Tranquillo
- Portatile
- Ideale per un utilizzo a breve termine o limitato
Scegliete un generatore per l’intera casa o per un backup a lungo termine. Scegliete un inverter da 750 watt per le attività più piccole e silenziose.

I migliori inverter da 750 Watt da considerare
Caratteristiche da ricercare
- Protezione da sovraccarico
- Allarme di bassa tensione
- Porte di ricarica USB
- Uscita a onda sinusoidale pura (per elettronica sensibile)
- Ventole di raffreddamento
I migliori casi d’uso
- RV e camper: Caricare i telefoni, far funzionare i ventilatori, alimentare le luci.
- Viaggi in campeggio: Mantenete i vostri dispositivi carichi senza dovervi trascinare dietro un generatore.
- Kit di emergenza: Rimanere online e illuminati durante i blackout.
Conclusione
L’inverter da 750 watt è un dispositivo piccolo ma potente per tutti coloro che vivono in viaggio, si preparano per le emergenze o si avvicinano all’alimentazione off-grid. Anche se non è in grado di far funzionare il frigorifero o l’aria condizionata, è un ottimo strumento per l’elettronica di tutti i giorni, soprattutto se abbinato alla giusta configurazione della batteria.
Vi state ancora chiedendo cosa si può utilizzare con un inverter da 750 watt? Limitatevi ai gadget da meno di 750 W in totale, evitate tutto ciò che ha un motore o un elemento riscaldante e sarete a posto. Per una fonte di energia silenziosa, priva di carburante e affidabile, l’inverter da 750 watt soddisfa tutte le esigenze.
Domande frequenti sugli inverter da 750 Watt
Quanto può funzionare un inverter da 750 watt?
Un inverter da 750 watt può alimentare un numero sorprendente di dispositivi di piccole e medie dimensioni. Pensate a computer portatili, piccoli televisori a LED, console di gioco, router, macchine CPAP, luci a LED, ventilatori e persino strumenti da cucina a basso consumo come frullatori o piccole macchine per il caffè (senza piastra). È inoltre possibile ricaricare contemporaneamente smartphone, tablet e altri dispositivi alimentati tramite USB.
Se vi state chiedendo: “Cosa posso far funzionare con un inverter da 750 watt?”. – la risposta breve è: la maggior parte degli apparecchi elettronici e a basso consumo che assorbono meno di 750 watt continui e che non richiedono un’elevata sovracorrente per essere avviati.
Quanto durerà una batteria da 12 volt con un inverter da 800 watt?
Anche se non direttamente legata all’inverter da 750 W, questa è una domanda rilevante per la pianificazione dell’energia. Una tipica batteria a ciclo profondo da 12 V e 100 Ah ha circa 1200 wattora di energia utilizzabile (assumendo un’efficienza di 100%, cosa che raramente si verifica). Un inverter da 800 watt a pieno carico scaricherebbe la batteria in circa 1,5 ore, senza tenere conto delle perdite di efficienza dell’inverter, che di solito sono di 85-95%.
Con un inverter da 750 watt, se si utilizzano costantemente tutti i 750 watt, si possono prevedere tempi di funzionamento simili. Tuttavia, se lo si utilizza a intermittenza o con un consumo di 300-500 watt, la batteria potrebbe durare molto di più, fino a 3-4 ore a seconda del carico.
Cosa non si deve collegare a un inverter?
Bella domanda e fondamentale. Non si devono mai collegare a un inverter da 750 watt apparecchi ad alto carico, ad alta intensità di sovratensione o che generano calore. Questo include:
- Microonde
- Asciugacapelli
- Bollitori elettrici
- Tostapane
- Riscaldatori per ambienti
- Frigoriferi a grandezza naturale
- Utensili elettrici come le seghe circolari
Questi dispositivi non solo superano il limite di 750 watt dell’alimentatore, ma possono anche produrre elevati picchi di potenza che potrebbero danneggiare l’inverter. Anche se il loro wattaggio nominale sembra al limite dell’accettabile, il loro assorbimento all’avvio può far scattare o surriscaldare l’unità.
Che dimensioni ha l’inverter per far funzionare una casa?
Se si cerca di far funzionare un’intera abitazione, compresi frigoriferi, pompe di pozzo, sistemi HVAC e dispositivi multipli, è necessario molto più di un inverter da 750 watt. Per le applicazioni a casa intera, in genere si tratta di inverter da 3000 a 8000 watt o più, a seconda della configurazione e degli apparecchi che si desidera far funzionare.
Un inverter da 750 watt può funzionare come sistema supplementare o di backup per i dispositivi critici, come l’illuminazione, le comunicazioni e l’elettronica di base, ma non per l’aria centralizzata o i grandi elettrodomestici.
Quanto è grande l’inverter di cui ho bisogno per far funzionare la corrente alternata?
La maggior parte dei condizionatori d’aria, anche le piccole unità portatili, richiedono almeno 1500-3000 watt per funzionare, con picchi di avvio spesso molto più elevati. Un inverter da 750 watt non è in grado di far funzionare le unità CA standard.
Ci sono alcune eccezioni: alcune unità CA ultra-efficienti da 5.000 BTU progettate per l’uso in camper o fuori rete possono funzionare con un inverter da 1000-1500 watt, ma anche in questo caso 750 watt non sono sufficienti per i carichi CA tipici.
Posso utilizzare un inverter da 750 watt nel mio camper o nel mio camper?
Assolutamente sì! In effetti, gli inverter da 750 watt sono i preferiti dai camperisti e dagli abitanti dei furgoni per le applicazioni leggere. È possibile utilizzarne uno per alimentare il televisore, ricaricare computer portatili e telefoni, far funzionare ventilatori, illuminazione a LED e persino utilizzare un piccolo frullatore per frullati o shake. Basta tenere sotto controllo i livelli della batteria e l’assorbimento di energia.
Per gli impianti off-grid più grandi, spesso si combina un inverter da 750 W con un impianto solare e più batterie per prolungare l’autonomia e coprire i carichi essenziali.
Un inverter da 750 watt è sicuro per le macchine CPAP?
Sì, nella maggior parte dei casi, un inverter da 750 watt fornisce una potenza più che sufficiente per le macchine CPAP, che in genere consumano 30-60 watt. Tuttavia, se il vostro apparecchio è dotato di un umidificatore riscaldato, il wattaggio potrebbe superare i 100 watt. Tuttavia, questo valore rientra nella gamma di funzionamento di un alimentatore da 750 watt.
Assicurarsi di utilizzare un inverter a onda sinusoidale pura per le apparecchiature mediche. Gli inverter a onda sinusoidale modificata possono causare problemi o ridurre l’efficienza della macchina.
Posso utilizzare un inverter da 750 watt con i pannelli solari?
Sicuramente. Un inverter da 750 watt si abbina bene ai sistemi di energia solare su piccola scala, soprattutto nei camper, nelle baite o nei kit di emergenza. Se l’impianto solare comprende un banco di batterie e un regolatore di carica, è possibile far funzionare le luci, caricare l’elettronica e alimentare piccoli elettrodomestici in modo efficiente.
Assicuratevi che l’inverter da 750 W sia collegato a una batteria con una capacità di ampere-ora sufficiente. Per le configurazioni solari, un banco di batterie da 100Ah o 200Ah è in genere l’ideale per questa taglia di inverter.
Un inverter da 750 watt può far funzionare un minifrigo?
Dipende. Alcuni mini-frigoriferi compatti, soprattutto quelli realizzati per i dormitori o i camper, consumano meno di 100 watt quando sono in funzione, ma possono avere un picco di avvio di 600-1000 watt. Se il vostro inverter da 750 watt ha una capacità di picco superiore a 1500 watt, potrebbe farcela. In caso contrario, potrebbe spegnersi o incendiarsi.
Controllate l’etichetta del produttore del frigorifero e siate prudenti. È più sicuro far funzionare i mini-frigoriferi con inverter da 1000 watt o superiori per far fronte alle sovratensioni di avvio.
Posso caricare le batterie degli utensili elettrici con un inverter da 750 W?
Sì, purché il caricabatterie non superi la capacità dell’inverter. La maggior parte dei caricabatterie per utensili a batteria consuma tra i 70 e i 150 watt, un valore che rientra nel range. Basta non caricare più utensili contemporaneamente, a meno che l’assorbimento combinato non sia inferiore a 750 watt.
Questo rende un inverter da 750 watt utile per i lavori in loco o per i progetti di bricolage a distanza, soprattutto se abbinato a una batteria portatile o a una stazione di ricarica solare.pecially when paired with a portable battery pack or solar charging station.