Inversor de 48V: o guia definitivo para sistemas de energia eficientes e dimensionáveis

Índice
Quando se trata de construir um sistema confiável de energia solar ou de energia fora da rede, um termo que você encontrará com frequência é o inversor de 48V. Mas o que ele é exatamente e por que é tão importante em sua configuração? Independentemente de você estar montando um sistema completo de energia solar para sua casa ou apenas tentando alimentar um trailer ou um campista de forma mais eficiente, compreender a função de um inversor de 48 V pode ser decisivo para todo o seu plano de energia.
Neste guia, vamos nos aprofundar no que é um inversor de 48V, como ele se compara a sistemas como um inversor de 24 volts CC e como escolher a melhor opção com base em suas necessidades energéticas exclusivas. Vamos desvendar tudo isso juntos.
O que é um inversor de 48V?
Um inversor de 48V é um dispositivo que converte 48 volts de corrente contínua (CC), que normalmente é armazenada em uma bateria, em corrente alternada (CA), que é usada para alimentar eletrodomésticos comuns. Isso é fundamental em sistemas de energia solar porque os painéis solares e as baterias usam energia CC, enquanto a maioria dos eletrodomésticos requer energia CA.
Em comparação com os sistemas de 12V ou 24V, os inversores de 48V oferecem o melhor equilíbrio entre eficiência e segurança, especialmente ao lidar com demandas de energia mais altas. Os sistemas de 48 V não transportam muita corrente pelos fios (o que pode levar à perda de calor), mas, em vez disso, usam corrente mais baixa em tensões mais altas, o que permite que todos os equipamentos funcionem de forma mais fria e eficiente.

Por que os inversores de 48V são tão populares atualmente?
O aumento da popularidade do inversor de 48V não é apenas uma tendência passageira - é uma resposta direta à crescente demanda por soluções de energia eficientes, confiáveis e escalonáveis. À medida que mais pessoas se voltam para a energia solar, a vida fora da rede e os sistemas de energia de reserva, o inversor de 48V se tornou a opção ideal para configurações residenciais e comerciais. Mas por que exatamente essa configuração de tensão está ganhando tanta força?
Eficiência aprimorada para as necessidades modernas de energia
Um dos principais motivos pelos quais os inversores de 48 V estão se tornando o novo padrão é sua eficiência superior em comparação com os sistemas de tensão mais baixa. Ao lidar com alta potência de saída - especialmente acima de 2.000 W - um sistema de 48 V reduz a quantidade de corrente necessária para fornecer a mesma potência. Uma corrente menor significa que menos energia é perdida na forma de calor, o que se traduz em mais potência utilizável e melhor desempenho geral do sistema. Isso é especialmente importante quando seu sistema de energia precisa operar vários aparelhos ou suportar cargas mais pesadas, como condicionadores de ar, máquinas de lavar ou até mesmo bombas de poço.
Ideal para sistemas de energia solar de médio a grande porte
À medida que os sistemas de energia solar crescem em tamanho e capacidade, aumenta a demanda por soluções de inversores estáveis e escalonáveis. Um inversor de 48 V é ideal para painéis solares acima de 3 kW porque oferece o equilíbrio perfeito entre custo-benefício e desempenho. Ao contrário de um inversor de 24 volts CC, que é mais adequado para configurações menores, um sistema de 48 V oferece mais espaço para expansão sem a necessidade de atualizar toda a sua infraestrutura posteriormente.
Custos reduzidos de fiação e simplicidade de instalação
Quanto maior a tensão, menor o consumo de corrente, de modo que podem ser usados fios mais finos, economizando nos custos de cabos de cobre e reduzindo a complexidade da instalação. Para instaladores e entusiastas do faça-você-mesmo, os sistemas de inversores de 48V são mais fáceis de gerenciar e mais seguros para expandir, especialmente em ambientes que exigem longas distâncias de fiação, como painéis solares no telhado ou garagens isoladas.
Melhor compatibilidade com bancos de baterias de lítio
À medida que as baterias de lítio se tornam mais acessíveis e populares, elas são frequentemente combinadas com inversores de 48V porque são compatíveis com sistemas de tensão mais alta. As baterias de lítio operam com mais eficiência em tensões mais altas e, quando combinadas com um inversor de 48 V, proporcionam tempos de operação mais longos, carregamento mais rápido e ciclo de vida mais longo do que quando se usa um inversor de 24 V CC.
Preparando seu sistema híbrido ou fora da rede para o futuro
Quer esteja construindo uma cabana totalmente fora da rede ou integrando a energia solar à sua casa ligada à rede, investir em um inversor de 48 V garante que seu sistema possa lidar com futuras atualizações. Precisa adicionar mais painéis? Adicionar mais capacidade de bateria? Usar um aparelho de maior potência? Um sistema de 48V oferece a flexibilidade e a sobrecarga para crescer com suas necessidades - sem começar do zero.

Inversor de 48V vs. Inversor de 24 Volts CC: Qual é a diferença?
Quando se trata de escolher um inversor para seu sistema de energia solar, de backup ou fora da rede, uma das primeiras decisões que você precisa tomar é a voltagem. O debate mais comum? Inversor de 48 V vs. inversor de 24 volts CC. Embora ambos possam converter CC (corrente contínua) em CA (corrente alternada) utilizável, as diferenças entre eles podem afetar muito a eficiência, o custo e a escalabilidade do seu sistema.
Vamos detalhá-lo para que você possa escolher o inversor certo para sua configuração.
Tensão e corrente: a diferença elétrica básica
A diferença mais fundamental é a tensão de operação. Um inversor CC de 24 volts funciona com um banco de baterias de 24V, enquanto um inversor de 48V funciona com uma configuração de bateria de 48V. Veja por que isso é importante:
Em uma tensão mais alta, é necessária menos corrente para fornecer a mesma quantidade de energia. Por exemplo, para alimentar uma carga de 1000 W:
- Um sistema de 24 V precisa de cerca de 41,6 amperes.
- Um sistema de 48 V precisa apenas de cerca de 20,8 amperes.
Uma corrente mais baixa significa menos perda de calor nos cabos e menos tensão nos componentes, tornando o inversor de 48 V uma opção mais eficiente para sistemas de médio a grande porte.
Tamanho e aplicação do sistema
Um inversor de 24 volts CC é comumente usado em sistemas menores, como trailers, pequenas casas, barcos e cabines compactas fora da rede. É uma ótima opção se você estiver usando algumas luzes, uma geladeira, talvez um ou dois laptops.
Por outro lado, um inversor de 48V é mais adequado para:
- Sistemas solares residenciais acima de 3kW
- Sistemas de energia de reserva para residências ou empresas
- Configurações de armazenamento de energia com bancos de baterias de lítio
- Aparelhos de alto consumo, como sistemas HVAC, ferramentas elétricas ou aquecedores de água
Se estiver planejando aumentar seu sistema no futuro ou se já tiver altas demandas de energia, começar com uma configuração de 48 V evita que você tenha que refazer a fiação de tudo no futuro.
Requisitos de fiação e implicações de custo
Os sistemas de tensão mais alta, como os que usam um inversor de 48 V, permitem uma fiação de menor bitola, pois a corrente é menor. Isso significa menos dinheiro gasto em cabos de cobre, conectores e disjuntores, especialmente se o seu sistema tiver longos trechos de fios entre o banco de baterias, o controlador de carga solar e o inversor.
Por outro lado, um inversor de 24 volts CC exigirá fios mais grossos para lidar com correntes mais altas, o que pode aumentar os custos e a complexidade da instalação.
Configuração do banco de baterias
Com um inversor CC de 24 volts, seu banco de baterias normalmente precisa ser configurado usando duas baterias de 12 V em série (ou quatro baterias de 6 V). Isso é bom para sistemas menores, mas a escalabilidade é limitada.
Uma configuração de inversor de 48 V geralmente requer quatro baterias de 12 V em série, ou configurações ainda mais avançadas quando se usam baterias de fosfato de ferro e lítio (LiFePO4). Essas configurações não são apenas mais eficientes, mas também reduzem a profundidade da descarga e prolongam a vida útil da bateria, o que é especialmente importante se você depende do seu sistema diariamente.
Eficiência de carregamento e compatibilidade com painéis solares
O carregamento de um banco de baterias de 48 V geralmente é mais rápido e eficiente, especialmente quando combinado com controladores de carga MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking). Muitos controladores de carga solar mais novos são otimizados para sistemas de 48 V e podem lidar com tensões de entrada mais altas de painéis solares. Se o seu painel solar for grande ou estiver espalhado por longas distâncias, uma configuração de inversor de 48V é mais prática e confiável.
Enquanto isso, um inversor CC de 24 volts pode ser suficiente para sistemas simples com conjuntos de painéis menores, mas seu teto de tensão mais baixo pode limitar o desempenho em condições de pico de energia solar.
Gerenciamento de segurança e calor
A corrente mais baixa nos sistemas de inversores de 48V também significa que menos calor é gerado na fiação e no próprio inversor. Isso contribui para um melhor desempenho térmico, maior vida útil dos componentes e maior segurança. Por outro lado, os inversores de 24 volts CC operando com altas cargas podem se aquecer mais rapidamente e podem exigir resfriamento adicional ou gerenciamento térmico.
Comparação de preços e valor a longo prazo
Inicialmente, os inversores de 24 volts CC são geralmente mais baratos e mais prontamente disponíveis. Mas para sistemas com demandas crescentes, essa economia de curto prazo pode se transformar em ineficiência de longo prazo. Embora os inversores de 48 V tendam a ter um custo inicial mais alto, eles geralmente compensam com despesas de fiação reduzidas, melhor eficiência energética e menos limitações no futuro.

Como funciona um inversor de 48V?
Se estiver procurando por sistemas solares ou fora da rede, é fundamental entender como funciona um inversor de 48V. Ele é mais do que apenas uma caixa que magicamente liga a energia, é o cérebro de seu sistema de energia. Não importa se você está alimentando uma cabana, uma casa ou um dispositivo móvel, um inversor manterá todos os seus aparelhos funcionando sem problemas com energia CA.
Então, como exatamente funciona um inversor de 48V? Vamos explicar brevemente.
Conversão de energia CC para CA
A função central de um inversor de 48V é converter a corrente contínua (CC) do seu banco de baterias de 48V em corrente alternada (CA), a energia necessária para que a maioria dos eletrodomésticos funcione adequadamente. Os painéis solares e as baterias armazenam energia como CC, mas as luzes, a TV, a geladeira e as ferramentas elétricas usam CA - geralmente 110V ou 220V, dependendo do país.
O inversor usa um transformador de alta frequência e elementos de comutação eletrônica para realizar essa conversão sem problemas. Como foi projetado para entrada de 48 V, ele lida com esse processo de forma mais eficiente do que os modelos de tensão mais baixa.
Gerenciamento do fluxo de energia de baterias e painéis solares
Em uma configuração solar, o inversor de 48 V trabalha em conjunto com controladores de carga e bancos de baterias. Aqui está um fluxo simplificado:
- Os painéis solares geram energia CC.
- Essa energia é regulada por um controlador de carga solar e armazenada em seu banco de baterias de 48V.
- O inversor extrai essa energia de 48 V CC das baterias e a converte em eletricidade CA.
- Essa energia CA é então encaminhada para o painel elétrico de sua casa ou diretamente para os aparelhos conectados.
Alguns inversores modernos de 48 V são modelos híbridos, o que significa que eles também podem gerenciar a entrada de energia da rede ou de um gerador, alternando perfeitamente entre as fontes de energia, dependendo da disponibilidade e da demanda de carga.
Regulação de tensão e frequência
Um bom inversor de 48V não apenas converte energia, mas também garante que a tensão e a frequência de saída sejam estáveis. As flutuações na tensão ou na frequência podem danificar eletrônicos sensíveis, como laptops ou smart TVs. É por isso que muitos inversores de alta qualidade apresentam sistemas de regulagem integrados que fornecem uma saída de onda senoidal pura - quase igual à energia limpa que você obteria de uma rede elétrica pública.
Esse é um dos principais motivos pelos quais as pessoas escolhem um inversor de 48 V em vez de um inversor de 24 VCC, especialmente em configurações em que a energia limpa e confiável é fundamental.
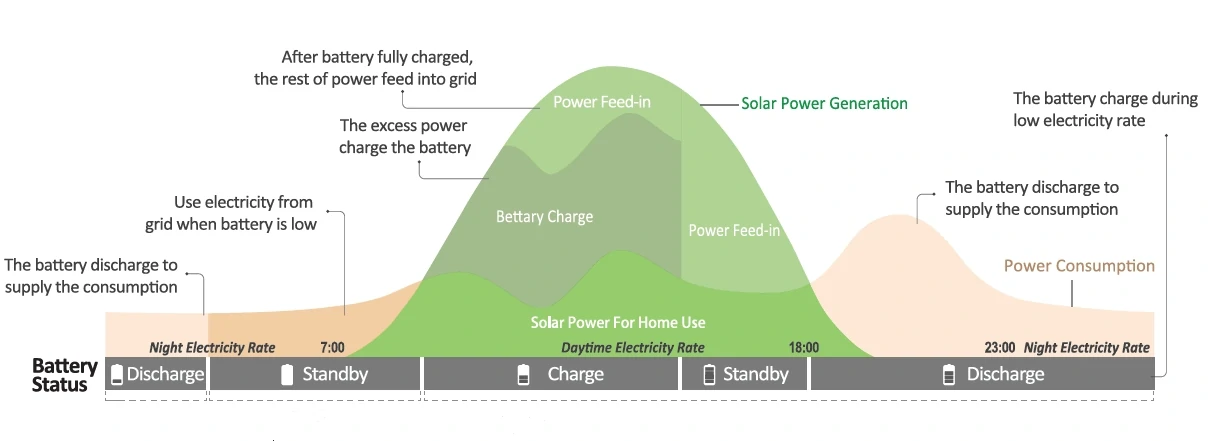
Onde você pode usar um inversor de 48V?
A beleza de um inversor de 48V está em sua flexibilidade. Ele não é apenas para os geeks da energia solar ou aventureiros fora da rede - esse poderoso equipamento se adapta a uma ampla gama de aplicações no mundo real. De casas residenciais a cabanas remotas, de trailers a instalações comerciais, o inversor de 48 V tornou-se discretamente a espinha dorsal da independência energética moderna.
Então, onde exatamente você pode usar um inversor de 48V? Vamos explorar alguns cenários comuns e outros inesperados.
Sistemas solares fora da rede
Um dos usos mais comuns dos inversores de 48V é para sistemas de energia solar fora da rede. Se você mora em uma área remota sem serviços públicos ou simplesmente quer se tornar independente em termos de energia, um inversor de 48V é ideal. Por quê? Porque ele equilibra eficiência e custo. Ele pode suportar cargas maiores sem superaquecimento, reduz os custos de fiação e combina perfeitamente com grandes painéis solares.
Por exemplo, geladeiras domésticas, bombas de poço, iluminação LED e computadores funcionarão melhor com um inversor de 48 V do que com uma opção de baixa tensão, como um inversor de 12 V ou mesmo de 24 V CC.
Energia de reserva residencial
As quedas de energia estão se tornando mais comuns em todo o mundo. Seja devido a tempestades, instabilidade da rede elétrica ou apagões, as pessoas estão recorrendo a sistemas de backup de bateria para manter as luzes acesas. Um inversor de 48V desempenha um papel fundamental nesses sistemas, geralmente integrado a bancos de baterias de lítio e chaves de transferência automática.
Quando combinado com energia solar ou um gerador, ele garante que você terá energia contínua e ininterrupta, seja para carregar telefones, operar uma máquina de CPAP ou manter a Internet ativa.
Uso comercial e industrial
Pequenas empresas, fazendas e instalações industriais leves estão adotando cada vez mais inversores de 48V para reduzir a dependência da rede elétrica e cortar os custos de energia. Para operações que usam equipamentos de alta demanda, como unidades de armazenamento a frio, sistemas de irrigação ou ferramentas de oficina, um sistema de 48 V fornece a energia necessária sem as ineficiências do alto consumo de corrente.
Além disso, os inversores solares comerciais com entrada de 48 V podem ser integrados a sistemas de monitoramento, gerenciamento de bateria e diagnóstico remoto, o que os torna um investimento inteligente de longo prazo.
RVs e configurações móveis
Embora a maioria dos trailers e campistas tradicionalmente utilizem sistemas de 12V ou 24V, as unidades móveis mais avançadas estão migrando para inversores de 48V. O motivo? Porque eles permitem que os viajantes alimentem mais aparelhos, como cooktops de indução, condicionadores de ar e micro-ondas, sem descarregar constantemente as baterias.
As principais vantagens são o menor consumo de corrente e a redução do cabeamento, o que é especialmente importante em ambientes móveis, onde o espaço é escasso.
Casas minúsculas e casas em contêineres
Se você estiver construindo uma casa minúscula ou um espaço de vida baseado em contêineres, a eficiência é tudo. Um inversor de 48V permite que você opere tudo, desde luzes e laptops até máquinas de lavar e aquecedores de água, em um sistema compacto e eficiente. Combine-o com uma matriz solar e um banco de baterias de lítio e você terá uma solução de energia limpa e de baixa manutenção que se encaixa perfeitamente em um estilo de vida minimalista.
Telecomunicações e infraestrutura remota
Você já se perguntou como as torres de telefonia celular ou as estações meteorológicas remotas são alimentadas 24 horas por dia, 7 dias por semana? Muitas delas dependem de sistemas de inversores de 48V. As baterias de nível de telecomunicações normalmente funcionam a 48 V, portanto, esses inversores são uma opção natural. Eles são projetados para serem confiáveis e continuarão a operar mesmo em condições climáticas adversas ou em áreas remotas.
Esse é um excelente exemplo de um sistema que não apenas atende às necessidades dos usuários domésticos, mas também desempenha um papel fundamental na conectividade do mundo moderno.
Barcos e aplicações marítimas
Os sistemas marítimos também se beneficiam de um inversor de 48V, especialmente em barcos e iates maiores que operam vários sistemas - radar, refrigeração, iluminação, entretenimento - todos ao mesmo tempo. Em comparação com as configurações de tensão mais baixa, um sistema de 48 V reduz a tensão nas baterias e na fiação, o que é vital em ambientes marítimos ricos em umidade e propensos à corrosão.
Por que o 48V faz sentido em todas as áreas
Em todos esses casos de uso, os temas consistentes são eficiência e escalabilidade. Os inversores de 48 V são adequados para sistemas com alta demanda de energia, grande capacidade de armazenamento de bateria ou onde o desempenho a longo prazo é fundamental. Embora um inversor de 24 V CC possa ser suficiente para instalações menores, a maioria das aplicações de crescimento ou de serviço pesado se beneficia muito com a atualização para 48 V.
Com a entrada no mercado de baterias de lítio e painéis solares mais acessíveis, a construção de sistemas de 48V nunca foi tão fácil.

Quantos painéis solares são necessários para um inversor de 48V?
Se estiver planejando configurar um sistema solar com um inversor de 48V, uma das perguntas mais comuns é: De quantos painéis solares eu realmente preciso? A resposta não é única - ela depende de alguns fatores importantes, incluindo seu uso diário de energia, a potência do painel, as horas de luz solar e a quantidade de armazenamento de bateria com a qual você está trabalhando.
Mas não se preocupe - nós o explicaremos passo a passo para que você possa obter uma estimativa sólida e adaptada às suas necessidades.
Comece com seu consumo de energia
Antes de mais nada: quanta eletricidade você usa diariamente? Isso é medido em quilowatts-hora (kWh). Uma pequena cabana fora da rede pode usar de 2 a 4 kWh por dia, enquanto uma casa de família pode consumir de 15 a 25 kWh ou mais.
Digamos que sua casa use 10 kWh por dia. Essa é sua meta de produção de energia a partir dos painéis solares.
Estimativa das horas de pico de luz solar em sua área
Seus painéis solares só podem produzir eletricidade quando o sol está brilhando. Portanto, você precisa descobrir quantas horas de sol de pico você tem por dia. Nos EUA, isso pode variar de 3 a 6 horas, dependendo do local e da estação.
Para o nosso exemplo, usaremos 5 horas de pico de sol.
Faça as contas: Potência e quantidade do painel
Agora, vamos fazer alguns cálculos rápidos usando um painel solar padrão de 400 watts.
Produção diária por painel = 400 watts × 5 horas = 2.000 watts-hora = 2 kWh
Portanto, para gerar 10 kWh por dia, você precisaria de:
10 kWh ÷ 2 kWh = 5 painéis (400W cada)
Esse é o caso ideal. Porém, em condições reais (cobertura de nuvens, ineficiência do painel, sombreamento), você deverá adicionar um buffer de 20-30%.
Portanto, 6 a 7 painéis de 400 W seriam mais realistas para uma configuração confiável com um inversor de 48 V.
Combine a tensão do sistema - Por que a configuração do painel é importante
É aqui que entra a importância do inversor de 48V. Seu conjunto de painéis solares precisa produzir uma tensão de carga superior a 48 volts (geralmente em torno de 60V a 80V) para carregar adequadamente o banco de baterias de 48V por meio do controlador de carga.
Isso pode ser feito conectando seus painéis solares em série, o que empilha as tensões de cada painel. Exemplo:
- 3 painéis classificados em 30V em série = tensão de matriz de 90V → ideal para sistemas de 48V.
Certifique-se de que seu controlador de carga solar (MPPT) e o inversor possam lidar com a tensão e a corrente combinadas.
Se estiver usando um inversor de 24V CC, você perceberá que os painéis estão configurados de forma ligeiramente diferente. Os sistemas de 24 V normalmente exigem tensões de matriz mais baixas (cerca de 36-50 V), portanto, menos painéis serão conectados em série, mas ao custo de uma corrente mais alta, o que significa fios mais grossos e mais perda de energia.
Esse é um dos motivos pelos quais muitos instaladores preferem usar um inversor de 48V em sistemas de médio a grande porte - ele é mais eficiente.
Considere o tamanho do seu banco de baterias
Seus painéis solares não apenas alimentam seus aparelhos - eles carregam suas baterias. Quanto maior for o seu banco de baterias, maior será a capacidade solar necessária para recarregá-lo totalmente todos os dias.
Digamos que você tenha um banco de baterias de lítio de 48V e 200Ah. Isso equivale a:
48V × 200Ah = 9.600Wh ou 9,6 kWh
Para recarregar isso em um dia (supondo que tenha sido drenado), você precisaria de painéis solares suficientes para gerar de 10 a 12 kWh, levando em conta as perdas. Novamente, isso o coloca na faixa de 6 a 8 painéis solares de 400 W cada.
Considerações sobre espaço e orçamento
Obviamente, a quantidade de painéis que você pode instalar também depende do espaço disponível no telhado ou no solo e do seu orçamento. Felizmente, a combinação de um inversor de 48 V com painéis de alta eficiência permite que você obtenha mais energia por metro quadrado, especialmente em comparação com um sistema de inversor de 24 VCC, que pode exigir mais painéis e fiação para a mesma saída.
E não se esqueça: se suas necessidades de energia aumentarem, um inversor de 48V é mais fácil de ser dimensionado sem a necessidade de reformar todo o sistema.
Referência rápida: Estimativas de painéis solares para sistemas de inversor de 48V
| Necessidade diária de energia | Horário de pico do sol | Potência do painel | Painéis necessários |
| 5 kWh | 5 horas | 400W | 3-4 painéis |
| 10 kWh | 5 horas | 400W | 6-7 painéis |
| 15 kWh | 5 horas | 400W | 9-10 painéis |
| 20 kWh | 5 horas | 400W | 12-14 painéis |
Sempre adicione uma capacidade extra de 20-30% para levar em conta o clima, o sombreamento e as perdas do sistema.

Como conectar painéis solares a um inversor de 48V
Passo a passo:
- Dimensione sua matriz: Certifique-se de que seus painéis atendam ou excedam suas demandas diárias de energia.
- Use um controlador de carga MPPT classificado para 48V.
- Conecte seus painéis em série ou série-paralelo para atender aos requisitos de tensão e corrente.
- Conecte-se a um banco de baterias de 48V.
- Conecte o banco de baterias ao inversor de 48V.
- Teste sua configuração para garantir que tudo esteja funcionando de forma eficiente.
Opções de bateria para sistemas de inversor de 48V
As opções mais populares incluem:
- Baterias de íons de lítio: Vida útil mais longa, melhor profundidade de descarga e carregamento mais rápido.
- Baterias de chumbo-ácido: Mais baratas no início, mas precisam de mais manutenção e espaço.
Ao escolher as baterias para seu inversor de 48V, procure ter pelo menos 100Ah de capacidade por kW de potência do inversor. Portanto, para um inversor de 5 kW, procure ter pelo menos 500 Ah em 48 V.
Escolhendo o inversor de 48V certo para suas necessidades
Escolher o inversor de 48V certo não é apenas escolher o modelo mais potente que você pode pagar. Trata-se de encontrar a opção certa para suas necessidades energéticas, orçamento e configuração do sistema. Quer esteja projetando uma cabine fora da rede, um sistema de energia de reserva ou uma configuração solar para sua casa, o inversor é o coração do sistema. Vamos analisar os principais fatores para ajudá-lo a tomar uma decisão segura.
Determine suas necessidades totais de energia
Comece calculando a potência total em watts de todos os dispositivos que estarão funcionando ao mesmo tempo. Isso inclui tudo, desde luzes e laptops até geladeiras e bombas de poço. Se o seu pico de uso for de 3.000 watts, você precisará de um inversor de 48 V com classificação pelo menos 20-25% mais alta para lidar confortavelmente com a energia de pico - portanto, algo em torno de 3.600 a 4.000 watts seria uma escolha inteligente.
Não se esqueça: aparelhos com motores, como condicionadores de ar ou ferramentas elétricas, geralmente têm uma classificação de surto que é de 2 a 3 vezes a potência de funcionamento. Certifique-se de que seu inversor possa suportar o pico de energia.
Onda senoidal pura vs. onda senoidal modificada
Se você planeja alimentar dispositivos eletrônicos sensíveis, como computadores, televisores ou equipamentos médicos, escolha um modelo de onda senoidal pura ao selecionar um inversor de 48V. Os inversores de onda senoidal pura produzem energia limpa e estável que imita a energia da rede elétrica, o que os torna ideais para aparelhos modernos.
Os inversores de onda senoidal modificada são mais baratos, mas, com o tempo, podem causar zumbido, ineficiência e até mesmo danos a alguns equipamentos. Para uso a longo prazo, vale a pena investir em um inversor de onda senoidal pura de 48V.
Fora da rede, híbrido ou ligado à rede?
Há diferentes tipos de inversores, dependendo de como o sistema está configurado:
- Os inversores 48V fora da rede são projetados para sistemas autônomos alimentados por baterias e painéis solares. Eles são ideais para cabines, trailers ou áreas remotas sem conexão com a rede elétrica. Se você estiver procurando um fabricante profissional especializado em inversores solares avançados, confira a página da Afore fabricação de inversores solares para soluções confiáveis e dimensionáveis.
- Os inversores híbridos combinam entrada solar, armazenamento de bateria e energia da rede. Eles oferecem flexibilidade e opções de backup em caso de falta de energia. Para um mergulho mais profundo na tecnologia de inversores híbridos, explore a seção inversor solar híbrido que são projetadas para lidar com cenários de energia residencial e comercial.
- Os inversores ligados à rede funcionam com painéis solares e alimentam a energia diretamente em sua casa e na rede elétrica, mas não usam baterias.
Portanto, se você precisa de independência energética e armazenamento de bateria, um inversor de 48 V híbrido ou fora da rede é sua melhor aposta.
Compatibilidade da bateria
Certifique-se de que o inversor escolhido seja compatível com seu tipo de bateria. A maioria dos inversores modernos de 48 V é compatível com baterias de íon-lítio e de chumbo-ácido, mas nem todos são igualmente otimizados. As baterias de lítio oferecem carregamento mais rápido, descargas mais profundas e vida útil mais longa. Portanto, se estiver investindo em lítio, verifique se o inversor é inteligente o suficiente para suportar sistemas de gerenciamento de bateria (BMS).
Isso é especialmente importante ao fazer o upgrade de um sistema inversor de 24 volts CC. As configurações de 48 V tendem a se combinar de forma mais eficiente com bancos de baterias de lítio de alta capacidade, o que as torna uma opção mais inteligente a longo prazo.
Recursos de carregamento e entradas solares
Se o inversor também funcionar como carregador ou controlador solar, observe atentamente:
- Tensão e corrente máximas de entrada fotovoltaica
- Eficiência do MPPT
- Corrente de carga para bancos de baterias de 48V
Alguns inversores de 48 V vêm com controladores de carga solar MPPT integrados, o que simplifica sua instalação. Outros podem precisar de um controlador separado, especialmente em configurações maiores. Verifique a tensão e a corrente de seu painel solar para evitar problemas de compatibilidade.
Eficiência do inversor e consumo em espera
Nem todos os inversores são criados da mesma forma em termos de perda de energia. Procure modelos com alta eficiência de conversão (acima de 90%) e baixo consumo de energia em modo de espera, especialmente para sistemas fora da rede ou em modo de espera, em que cada watt é importante. Modelos menos eficientes podem custar menos no início, mas custarão mais no longo prazo devido ao desperdício de energia.
Recursos inteligentes e monitoramento
Muitos dos inversores de 48 V de ponta atuais são equipados com conectividade Bluetooth ou Wi-Fi, permitindo monitorar o uso de energia, o status da bateria e a entrada de energia solar por meio de um aplicativo móvel ou painel de controle baseado na Web. Alguns inversores até suportam atualizações remotas de firmware para melhorar o desempenho.
Se você estiver construindo uma casa inteligente ou quiser monitorar o seu sistema em tempo real, esses recursos podem ser prejudiciais.
Segurança, certificações e garantia
Por fim, não deixe de lado as certificações de segurança, como UL, CE ou ISO. Um inversor de 48V certificado garante que ele atenda aos padrões de segurança elétrica e térmica. Além disso, verifique a garantia - a maioria dos modelos de qualidade vem com 2 a 5 anos de cobertura, o que lhe dá tranquilidade.
Evite inversores genéricos ou sem marca com preços suspeitosamente baixos. Quando se trata de sistemas de energia, a confiabilidade não é negociável.

Perguntas frequentes sobre inversores de 48V
O que exatamente faz um inversor de 48V?
Um inversor de 48 V converte 48 volts de corrente contínua (CC) de uma bateria ou sistema solar em corrente alternada (CA) usada por eletrodomésticos. Ele é a ponte entre sua fonte de energia fora da rede e suas necessidades diárias de energia. Ele alimenta luzes, geladeiras, condicionadores de ar e até ferramentas elétricas, dependendo de sua capacidade.
Um inversor de 48 V é mais eficiente do que um inversor de 24 VCC?
Sim, em sua maior parte. Os inversores de 48 V geralmente são mais eficientes e têm fiação mais fina, o que significa menos perda de energia e custos de instalação mais baixos. Os inversores de 48 V também podem lidar com cargas maiores com mais eficiência do que os inversores de 24 VCC, o que os torna ideais para sistemas solares ou de backup de médio a grande porte.
Posso usar um inversor de 48V com meus painéis solares existentes?
Com certeza - desde que a tensão e a corrente totais do seu painel solar correspondam aos requisitos de entrada do seu inversor de 48V (especialmente se ele tiver um controlador de carga MPPT integrado). Talvez seja necessário reconfigurar seus painéis em série ou em paralelo para atingir a faixa de tensão correta.
Quantas baterias são necessárias para um sistema de inversor de 48V?
Isso depende de seu uso de energia e do tipo de bateria. Normalmente, você precisará de quatro baterias de 12 V conectadas em série para obter 48 V ou de um banco de baterias de lítio de 48 V dedicado. Para obter maior capacidade, várias baterias de 48 V podem ser conectadas em paralelo para aumentar o armazenamento.
Um inversor de 48 V é seguro para uso doméstico?
Sim - se instalado corretamente e certificado. Muitos inversores de 48V vêm com recursos de segurança essenciais, como proteção contra sobrecarga, desligamento por curto-circuito, monitoramento de temperatura e alarmes. Procure modelos com certificações como UL ou CE para maior tranquilidade.
Um inversor de 48V pode alimentar toda a minha casa?
Um inversor de 48V de tamanho adequado pode absolutamente operar uma casa inteira - especialmente se for combinado com um banco de baterias robusto e painéis solares suficientes. Por exemplo, um inversor de 48V de 5kW ou 6kW pode lidar com a maioria das cargas domésticas, incluindo unidades de CA, refrigeradores e máquinas de lavar.
Qual é a diferença entre a instalação de um inversor de 48V e a de um inversor de 24V CC?
A instalação é bastante semelhante, mas os inversores de 48 V exigem menos corrente para a mesma saída de energia, o que significa cabos mais finos e menos acúmulo de calor. Se estiver fazendo o upgrade de um inversor de 24 volts CC, talvez seja necessário ajustar a configuração do banco de baterias e as classificações dos fusíveis.
Qual é o tamanho do inversor necessário para um sistema de 48V?
Isso depende de sua carga. Para cabines básicas fora da rede ou trailers, um inversor de 1000W-2000W 48V pode ser suficiente. Para backup de toda a casa ou grandes sistemas solares, procure uma unidade de 3000W-6000W. Sempre leve em conta os picos de carga e a expansão futura ao escolher seu tamanho.