Guia definitivo para bateria em inversor: escolha e manutenção corretas

Índice
Em um mundo cada vez mais dependente do acesso ininterrupto à eletricidade, ter um sistema de backup confiável não é apenas inteligente - é essencial. No centro desses sistemas de backup está um componente crucial: a bateria no inversor. Se você mora em uma região com frequentes cortes de energia ou simplesmente deseja ter tranquilidade durante interrupções inesperadas, é fundamental entender como as baterias do inversor funcionam, quanto tempo duram e como fazer sua manutenção. Este guia abrangente aborda tudo o que você precisa saber sobre como escolher a melhor combinação de bateria e inversor de energia para suas necessidades - sem complicações ou jargões. De conselhos práticos a insights de especialistas, você aprenderá a tirar o máximo proveito da bateria do inversor de energia e a garantir que sua casa ou escritório permaneça alimentado quando for mais importante.
Introdução à bateria em sistemas de inversores
O que é um inversor de energia e como ele funciona
No mundo digitalmente conectado e sempre ligado de hoje, uma fonte confiável de energia de backup não é mais um luxo - é uma necessidade. No centro de muitos sistemas de backup está um dispositivo conhecido como inversor de energia. Mas o que exatamente faz um inversor de energia?
Um inversor de energia é um dispositivo eletrônico que converte a corrente contínua (CC) de fontes como baterias ou painéis solares em corrente alternada (CA) que alimenta nossos eletrodomésticos. A maioria dos aparelhos domésticos - de televisores a geladeiras - funciona com corrente alternada. Sem um inversor, a energia armazenada em uma bateria seria praticamente inútil para alimentar esses dispositivos baseados em CA.
Importância das baterias em sistemas de inversores
Um inversor sem bateria é como um carro sem motor. A bateria nos sistemas de inversor armazena a energia que será posteriormente convertida em eletricidade CA utilizável. Pense na bateria como o tanque de combustível. O inversor pode fazer a conversão, mas sem uma bateria carregada, não há nada para converter.
Quer esteja lidando com interrupções de energia frequentes ou se preparando para um backup de emergência, a escolha da combinação certa de bateria e inversor de energia pode afetar drasticamente sua experiência.
Aplicações comuns das baterias do inversor em residências e escritórios
De apartamentos urbanos a casas rurais, as baterias do inversor se tornaram essenciais. Os escritórios dependem delas para manter roteadores, computadores e sistemas de vigilância ativos. Os proprietários de residências contam com elas para iluminação, ventiladores, dispositivos médicos e refrigeradores. A versatilidade da bateria das configurações do inversor faz delas uma solução universal.

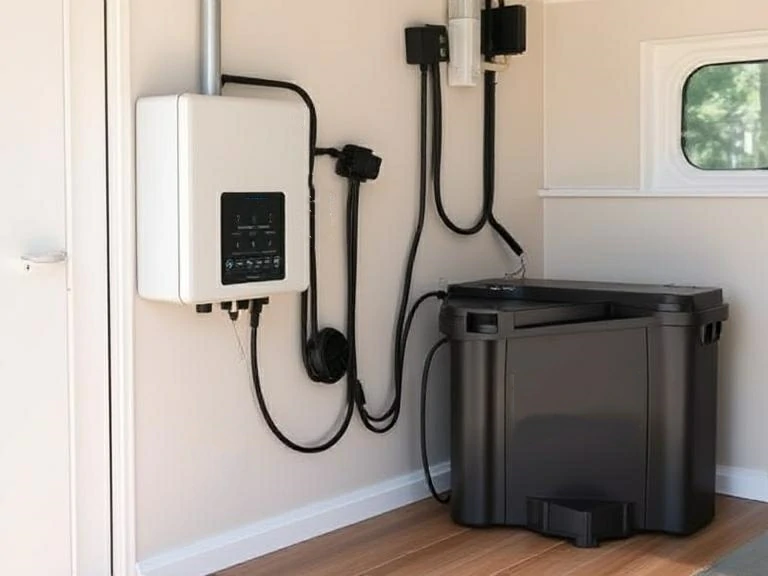
Entendendo a bateria do inversor
O que é uma bateria de inversor?
Uma bateria de inversor é uma solução de armazenamento de energia especialmente projetada que alimenta um inversor durante interrupções de eletricidade. Diferentemente das baterias automotivas ou de arranque - que fornecem rajadas curtas de alta corrente para dar partida nos motores -, as baterias do inversor são construídas para desempenho de ciclo profundo, o que significa que elas liberam uma quantidade constante de energia por um período mais longo.
Quando a alimentação da rede principal falha, o inversor extrai a energia armazenada da bateria e a converte em eletricidade CA para manter os aparelhos essenciais funcionando. A bateria nas configurações do inversor deve ser durável o suficiente para suportar ciclos frequentes de carga e descarga sem se deteriorar rapidamente. Por esse motivo, elas são projetadas com placas mais grossas e materiais de maior qualidade do que as baterias comuns.
Essas baterias desempenham um papel fundamental nos sistemas de backup de energia residencial e comercial. Seja para manter o roteador de Internet on-line ou para garantir a iluminação ininterrupta, a bateria do inversor é a salvação por trás de cada mudança bem-sucedida para a energia de reserva.
Qual bateria é usada em sistemas de inversor?
Não existe um modelo único para todas as baterias de inversor de energia, mas alguns tipos de baterias dominam o mercado devido às suas características de confiabilidade e desempenho.
Baterias de chumbo-ácido de placa plana
São econômicos e adequados para áreas com cortes de energia curtos e infrequentes. Oferecem eficiência decente, mas exigem manutenção regular, como recargas de eletrólitos.
Baterias tubulares de chumbo-ácido
Conhecidas por sua longa vida útil e capacidade de descarga profunda, as baterias tubulares são ideais para regiões com interrupções de energia prolongadas ou frequentes. Elas são mais caras do que as de placa plana, mas oferecem melhor desempenho e longevidade, o que as torna uma escolha popular para a maioria das configurações de baterias de inversores residenciais.
Baterias de íon-lítio
As baterias de íons de lítio, leves, livres de manutenção e de carregamento rápido, estão se tornando cada vez mais populares, especialmente em configurações de baterias movidas a energia solar e inversores de energia. Embora o investimento inicial seja maior, os custos operacionais mais baixos e a longa vida útil geralmente compensam o preço inicial.
Baterias seladas livres de manutenção (SMF)
Incluindo os tipos GEL e AGM, essas baterias são à prova de derramamento, não exigem manutenção e são perfeitas para espaços fechados. Elas são amplamente usadas em escritórios ou ambientes onde a segurança e a limpeza são prioridades.
Ao selecionar a bateria para o inversor, é essencial considerar fatores como padrão de uso, duração do backup necessário, compatibilidade do inversor e condições ambientais.
O que é o modo de bateria em um inversor?
O modo de bateria em um inversor refere-se ao estado operacional quando a alimentação elétrica principal não está disponível e o inversor passa a usar a energia armazenada da bateria do inversor. Esse modo é acionado automaticamente no momento em que ocorre um corte de energia.
Veja o que normalmente acontece no modo de bateria:
- O inversor detecta instantaneamente a falta de energia e alterna para a energia CC da bateria.
- Ele converte essa energia CC em CA para continuar a operar os aparelhos conectados.
- Essa transição contínua geralmente leva menos de um segundo, garantindo uma operação ininterrupta.
O inversor permanece no modo de bateria até que a alimentação da rede seja restaurada. Quando a rede elétrica retorna, ele reverte automaticamente para o modo de carregamento para reabastecer a bateria no inversor. Durante interrupções prolongadas, o uso eficiente da energia torna-se essencial para evitar o rápido esgotamento da bateria.
O modo de bateria também reflete a saúde geral e a prontidão do seu sistema de backup. Se a bateria do inversor de energia descarregar muito rapidamente nesse modo, isso pode indicar células envelhecidas, gerenciamento incorreto da carga ou manutenção inadequada - tudo isso pode enfraquecer a confiabilidade do sistema.
Escolhendo a bateria certa para o inversor de energia
A escolha da melhor bateria de inversor de energia é fundamental para garantir que seu sistema de energia de reserva funcione de forma confiável durante as interrupções. A escolha certa não só garante tempo de backup suficiente, mas também prolonga a vida útil da bateria e do inversor. Com tantas opções disponíveis, entender os prós e os contras dos diferentes tipos de bateria e os principais fatores que influenciam sua decisão pode fazer toda a diferença.
Fatores a considerar ao selecionar uma bateria de inversor
A escolha da bateria certa no inversor envolve mais do que apenas escolher um tipo. Aqui estão os fatores essenciais que você deve ter em mente:
- Capacidade (Ampere-hora, Ah): A capacidade da bateria determina por quanto tempo ela pode fornecer energia durante uma interrupção. Por exemplo, uma bateria de 150 Ah pode oferecer mais tempo de backup do que uma de 100 Ah. Avalie sua carga total para calcular com precisão a capacidade necessária.
- Compatibilidade de voltagem: A maioria dos inversores domésticos usa baterias de 12V, mas sistemas maiores podem exigir configurações de 24V ou 48V. Sempre verifique se a tensão da bateria corresponde às especificações do inversor.
- Necessidade de carga: Saiba a potência em watts dos aparelhos que você deseja usar como reserva. Cargas pesadas precisam de baterias com capacidades mais altas e melhores recursos de descarga.
- Necessidade de manutenção: As baterias de chumbo-ácido requerem limpeza e reposição periódica do eletrólito, enquanto as baterias de íons de lítio e SMF são praticamente isentas de manutenção.
- Espaço e ventilação: As baterias produzem gases durante o carregamento. A ventilação adequada evita o superaquecimento e garante a segurança.
- Orçamento: Embora baterias mais baratas possam parecer atraentes, elas geralmente têm vida útil e eficiência reduzidas. Considere o custo total de propriedade, incluindo manutenção e substituição.
Ao avaliar cuidadosamente esses fatores, você pode garantir que a bateria do inversor de energia se alinhe perfeitamente às suas necessidades de energia e padrões de uso.
Todos os inversores precisam de uma bateria?
Nem todo inversor requer uma bateria, e entender isso pode ajudá-lo a tomar uma decisão informada sobre a configuração do backup de energia.
- Inversores ligados à rede: Esses inversores trabalham diretamente com a rede elétrica e não precisam de baterias. São comumente usados em sistemas de energia solar em que o excesso de eletricidade é devolvido à rede. Como não há bateria de reserva, esses sistemas não fornecem energia durante interrupções.
- Inversores fora da rede: Projetados para locais remotos sem acesso confiável à rede elétrica, esses inversores devem ser combinados com baterias para armazenar energia e fornecer energia de forma independente.
- Inversores híbridos: Essas unidades versáteis combinam entrada solar, energia da rede e armazenamento de bateria, alternando entre as fontes conforme necessário para otimizar o uso de energia.
Para a maioria das configurações residenciais e comerciais de pequeno porte, a combinação tradicional de bateria e inversor de energia é a escolha preferida para garantir o fornecimento contínuo de energia durante apagões. Portanto, embora alguns tipos de inversores não exijam baterias, se sua prioridade for energia de reserva ininterrupta, é essencial investir em um sistema de inversor com bateria de qualidade.

Vida útil e desempenho da bateria do inversor
Um aspecto crítico, mas muitas vezes negligenciado, de qualquer bateria em um sistema de inversor é entender quanto tempo a bateria durará e quais fatores afetam seu desempenho. A vida útil e a eficiência da bateria do inversor de energia afetam não apenas a confiabilidade do backup, mas também os custos contínuos. Vamos explorar o que influencia a vida útil da bateria, a duração típica que você pode esperar e como manter a bateria do inversor saudável a longo prazo.
Quanto tempo dura uma bateria em um inversor?
A duração do fornecimento de energia por uma bateria ou inversor depende de diversas variáveis, incluindo a capacidade da bateria, a demanda de carga e a saúde da bateria. Por exemplo, uma bateria tubular de 150Ah conectada a um inversor de 600VA que opera aparelhos essenciais, como luzes e ventiladores, pode durar de 4 a 6 horas durante uma queda de energia.
No entanto, vários fatores podem influenciar isso:
- Tamanho da carga: Quanto mais pesada a carga (mais aparelhos ou dispositivos de maior potência), mais rapidamente a bateria se esgota.
- Capacidade da bateria: As baterias de maior capacidade (medidas em Ampères-hora, Ah) proporcionam um backup mais longo.
- Idade e condição da bateria: Baterias mais antigas com células gastas perdem eficiência e descarregam mais rapidamente.
- Eficiência do inversor: Alguns inversores têm melhor eficiência de conversão, reduzindo o desperdício de energia.
Em média, a maioria das baterias de chumbo-ácido do inversor oferece cerca de 3 a 5 horas de backup sob cargas moderadas, enquanto as baterias de íons de lítio podem durar mais tempo devido à melhor densidade e eficiência de energia.
O que consome a bateria do inversor?
Entender o que consome a bateria do inversor ajuda a gerenciar o uso e aumentar o tempo de backup:
- Aparelhos de alta potência: Dispositivos como geladeiras, condicionadores de ar e aquecedores elétricos consomem muita energia, esgotando rapidamente a bateria.
- Cargas fantasmas: Os aparelhos deixados em modo de espera ou os carregadores conectados sem uso ativo podem drenar energia silenciosamente.
- Distribuição inadequada de carga: A conexão de cargas incompatíveis ou excessivas pode levar ao esgotamento mais rápido da bateria.
- Autodescarga da bateria: As baterias perdem carga naturalmente com o tempo, mesmo quando não estão em uso, especialmente as de chumbo-ácido.
- Troca frequente: cortes de energia repetidos que fazem com que o inversor troque de modo com frequência podem aumentar um pouco o consumo da bateria.
Ficar atento ao que você conecta ao inversor e gerenciar as cargas com eficiência pode evitar a drenagem desnecessária e ajudar a manter a saúde da bateria.
O que enfraquece uma bateria de inversor?
Vários fatores contribuem para o enfraquecimento gradual de sua bateria no inversor:
- Ciclos de descarga profunda: A drenagem regular da bateria abaixo dos níveis recomendados reduz sua vida útil.
- Sobrecarga: A carga prolongada além da capacidade total pode causar evaporação do eletrólito e danos à placa.
- Altas temperaturas: O calor acelera as reações químicas no interior da bateria, causando uma degradação mais rápida.
- Manutenção deficiente: No caso das baterias de chumbo-ácido, negligenciar a recarga ou a limpeza do eletrólito leva à sulfatação e à perda de capacidade.
- Instalação incorreta: Conexões soltas ou emparelhamentos errados entre o inversor e a bateria podem sobrecarregar a bateria.
As condições ambientais e os hábitos do usuário desempenham papéis cruciais na rapidez com que uma bateria de inversor perde sua eficácia ao longo do tempo.
Dicas para prolongar a vida útil da bateria do inversor
Para maximizar a vida útil e o desempenho da bateria do inversor de energia, considere estas dicas práticas:
- Use uma carga adequada: Evite sobrecarregar o inversor. Conheça a potência em watts de seus aparelhos conectados e mantenha as cargas dentro dos limites recomendados.
- Manutenção regular: Para baterias de chumbo-ácido, verifique os níveis de eletrólito mensalmente e reabasteça com água destilada conforme necessário. Limpe os terminais para evitar corrosão.
- Evite descargas profundas: Tente não descarregar a bateria completamente. A recarga antes que ela caia abaixo de 50% pode aumentar significativamente a vida útil da bateria.
- Garanta a ventilação adequada: Mantenha a bateria em um local fresco, seco e bem ventilado para evitar superaquecimento.
- Use carregadores de qualidade: Certifique-se de que o carregador do inversor mantenha a tensão correta e evite a sobrecarga.
- Testes periódicos: Teste regularmente a integridade da bateria com um multímetro ou consulte profissionais para verificar as condições.
Ao seguir essas diretrizes, seu sistema de bateria e inversor de energia fornecerá energia de reserva confiável por mais tempo e com menos problemas.

Dicas de segurança e manutenção de baterias e inversores de energia
A manutenção da bateria no sistema do inversor é fundamental para garantir o desempenho e a segurança a longo prazo. O cuidado adequado não apenas prolonga a vida útil da bateria do inversor de energia, mas também protege sua casa e seus eletrodomésticos de falhas inesperadas. Nesta seção, discutiremos o que deve ser evitado ao se conectar a um inversor, problemas comuns com a bateria e suas soluções, além de dicas de especialistas para evitar a drenagem desnecessária da bateria.
O que não deve ser conectado a um inversor?
Embora os inversores forneçam energia de reserva essencial, eles têm limitações quanto aos tipos de dispositivos que podem suportar com segurança. A conexão de aparelhos inadequados pode danificar a bateria do inversor e o próprio inversor. Aqui estão alguns dispositivos que você deve evitar:
- Aparelhos com alta carga de surto: Dispositivos como aquecedores elétricos de água, fornos de micro-ondas e condicionadores de ar têm altas correntes de inicialização (cargas de surto) que podem sobrecarregar o inversor e drenar a bateria do inversor rapidamente.
- Cargas indutivas: Motores e compressores consomem muita energia inicialmente, o que pode fazer com que o inversor desarme ou a bateria se esgote rapidamente.
- Eletrônicos não compatíveis: Alguns dispositivos médicos sensíveis e instrumentos de precisão podem não tolerar as leves flutuações de tensão dos inversores comuns.
- Aparelhos desnecessários em standby: deixar aparelhos como TVs ou carregadores conectados sem uso ativo pode causar cargas fantasmas, drenando silenciosamente a bateria e a configuração do inversor de energia.
Para proteger seu sistema e otimizar a vida útil da bateria, é melhor conectar apenas dispositivos essenciais e de baixo a moderado consumo de energia durante as interrupções.
Solução de problemas comuns da bateria do inversor
Mesmo com os devidos cuidados, você pode enfrentar problemas ocasionais com a bateria do inversor de energia. Veja a seguir como solucionar alguns problemas comuns:
- O inversor não está mudando para o modo de bateria: Verifique a tensão da bateria; uma bateria fraca ou descarregada pode impedir que o inversor mude de modo. Além disso, inspecione a fiação e as conexões quanto a corrosão ou terminais soltos.
- Bateria descarregando rapidamente: A sobrecarga do inversor com muitos aparelhos ou com aparelhos de alta potência é uma causa comum. Verifique a compatibilidade da carga e considere atualizar a capacidade da bateria, se necessário.
- A bateria não está carregando totalmente: Circuitos do carregador com defeito no inversor ou células da bateria danificadas podem causar esse problema. É recomendável fazer verificações regulares da integridade da bateria e da manutenção do inversor.
- Superaquecimento frequente da bateria: Certifique-se de que haja ventilação adequada ao redor da bateria. Sobrecarga ou curtos-circuitos também podem causar excesso de calor; consulte um técnico profissional se não tiver certeza.
- O inversor emite bipes ou exibe códigos de erro: Consulte o manual do inversor para obter os significados específicos dos erros; muitos estão relacionados a problemas com a bateria, como baixa tensão ou sobrecarga.
A solução imediata desses problemas ajuda a evitar danos permanentes e substituições dispendiosas.
Dica bônus - Criar um ambiente doméstico confortável.
Mesmo quando o sistema do inversor é usado principalmente para energia de reserva, você ainda pode melhorar o ambiente e o aspecto do estilo de vida da sua casa durante interrupções de energia ou ao usar circuitos de energia armazenada. Por exemplo, considere adicionar um difusor de aroma ou outros dispositivos de descanso que consomem pouca energia.
Conselhos de especialistas sobre como evitar a drenagem da bateria
Evitar a drenagem desnecessária de sua bateria no inversor garante tempos de backup mais longos e melhor saúde da bateria. Aqui estão dicas de especialistas para manter seu sistema eficiente:
- Gerencie sua carga com sabedoria: Priorize os aparelhos essenciais e evite usar dispositivos de alta potência simultaneamente no backup.
- Desligue os aparelhos que não estão sendo usados: Sempre desconecte ou desligue os aparelhos que não estiverem em uso durante os cortes de energia para conservar a energia da bateria.
- Use eletrodomésticos com eficiência energética: Substitua os eletrodomésticos antigos que consomem muita energia por modelos com eficiência energética que consomem menos energia da bateria e do sistema inversor de energia.
- Monitore regularmente a tensão da bateria: Use um voltímetro ou um visor do inversor para verificar a integridade da bateria e evitar descargas profundas.
- Mantenha as baterias limpas e secas: Limpe os terminais regularmente e evite o acúmulo de umidade, que pode levar à corrosão e à perda de energia.
- Evite longos períodos de espera sem carregar: Se a bateria ficar inativa por longos períodos, recarregue-a ocasionalmente para manter a capacidade ideal.
Seguindo essas diretrizes, a bateria do inversor ficará mais saudável por mais tempo, fornecendo energia consistente quando você mais precisar dela.
Tendências futuras na tecnologia de baterias do inversor
Baterias de íons de lítio em sistemas de inversores residenciais
Eles estão transformando a bateria no espaço do inversor:
- Ciclos de vida mais longos (até 10 anos)
- Livre de manutenção
- Tempos de carregamento rápidos
- Mais compacto e leve
Apesar do custo, mais famílias estão optando por essa opção devido à economia de longo prazo.
Configurações de bateria solar + inversor
O futuro verde está na energia híbrida:
- Os painéis solares carregam a bateria durante o dia
- O inversor alimenta os aparelhos após o pôr do sol
- Reduz significativamente as contas de eletricidade
A combinação de energia solar com uma bateria de inversor de qualidade oferece independência e sustentabilidade.

Conclusão
Resumindo, a configuração da bateria no inversor que você escolher pode ser decisiva para sua experiência com energia de reserva. Desde a compreensão dos tipos de baterias até o conhecimento do que afeta a vida útil delas, estar informado coloca você no controle.
Quer esteja atualizando um sistema antigo ou começando do zero, escolha sabiamente. Combine suas necessidades de energia com a bateria certa e com o sistema de energia ideal. inversor de energia configuração. Mantenha a manutenção. E sempre planeje o futuro - integrações solares, monitoramento inteligente e tecnologias modernas de lítio estão abrindo caminho.
Seu backup de energia não se trata apenas de sobreviver a apagões. Trata-se de criar uma experiência energética perfeita e sem estresse.
Perguntas frequentes
1. Qual bateria é usada no inversor?
As baterias mais comumente usadas em sistemas de inversores são as baterias tubulares de chumbo-ácido e as baterias de chumbo-ácido de placa plana, com as baterias de íon-lítio se tornando mais populares nos últimos anos. As baterias tubulares são preferidas por sua capacidade de descarga profunda e longa vida útil, o que as torna ideais para residências com frequentes cortes de energia. As baterias de íon-lítio oferecem maior eficiência, menor manutenção e vida útil mais longa, mas têm um custo inicial mais alto.
2. O que é um inversor em uma bateria?
Um inversor em si é um dispositivo eletrônico que converte CC (corrente contínua) de uma bateria em CA (corrente alternada) usada por eletrodomésticos. Portanto, a frase "inversor em uma bateria" é um pouco enganosa; em vez disso, um inversor funciona com uma bateria. A bateria armazena energia elétrica e o inversor a converte em energia utilizável durante as interrupções.
3. O que é o modo de bateria em um inversor?
O modo de bateria é o estado operacional quando um inversor alterna da energia da rede elétrica para a energia da bateria devido a uma falha na rede elétrica ou a um blecaute. Nesse modo, o inversor extrai energia da bateria do inversor e a converte em CA para alimentar seus aparelhos sem interrupções até que a energia da rede seja restaurada.
4. Quanto tempo dura uma bateria em um inversor?
A duração da bateria reserva varia de acordo com a capacidade, a carga e a integridade da bateria. Uma bateria típica de inversor tubular de 150Ah com uma carga moderada de luzes e ventiladores pode durar de 4 a 6 horas. Aparelhos pesados ou cargas maiores reduzirão esse tempo. A manutenção regular e o gerenciamento adequado da carga ajudam a maximizar a duração do backup de sua bateria e do sistema do inversor de energia.
5. Todos os inversores precisam de uma bateria?
Não, nem todos os inversores precisam de baterias. Os inversores ligados à rede funcionam diretamente com a rede elétrica e não precisam de baterias, enquanto os inversores fora da rede e os inversores híbridos precisam de baterias para armazenar e fornecer energia quando a rede não está disponível. Para obter uma fonte de alimentação ininterrupta durante as interrupções, é essencial ter uma boa bateria de inversor.
6. O que consome a bateria do inversor?
Diversos fatores podem drenar rapidamente a bateria de um inversor, incluindo a execução de cargas indutivas ou de alta potência, como condicionadores de ar e refrigeradores, deixar dispositivos conectados no modo de espera e alternar frequentemente entre os modos de rede e de bateria. O gerenciamento adequado da carga e a prevenção de aparelhos desnecessários durante as interrupções ajudam a evitar a rápida drenagem da bateria.
7. O que enfraquece uma bateria de inversor?
A bateria do inversor enfraquece devido a descargas profundas abaixo dos níveis recomendados, sobrecarga, altas temperaturas de operação, manutenção inadequada (especialmente para baterias de chumbo-ácido) e instalação incorreta. A manutenção regular, o carregamento adequado e a prevenção de condições extremas ajudam a prolongar a vida útil da bateria.