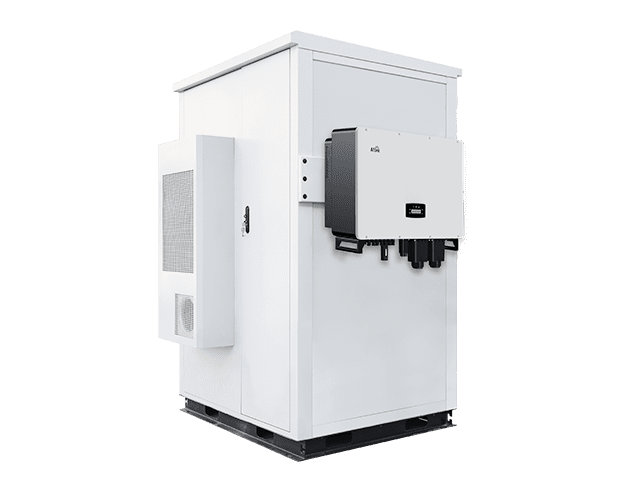
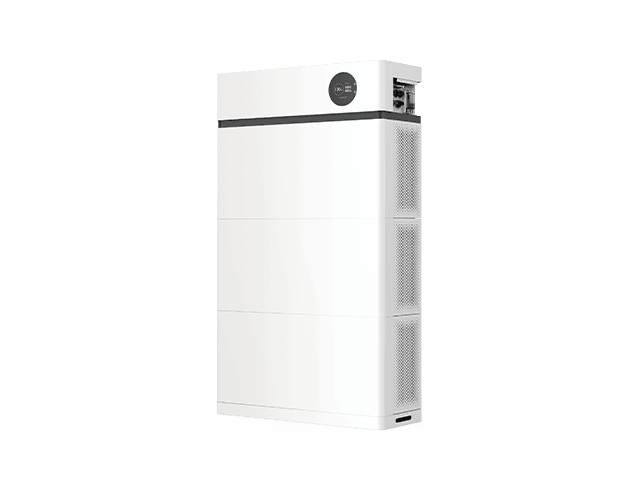
Повний посібник з вибору найкращої автономної інверторної системи

Зміст
У світі, де енергонезалежність - це не просто тренд, а необхідність, автономний інвертор є наріжним каменем автономного життя та сталих енергетичних рішень. Незалежно від того, чи забезпечуєте ви енергією віддалений будиночок, чи готуєтеся до перебоїв в електропостачанні, чи зменшуєте залежність від традиційних комунальних послуг, розуміння того, як функціонує сонячний інвертор поза мережею, є ключовим фактором. Але з такою великою кількістю типів інверторів - автономні, мережеві, гібридні - як дізнатися, яка система відповідає вашому стилю життя та енергетичним цілям? У цьому посібнику ми розповімо про все, що вам потрібно знати про автономні інверторні технології: від того, як вони працюють і як довго служать, до вибору правильного розміру для вашої сонячної установки. Давайте розкладемо все по поличках, щоб ви могли взяти під контроль своє енергетичне майбутнє.
Вступ до автономних інверторів
Що таке автономний інвертор?
Уявіть, що ви живете у віддаленій хатині, розташованій глибоко в лісі, або в еко-будинку далеко від найближчого стовпа. Як ви забезпечуєте своє життя без електрики? Саме тут на допомогу приходить автономний інвертор. Цей розумний автономний пристрій перетворює постійний струм (DC) від сонячних панелей або акумуляторів на змінний струм (AC) для живлення ваших приладів - без потреби в електромережі.
На відміну від традиційних сонячних інверторів, прив'язаних до електромережі, автономний інвертор працює незалежно. Це серце будь-якої автономної сонячної електростанції, що забезпечує зв'язок між накопиченою сонячною енергією та повсякденними потребами в електроенергії. Його також часто називають автономним інвертором, але багато домовласників і ентузіастів сонячної енергетики також називають його автономною інверторною системою.
Навіщо йти поза мережею?
Автономне живлення - це більше, ніж технічний вибір, це стиль життя. Незалежно від того, чи готуєтеся ви до надзвичайних ситуацій, чи зменшуєте вплив на навколишнє середовище, чи досягаєте енергетичної незалежності, автономний інвертор дає вам цю свободу. Ці системи ідеально підходять для:
- Віддалені каюти та крихітні будиночки
- Автономні садиби та ферми
- Аварійні системи резервного копіювання
- Автофургони та човни
Покладаючись на власну генерацію та зберігання електроенергії, ви не залежите від перебоїв у постачанні електроенергії та стрибків цін - безцінна перевага в сьогоднішньому нестабільному енергетичному кліматі.
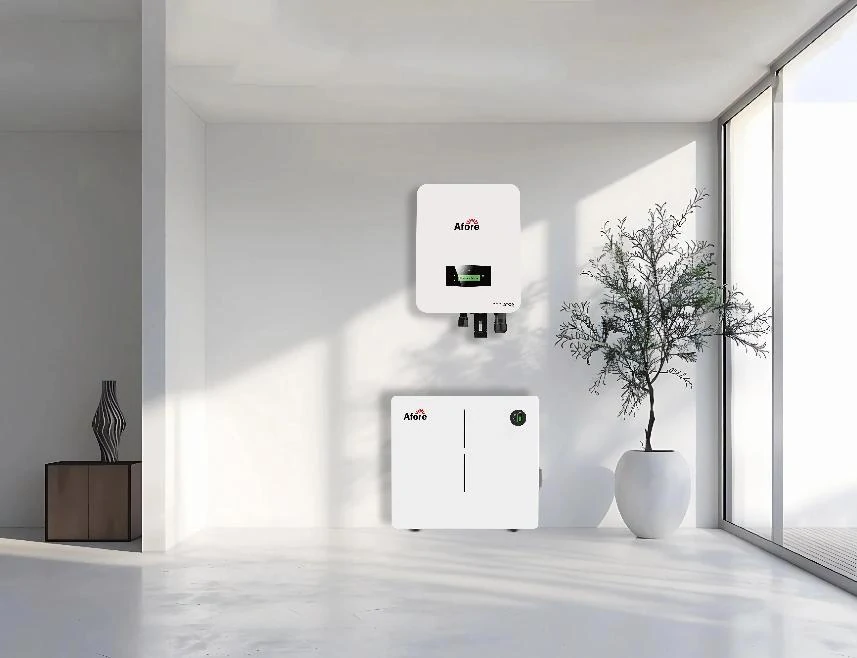

Як працюють автономні інвертори в сонячних електростанціях
Розуміння того, як функціонує автономний інвертор, має важливе значення при проектуванні надійної, автономної сонячної системи. На відміну від традиційних систем, енергетична стабільність яких залежить від електромережі, автономна конфігурація інвертора повністю покладається на локальну генерацію та зберігання електроенергії. Така незалежність вимагає надійної, добре інтегрованої системи, в центрі якої знаходиться високопродуктивний сонячний інвертор, щоб забезпечити безперебійну роботу вдень і вночі, в дощ і в спеку.
Роль сонячного інвертора в перетворенні енергії
По суті, кожен сонячний інвертор - незалежно від того, чи є він частиною мережевої, гібридної або автономної установки - виконує одне важливе завдання: перетворює електроенергію постійного струму (DC) від сонячних панелей на змінний струм (AC), який живить побутові прилади.
Але в автономній інверторній системі інвертор робить набагато більше, ніж просто перетворює енергію. Він стає інтелектуальним серцем енергосистеми, керуючи численними входами та виходами. Ось як це виглядає на практиці:
- Перетворення постійного струму в змінний: Сонячні панелі генерують електроенергію постійного струму, яку більшість побутових приладів не можуть використовувати безпосередньо. Автономний інвертор перетворює її на стандартну електроенергію змінного струму (зазвичай 120 або 230 В, залежно від країни).
- Керування акумулятором: Відстежує напругу, стан заряду та межі розряду акумулятора, щоб забезпечити довговічність та надійність системи.
- Пріоритезація навантаження: Під час дефіциту електроенергії (наприклад, у похмурі дні) інверторна система автономного живлення визначає пріоритети основних навантажень - охолодження, освітлення, зв'язок, - гарантуючи, що ви ніколи не залишитеся повністю в темряві.
- Захист від перенапруги: Високоякісні інвертори можуть впоратися з раптовими стрибками навантаження від двигунів або компресорів, не виводячи систему з ладу.
На відміну від мережевих інверторів, які вимикаються при збої в мережі, автономний інвертор завжди активний, підлаштовуючись до коливань сонячного навантаження і стану акумулятора в режимі реального часу.
Ключові компоненти в автономному налаштуванні
Побудова ефективної автономної сонячної системи - це не просто купівля сонячного інвертора та підключення його до панелей. Йдеться про створення збалансованої екосистеми, де кожен компонент доповнює інші. Ось основні складові автономної системи та їх взаємозв'язок:
- Сонячні панелі: Це ваше основне джерело енергії. Сонячні панелі перетворюють сонячне світло в електрику постійного струму. Чим ефективніший ваш масив, тим більше енергії ви можете зберігати та використовувати.
- Контролер заряду: Контролер заряду, про який часто забувають, але який є життєво важливим, регулює напругу і струм, що надходять до акумуляторної батареї. Це захищає батареї від перезарядки, яка може скоротити термін їхньої служби або навіть призвести до пошкодження.
- Акумуляторна батарея: Жодна автономна система не обходиться без зберігання енергії. Батареї зберігають надлишкову енергію протягом дня для використання вночі або під час поганої погоди. Літій-іонні акумулятори стають кращим вибором для сучасних автономних інверторних установок завдяки їх довговічності та глибині розряду.
- Автономний інвертор: це командний центр. Він перетворює енергію постійного струму в корисний змінний струм, керує заряджанням і розряджанням акумулятора і часто включає в себе інтелектуальні функції, такі як моніторинг Wi-Fi або інтеграція з генератором.
- Навантажувальна панель: Де перетворена енергія змінного струму розподіляється між електроприладами у вашому домі. У багатьох системах використовуються роздільні панелі для відокремлення критичних навантажень від другорядних.
Кожен компонент повинен бути правильно підібраний за розміром і встановлений, щоб забезпечити безпеку та ефективність. Невідповідність - наприклад, недостатній розмір інвертора або занадто великий масив панелей - може призвести до проблем з продуктивністю або виходу обладнання з ладу.
Чи може інвертор працювати без мережі?
Так, може, і в цьому вся суть автономного інвертора. Це питання задають багато людей, які вперше використовують сонячну енергію, особливо якщо вони звикли до мережевих систем, які вимикаються під час відключення електроенергії.
Ось у чому суть: автономні інвертори спеціально розроблені для роботи без підключення до електромережі. Вони генерують, керують і постачають електроенергію повністю незалежно. Ось як це відбувається:
- Автономна функціональність: Інверторна автономна система не залежить від зовнішнього сигналу мережі для роботи. Вона створює власну опорну частоту і напругу для внутрішньої стабілізації електроживлення.
- Залежність від батареї: Ці інвертори отримують енергію безпосередньо від підключеної акумуляторної батареї. Якщо сонячної енергії недостатньо, накопичений заряд акумулятора підтримує роботу.
- Підтримка генератора (опціонально): Багато автономних інверторів також можуть інтегруватися з резервними дизельними або газовими генераторами, забезпечуючи додатковий захист під час тривалих похмурих періодів або високого енергоспоживання.
Така автономна робота робить автономні сонячні системи ідеальними для віддалених районів, для забезпечення готовності до стихійних лих і для всіх, хто хоче звільнитися від залежності від комунальних послуг. У поєднанні з високоефективними сонячними панелями та інтелектуальними акумуляторними батареями автономний інвертор забезпечує повну енергетичну безпеку.
Пояснення типів сонячних інверторів
Автономний інвертор
Отже, що таке автономний інвертор? Це автономний пристрій, призначений для роботи незалежно від будь-якої електромережі. Зазвичай він потребує надійної акумуляторної батареї та інтелектуального управління для керування навантаженням, визначення пріоритетів для найважливіших приладів та оптимізації використання енергії.
Від живлення віддалених будиночків в австралійській глибинці до забезпечення роботи критично важливих систем під час ураганів у Флориді - автономні інвертори розроблені для забезпечення надійності.
Мережевий інвертор з прив'язкою до мережі
З іншого боку, у нас є мережеві інвертори. Вони працюють в гармонії з електромережею. Вони віддають надлишок сонячної енергії назад в мережу (мережевий облік) і беруть енергію, коли її не вистачає. Однак вони припиняють роботу під час відключення електроенергії, щоб захистити енергетиків.
Гібридний інвертор
A гібридний інвертор це своєрідний хамелеон - він може працювати як з мережею, так і без неї. Він розроблений для перемикання між сонячними, акумуляторними та мережевими джерелами, що робить його ідеальним для людей, які хочуть отримати найкраще з обох світів.
Що краще: Гібридний або автономний інвертор?
Це залежить від ваших цілей. Хочете повної незалежності? Обирайте автономний інвертор. Потрібна резервна копія під час відключень, але все ще підключена до мережі? Гібридний інвертор пропонує більшу гнучкість.
| Особливість | Автономний інвертор | Гібридний інвертор |
| Незалежність від мережі | Повний | Частково |
| Вартість | Помірний | Вище. |
| Складність | Помірний | Високий |
| Можливості резервного копіювання | Так. | Так. |
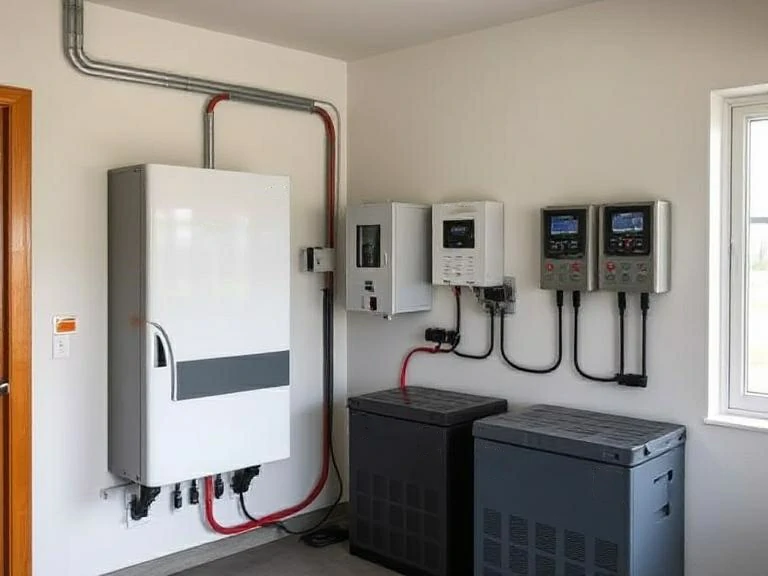

Вибір розміру мережевого інвертора для підвищення ефективності
Коли справа доходить до встановлення автономної сонячної системи, одним з найбільш важливих рішень є вибір правильного розміру мережевого інвертора. Занадто малий, і ви перевантажите його. Занадто великий - ви втратите гроші та ефективність. Правильний вибір розміру не тільки забезпечує надійність системи, але й максимізує рентабельність інвестицій та довгострокові енергетичні показники.
Який розмір інвертора мені потрібен для автономної сонячної системи?
Це одне з найпоширеніших і найважливіших питань для тих, хто планує сонячну інверторну систему, не прив'язану до електромережі.
Розмір вашого автономного інвертора повністю залежить від ваших потреб в енергії та способу життя. Ви живите невеликий будиночок з освітленням і міні-холодильником? Або ви керуєте повнорозмірним автономним будинком з побутовою технікою, насосами та опалювальними системами? Кожен випадок вимагає унікального підходу.
Крок 1: Розрахуйте ваші потреби в навантаженні
Почніть з переліку всіх приладів та електроніки, які ви плануєте живити, включаючи їхню потужність та щоденні години використання. Потім порахуйте:
Загальна кількість ват-годин на день = потужність приладу × години, використані за день
Складіть усі ваші пристрої, щоб отримати щоденне споживання енергії у ват-годинах (Вт-год). Наприклад:
| Прилад | Потужність | Години/день | Щоденне споживання (Вт-год) |
| Світлодіодні ліхтарі (x5) | 60W | 5 годин | 300 Вт |
| Холодильник. | 150W | 24 години | 3600 Вт |
| Ноутбук | 100W | 4 години | 400 Вт |
| Водяний насос | 800W | 1 год | 800 Вт |
Всього: 5 100 Вт-год/день
Крок 2: Визначте постійні та імпульсні навантаження
Інвертори оцінюються за їхньою тривалою потужністю та імпульсною потужністю. Багато приладів - особливо ті, що мають двигуни - під час запуску споживають більший імпульс.
Якщо для роботи водяного насоса потрібно 800 Вт, але під час запуску його потужність зростає до 1600 Вт, ваш автономний інвертор повинен витримувати таке пікове навантаження. Завжди розраховуйте інвертор так, щоб він витримував найбільшу сумарну потужність пристроїв, які можуть працювати одночасно.
Крок 3: Виберіть розмір інвертора
Після того, як ви знаєте свої пікові та безперервні навантаження, виберіть інвертор з номіналом, що трохи перевищує ваш максимальний безперервний попит. Наприклад:
- Інвертор потужністю 3 000 Вт для малих і середніх автономних будинків
- Інвертор потужністю 5 000 Вт - 8 000 Вт для постійних сімейних будинків або будинків з інтенсивним використанням електроприладів
Часто рекомендується включати буфер 20-30% понад розраховані потреби, щоб уникнути перевантаження автономного інвертора. Якщо ви плануєте розширення в майбутньому, краще зробити трохи більше зараз, ніж потім замінити інвертор.
Не забувайте про сумісність акумуляторів
Система автономного живлення інвертора також повинна відповідати напрузі акумуляторної батареї (наприклад, 24 В, 48 В). Системи з вищою напругою більш ефективні для великих установок і зменшують розмір кабелю та тепловтрати.
Оптимізація ефективності системи сонячних панелей за допомогою вибору розміру інвертора
Підбір розміру - це не тільки підбір інвертора до ваших приладів, а й його збалансування з масивом сонячних інверторів для максимального збору енергії та довговічності системи.
Як уникнути надмірного або недостатнього розміру інвертора
Згідно з дослідженнями, ефективність інвертора є найвищою, коли ваш масив сонячних панелей добре підібраний до потужності інвертора. Збільшення або зменшення розміру будь-якого з компонентів може зменшити вихідну потужність або спричинити знос.
- Малогабаритний інвертор: обмежує енергію, яку ви можете отримати з ваших панелей. У сонячні дні надлишкова сонячна енергія "відсікається" і витрачається даремно.
- Негабаритний інвертор: може працювати неефективно при низькому рівні сонячного світла і коштувати дорожче, ніж потрібно.
Для типової автономної інверторної системи намагайтеся вибрати такий розмір інвертора, щоб загальна потужність сонячних панелей становила від 100% до 130% від потужності інвертора. Такий підхід гарантує, що ваш інвертор досягне піку ефективності з середини ранку до початку дня, коли сонячне випромінювання є найсильнішим.
Врахування сезонної мінливості
Правильно підібраний автономний інвертор повинен враховувати похмурі дні, роботу взимку та різні потреби в енергії. Використання інструментів моніторингу сонячної енергії або енергоаудиту допоможе точно налаштувати вашу систему для цілорічної надійності.
Наприклад, якщо влітку ви використовуєте кондиціонер, а взимку - дров'яну піч, то літнє навантаження на інвертор буде значно вищим. Дещо збільшивши розмір мережі інвертора для таких пікових навантажень, ви не будете відчувати дефіцит електроенергії.
Реальний приклад
Сім'я з Квінсленду, яка має автономний будинок, використовує автономний інвертор потужністю 5,5 кВт у парі з сонячними панелями потужністю 7 кВт і літієвою батареєю ємністю 20 кВт-год. Інвертор розрахований на велике вечірнє навантаження (приготування їжі, розваги, насоси для гарячої води), а великі розміри панелей забезпечують достатню генерацію навіть у частково хмарні дні.
Моніторинг та коригування
Сучасні мережеві інвертори часто оснащені інтелектуальними системами моніторингу. Ці інструменти надають дані в режимі реального часу про генерацію, споживання та стан акумулятора. Використовуйте ці дані, щоб регулювати навантаження, виявляти неефективність і переконатися, що ваша система продовжує відповідати вашим потребам у міру їхнього розвитку.
Вдумливо підбираючи розмір сонячного інвертора та належним чином інтегруючи його з сонячними панелями, акумуляторною батареєю та очікуваним навантаженням, ви не просто оптимізуєте продуктивність - ви інвестуєте в надійне, стале енергетичне майбутнє. Незалежно від того, чи забезпечуєте ви енергією заміський будинок на вихідних, чи живете повністю автономно, вибір правильного розміру автономного інвертора - одне з найвпливовіших рішень, яке ви коли-небудь приймали.
Термін служби та обслуговування автономних інверторів
При розробці або інвестуванні в довгострокове енергетичне рішення розуміння вимог до довговічності та обслуговування автономного інвертора так само важливо, як і вибір правильного розміру або конфігурації. Хоча сучасна технологія автономних інверторів створена для надійного та безперервного використання, вона не є невразливою. Як і будь-який інший важливий компонент енергосистеми, вона потребує регулярного догляду та розумного планування, щоб витримати і перевищити очікуваний термін служби.
Який термін служби автономного інвертора?
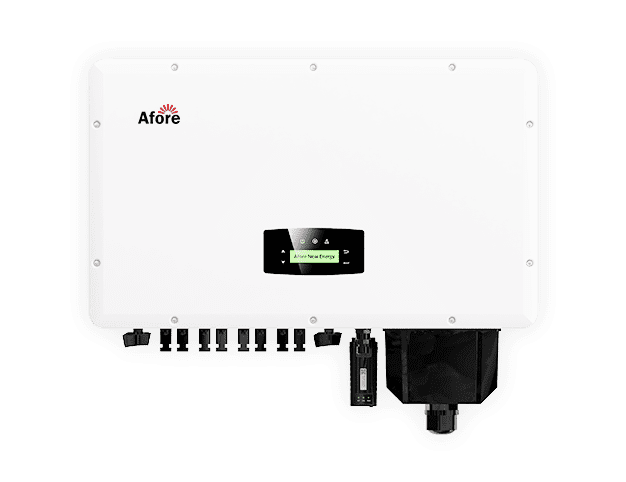
В середньому, високоякісний автономний інвертор працює від 8 до 15 років, залежно від бренду, умов використання, вимог до навантаження та практики технічного обслуговування. Деякі з найвідоміших виробників, такі як Afore, розробляють свої інвертори так, щоб вони витримували суворі умови, характерні для щоденної їзди на велосипеді та відключення інвертора від мережі.
Але не всі інвертори однакові. Існують фактори, які суттєво впливають на термін служби інвертора:
1. Якість виготовлення
Сонячні інвертори преміум-класу часто мають вищу ціну, але додаткова вартість відображає кращі внутрішні компоненти, кращі системи охолодження і більш надійне програмне забезпечення. Наприклад, інвертори Afore виготовляються з використанням компонентів промислового класу для кращої термостійкості та стійкості до перенапруги, що робить їх ідеальними для використання поза мережею.
2. Умови навколишнього середовища
Спека, пил і волога - тихі вбивці будь-якого автономного інвертора. У тропічному або пустельному середовищі термін служби інверторів може скоротитися на кілька років, якщо системи не захищені від екстремальних температур або накопичення частинок. Особливому ризику піддаються зовнішні установки, особливо в невентильованих шафах, якщо вони не захищені належним чином.
3. Схеми навантаження та цикли використання
Щоденна робота автономного інвертора майже на максимальній номінальній потужності створює постійне навантаження на систему. Подібно до надмірного збільшення обертів двигуна, постійне виведення інвертора за межі його зони комфорту - особливо в години пікового навантаження - може значно скоротити термін його експлуатації.
4. Сумісність з акумуляторними системами
Невідповідність між напругою інвертора та акумулятора або хімічним складом (наприклад, використання інвертора, призначеного для свинцево-кислотних акумуляторів, з літій-іонними батареями) може призвести до нестабільної зарядки або пошкодження будь-якої з систем. Правильна інтеграція та моніторинг гарантують, що і батарея, і інвертор старіють відповідно до запланованих темпів.
5. Обслуговування та оновлення прошивки
Навіть найнадійніші сонячні інверторні системи потребують періодичних перевірок. Застаріле програмне забезпечення, засмічені ребра охолодження або корозія клем - все це може призвести до передчасного виходу з ладу. Багато сучасних автономних інверторів пропонують дистанційну діагностику або моніторинг за допомогою додатків - скористайтеся цими інструментами.
Коротше кажучи, якщо ви працюєте в помірному кліматі, в межах проектних навантажень і виконуєте базове технічне обслуговування, ви можете розраховувати на те, що ваш автономний інвертор буде надійно служити вам більше десяти років.
Поради щодо продовження терміну служби інвертора
Хоча довговічність інвертора частково залежить від конструкції та навколишнього середовища, значна частина залежить від вас. Ось перевірені на практиці поради, які допоможуть продовжити термін служби вашого інвертора в автономному режимі та отримати максимальну віддачу від ваших інвестицій.
1. Встановлюйте в прохолодному, сухому, добре провітрюваному місці
Спека - ворог #1 для електронних пристроїв. Завжди встановлюйте автономний інвертор у затіненому, захищеному місці - бажано в приміщенні або у спеціальній стійкій до атмосферних впливів шафі. Уникайте гаражів, які досягають надмірних літніх температур, якщо у вас немає достатнього потоку повітря.
Якщо ви встановлюєте обладнання на відкритому повітрі, обирайте всепогодні корпуси з вбудованою вентиляцією або матеріалами, що розсіюють тепло. Розгляньте можливість використання пасивного охолодження або невеликих вентиляторів для забезпечення потоку повітря в умовах спекотного клімату.
2. Підтримуйте чистоту навколишнього середовища
Пил і волога можуть накопичуватися всередині вентиляційних отворів та електронних компонентів, що призводить до перегріву або корозії. Регулярно оглядайте та очищайте зовнішню поверхню інвертора м'якою щіткою або повітрям низького тиску, щоб видалити накопичення.
Якщо ваш інвертор встановлено в сільськогосподарському або прибережному середовищі, де частинки повітря або солі можуть накопичуватися швидше, збільште частоту перевірок.
3. Регулярно контролюйте продуктивність системи
Сучасні автономні інвертори часто оснащені інтегрованими системами моніторингу або додатками, які в режимі реального часу показують вхідні та вихідні дані, стан акумулятора та коди помилок. Регулярний перегляд цих даних допомагає виявити невеликі проблеми до того, як вони перетворяться на загальносистемні збої.
Дійте на випередження: Раптове падіння напруги або попередження про перегрів повинні спонукати до негайного усунення несправностей. Раннє виявлення є ключовим.
4. Не перевантажуйте інвертор
Постійне використання інвертора на повну потужність скорочує термін його служби. Проектуйте систему з запасом міцності - в ідеалі, щоденне споживання енергії має становити близько 70-80% від безперервного номіналу вашого інвертора.
Слідкуйте за імпульсними навантаженнями, особливо від таких пристроїв, як холодильники, насоси та електроінструменти. Якщо ви сумніваєтеся, подумайте про сонячний інвертор з більшою потужністю або розподіліть навантаження між двома інверторами для більших систем.
5. Оновлення мікропрограми та програмного забезпечення за потреби
Багато нових моделей мережевих інверторів постачаються з оновлюваною прошивкою. Виробники регулярно випускають оновлення для виправлення помилок, підвищення продуктивності та покращення сумісності системи. Кожні 6-12 місяців перевіряйте наявність оновлень на порталі підтримки виробника або у свого інсталятора.
6. Підтримуйте належну синхронізацію акумуляторів та інверторів
У міру старіння або зміни акумуляторної батареї (наприклад, заміни AGM на літій-іонну) переконайтеся, що система автономного живлення інвертора налаштована відповідним чином. Профілі заряду та напруги відсікання повинні відповідати один одному, щоб уникнути пошкодження будь-якого з компонентів. Використання акумуляторного інвертора, який підтримує програмовані налаштування, полегшує цей процес.
7. Заплануйте періодичне професійне обслуговування
Навіть якщо вам зручно виконувати базові перевірки, щорічна перевірка вашої системи професіоналом гарантує, що такі речі, як заземлення, герметичність кабелів, температурні показники та захист від перенапруги, функціонують належним чином.
Поради з реального світу: Профілактика важливіша за ремонт
Багато проблем з інверторами, які призводять до передчасної заміни, можна було б запобігти за допомогою простого моніторингу та контролю навколишнього середовища. Як поділився один досвідчений інсталятор з Afore: "Найбільший вбивця інверторів, якого ми бачимо? Спека, пил і недбалість. Захищайте його, стежте за ним, і він переживе ваші батареї".
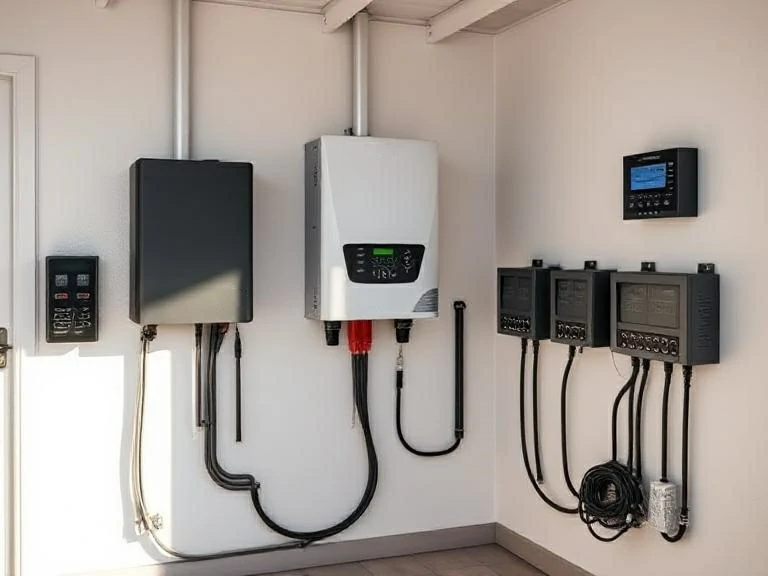

Основні переваги та обмеження автономних інверторів
Вибір автономного інвертора - це не просто технічне рішення, це стратегічне рішення. Хоча ці системи пропонують величезну автономність і гнучкість, вони також мають певні компроміси. Незалежно від того, чи будуєте ви новий автономний будинок, чи модернізуєте існуючу систему, чи вивчаєте питання енергетичної незалежності, дуже важливо зважити обидві сторони рівняння.
Переваги
Почнемо з переваг - адже при правильній реалізації автономний інвертор відкриває світ можливостей, недосяжних для традиційних систем, підключених до електромережі.
1. Повна енергетична незалежність
Однією з найвагоміших причин, чому люди звертаються до автономних інверторів, є свобода, яку вони пропонують. Ви більше не залежите від електромережі, підвищення тарифів або відключень електроенергії. З правильно підібраною сонячною системою та акумуляторною батареєю ви можете жити повністю автономно. Це душевний спокій, який не може запропонувати жодне прив'язане до електромережі рішення.
2. Надійне живлення у віддалених місцях
У сільських або ізольованих районах, де доступ до електромережі ненадійний або взагалі відсутній, сонячний інвертор, налаштований на автономне використання, часто є єдиним практичним рішенням. Від гірських будиночків у Колорадо до ферм у Західній Австралії, автономні інверторні системи живлять будинки, колодязі та необхідне обладнання чистою, відновлюваною енергією.
3. Резервне живлення під час відключень
Навіть у заміських умовах автономний інвертор може слугувати потужним резервним джерелом живлення. На відміну від прив'язаних до електромережі систем, які вимикаються під час відключень, автономний інвертор продовжує працювати, споживаючи енергію з резерву акумулятора, щоб підтримувати роботу критично важливих навантажень. Для будинків з медичним обладнанням або підприємств, які не можуть дозволити собі простої, це суттєво змінює правила гри.
4. Екологічна стійкість
Поєднання автономного інвертора з системою сонячних панелей дозволяє генерувати екологічно чисту електроенергію без шкідливих викидів. Ви зменшуєте свій вуглецевий слід, усуваєте залежність від викопного палива та робите свій внесок у більш стале майбутнє - особливо в поєднанні з літієвими або морськими акумуляторами, які менш токсичні та більш придатні для переробки, ніж старі хімічні речовини.
5. Масштабованість та модульність
Сучасні автономні інвертори дозволяють гнучко розширювати систему. Незалежно від того, чи починаєте ви з малого, чи плануєте зростання навантаження в майбутньому, ці системи підтримують модульне масштабування. Ви можете почати з декількох панелей і батарей, а потім додавати більше потужності в міру зростання ваших потреб в енергії - без заміни всієї системи.
6. Довгострокова економія коштів
Хоча початкові інвестиції вищі, ніж у прив'язаних до мережі систем, довгострокова економія може бути значною. Після встановлення автономна інверторна система виробляє "безкоштовну" електроенергію рік за роком. Не потрібно сплачувати рахунки за комунальні послуги, а належним чином обслуговуване обладнання може прослужити десятиліття і більше - що робить його розумною фінансовою грою для тих, хто думає про довгострокову перспективу.
Обмеження
Незважаючи на свої численні переваги, автономні інверторні системи не є ідеальними для всіх. Існують технічні, фінансові та логістичні міркування, які необхідно враховувати - особливо якщо ви переходите від залежності від мережі до повної енергетичної автономії.
1. Високі початкові інвестиції
Однією з найбільших перешкод для впровадження автономних інверторних систем є початкові витрати. На відміну від підключених до електромережі установок, які не потребують акумуляторів, перехід на автономне живлення означає інвестиції в акумуляторні батареї, високоякісний сонячний інвертор і додаткові компоненти, такі як контролери заряду і перемикачі. Хоча ціни падають, це все ще значні фінансові зобов'язання.
2. Обслуговування та заміна акумулятора
Акумуляторні батареї, особливо свинцево-кислотні, потребують постійного обслуговування. Навіть нові літій-іонні батареї з часом деградують і з часом потребують заміни, як правило, кожні 8-12 років. Неправильне заряджання, глибокі розряди або високі температури навколишнього середовища можуть скоротити термін служби акумулятора, що вплине на загальну надійність вашої інверторної системи поза мережею.
3. Обмеження щодо зберігання енергії
Сонце не світить 24 години на добу 7 днів на тиждень, а ваш акумулятор має обмежену ємність. Під час тривалих похмурих періодів або більш інтенсивного, ніж очікувалося, використання, ви можете розрядити накопичену енергію. Без резервного генератора або достатньої кількості панелей це може призвести до дефіциту енергії - особливо взимку або за поганих погодних умов.
4. Складність системи
Автономна інверторна система складніша, ніж просте рішення, що підключається до мережі за принципом "підключи і працюй". Вам потрібно розуміти управління навантаженням, хімічний склад акумуляторів, конструкцію сонячних батарей та системну інтеграцію. Хоча багато сучасних систем є простими у користуванні, самостійна збірка без досвіду може призвести до дорогих помилок або небезпечних налаштувань.
5. Вимоги до простору
Батареї, інвертори та супутнє обладнання потребують фізичного простору та належної вентиляції. Якщо ви живете в компактному будинку або пересувній установці (наприклад, фургоні або крихітному будиночку), вам потрібно подумати про те, де ці компоненти будуть безпечно розміщені. Погане розташування або недостатня вентиляція можуть призвести до перегріву або проблем з продуктивністю.
6. Відсутність переваг нетто-обліку
Коли ви перебуваєте поза мережею, у вас немає можливості продавати надлишок сонячної енергії назад в енергосистему за допомогою мережевого обліку - перевага, яку часто використовують прив'язані до мережі системи для зниження щомісячних рахунків. Замість цього ви повинні використовувати, зберігати або перенаправляти всю сонячну енергію. Це означає більшу увагу до балансу системи та енергоефективності.
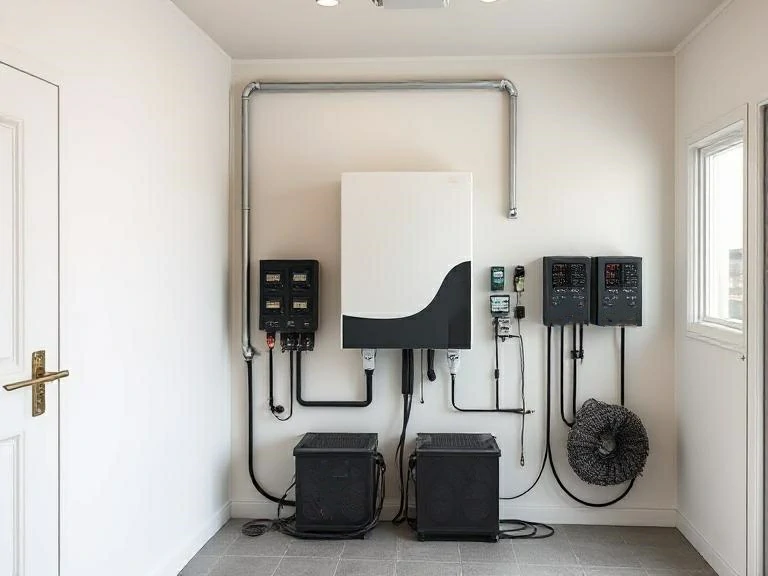

Посібник з купівлі: Як правильно вибрати мережевий інвертор
Вибір мережевого інвертора - це не просто вибір першого-ліпшого продукту з пристойною ціною, це стратегічна інвестиція, яка безпосередньо впливає на вашу енергонезалежність, надійність системи та довгострокову економію. Оскільки на ринку представлені десятки моделей, вибір правильної моделі для вашої автономної системи вимагає ретельного вивчення технічних характеристик, сертифікатів безпеки та сумісності з вашими сонячними панелями та акумуляторами.
У цьому посібнику з купівлі ви знайдете інформацію про те, на що слід звертати увагу при виборі високоякісного автономного інвертора, включаючи обов'язкові функції та галузеві сертифікати, які гарантують продуктивність і безпеку. Незалежно від того, чи забезпечуєте ви енергією віддалений будиночок, будинок, який постійно знаходиться поза мережею, або автофургон, вибір правильного сонячного інвертора має вирішальне значення для успіху та безпеки вашої інверторної системи, що працює поза мережею.
Важливі функції, на які слід звернути увагу
Якісний мережевий інвертор повинен бути не просто функціональним - він повинен бути ефективним, довговічним та інтелектуальним. Ось ключові характеристики, на які слід звертати увагу при порівнянні моделей:
1. Вихід чистої синусоїди
Це не підлягає обговоренню для будь-якої серйозної автономної установки. Інвертори з чистою синусоїдою виробляють плавну, стабільну хвилю, яка точно відтворює мережеву енергію. Це важливо для роботи чутливої електроніки, такої як ноутбуки, холодильники, пральні машини та медичне обладнання, без ризику пошкодження.
Модифіковані синусоїдальні інвертори дешевші, але можуть викликати проблеми з двигунами, скоротити термін служби приладу і навіть створювати перешкоди для світлодіодного освітлення. Завжди обирайте чисту синусоїду в сонячному інверторі - особливо для домашніх систем.
2. Перенапруга (пікова) пропускна здатність
Багато приладів споживають значно більше енергії під час запуску, ніж під час роботи. Ваш автономний інвертор повинен витримувати такі перенапруги, не вимикаючись і не пошкоджуючи компоненти. Шукайте інвертор з перенапругою щонайменше 200% (наприклад, інвертор потужністю 3000 Вт повинен витримувати перенапругу 6000 Вт протягом декількох секунд).
3. Напруга акумулятора та сумісність
Переконайтеся, що модель інвертора, що працює від мережі, відповідає напрузі вашої акумуляторної батареї (12, 24, 48 або вище). Інвертори, призначені для літій-іонних акумуляторів, часто мають розширені функції керування акумулятором, такі як настроювані профілі заряду та відключення низької напруги, що є критично важливими для здоров'я та ефективності акумулятора.
Деякі мережеві інвертори преміум-класу сумісні з гібридними пристроями, тобто вони можуть легко перемикатися між живленням від акумулятора, сонячної батареї і навіть генератора. Якщо ви плануєте розширити або інтегрувати резервні джерела, така гнучкість є безцінною.
4. Вбудований контролер заряду MPPT (опція)
Деякі автономні інвертори "все в одному" оснащені вбудованим контролером заряду сонячних панелей з відстеженням точки максимальної потужності (MPPT). Це дозволяє отримувати більше енергії від сонячних панелей і спрощує установку. Хоча це не є обов'язковим (особливо у великих системах з окремими контролерами заряду), це бонус для малих і середніх систем, де простір і простота проводки мають значення.
5. Інтелектуальний моніторинг та підключення
Сучасні сонячні інвертори мають вбудовані РК-екрани, додатки Bluetooth або Wi-Fi. Ці функції дозволяють відстежувати виробництво і споживання енергії, стан акумулятора, журнали помилок і багато іншого - з телефону або комп'ютера. Для серйозних користувачів, які працюють поза мережею, діагностика в режимі реального часу може запобігти простою і виявити проблеми з продуктивністю на ранніх стадіях.
6. Механізм охолодження
Перегрів скорочує термін служби інвертора. Шукайте моделі з ефективним пасивним охолодженням (радіатори) або тихими вентиляторами з логікою терморегулювання. Система охолодження повинна відповідати умовам середовища, в якому буде встановлений ваш автономний інвертор - особливо в жарких або закритих приміщеннях.
7. Паралельна або модульна конструкція (на вибір)
Плануєте розширення? Деякі автономні інвертори є стековими або модульними, що дозволяє вам додавати блоки паралельно в міру зростання ваших потреб в енергії.
8. Інтеграція генератора
Якщо ви живете в регіоні з довгими похмурими сезонами або підвищеним зимовим навантаженням, обирайте інвертор, який забезпечує плавне перемикання на резервний генератор. Це запобігає надмірному розрядженню акумуляторів і підтримує роботу основних систем при низькому рівні сонячної енергії.
Сертифікація та стандарти безпеки
Надійний мережевий інвертор повинен відповідати суворим стандартам безпеки та якості - не тільки для продуктивності, але й для захисту вашого будинку та сім'ї. Ось на що слід звернути увагу:
1. UL 1741 (США)
Ця сертифікація гарантує, що інвертор відповідає стандартам електробезпеки і може безпечно працювати з акумуляторами та сонячними батареями. Навіть для автономних систем сертифікація UL свідчить про те, що продукт пройшов ретельне тестування на безпеку.
2. Відповідність стандарту IEEE 1547
Хоча це більш актуально для мережевих систем, багато сонячних інверторів високого класу мають подвійну номінальну потужність і все ще дотримуються цього стандарту. Це гарантує, що інвертор може безпечно керувати напругою, частотою та захистом від острівного замикання - ознака якості та надійної внутрішньої архітектури.
3. Знак CE (Europe & International)
Маркування CE означає, що інвертор відповідає європейським нормам безпеки, охорони здоров'я та захисту навколишнього середовища. Це важливо для систем, встановлених в Європі або придбаних у міжнародних виробників.
4. IEC 62109-1/-2
Цей глобальний стандарт застосовується безпосередньо до автономних інверторних систем і засвідчує, що вони безпечні для кінцевих користувачів та інсталяторів. Він стосується захисту від ураження електричним струмом, зменшення пожежної небезпеки та механічної міцності.
5. AS/NZS 4777 (Австралія та Нова Зеландія)
Якщо ви встановлюєте систему в Австралії, зверніть увагу на цей сертифікат. Він підтверджує, що модель інвертора з автономним живленням відповідає вимогам взаємодії з місцевою електромережею та вимогам безпеки - навіть якщо ви не під'єднані до електромережі.
6. Рейтинг IP (захист від проникнення)
Це особливо важливо для інверторів, встановлених на відкритому повітрі або в запиленому середовищі. Ступінь захисту IP65 або вище гарантує, що ваш автономний інвертор захищений від пилу та струменів води під низьким тиском, що збільшує термін його служби на роки.
Остання порада: Завжди вимагайте документацію або технічні паспорти від постачальника або інсталятора, щоб перевірити ці сертифікати. Поважні виробники з гордістю надають сертифікаційні номери та результати лабораторних випробувань. Якщо ви не можете їх перевірити - відмовтеся.

Висновок
Якщо ви шукаєте справжню енергетичну незалежність, стійкість під час відключень або живлення віддаленого місця, то інвертор з вимкненою мережею це не просто інструмент - це рятівне коло. Ці системи дають вам свободу контролювати використання енергії, зменшити залежність від електромережі та зробити свій вибір на користь сталого майбутнього.
Незалежно від того, чи плануєте ви свій перший автономний проект, чи модернізуєте існуючу систему, вибір правильного автономного інвертора має велике значення. Не поспішайте, зробіть розрахунки та інвестуйте в якість. Тому що, коли мережа вийде з ладу, ви все одно будете працювати - завдяки вашому автономному інверторному рішенню.
ПОШИРЕНІ ЗАПИТАННЯs
1. Чи може інвертор працювати без мережі?
Так, безумовно. Автономний інвертор спеціально розроблений для роботи незалежно від підключення до електромережі. На відміну від мережевих інверторів, які покладаються на мережу і вимикаються під час відключення електроенергії, сонячний інвертор, налаштований на автономне використання, генерує і постачає електроенергію повністю самостійно.
Він отримує енергію безпосередньо від акумуляторів або сонячних панелей і виробляє власну частоту та напругу для роботи побутових приладів. Саме це робить автономний інвертор ідеальним для віддалених місць, енергетичної самодостатності та готовності до надзвичайних ситуацій.
2. Що таке автономний інвертор?
Автономний інвертор - це тип сонячного інвертора, який перетворює електроенергію постійного струму (від сонячних панелей або акумуляторних батарей) в корисну електроенергію змінного струму для дому та обладнання - без необхідності підключення до мережі.
Він слугує центральним вузлом інверторної автономної системи, керуючи потоком енергії від сонячних панелей, регулюючи заряджання та розряджання акумуляторів і забезпечуючи стабільну напругу в домашніх мережах. В автономних системах цей інвертор необхідний для забезпечення вашого життя електроенергією 24/7, незалежно від того, чи є поблизу лінія електропередач.
3. Який термін служби автономного інвертора?
Високоякісний автономний інвертор зазвичай служить від 8 до 15 років, залежно від марки, умов експлуатації та практики обслуговування. Afore виробляє якісні інвертори, які зберігають тривалий термін служби і довговічність навіть у суворих умовах експлуатації.
На термін служби інвертора впливають кілька факторів, зокрема:
- Щоденні навантаження та обробка перенапруг
- Вентиляція та охолодження
- Вплив пилу, тепла та вологи
- Обслуговування прошивки та оновлення програмного забезпечення
При належному догляді автономний інвертор, що обслуговується належним чином, може надійно служити більше десяти років, часто навіть довше, ніж сама акумуляторна батарея.
4. Який розмір інвертора мені потрібен для автономної сонячної системи?
Розмір мережевого інвертора повинен відповідати вашому енергоспоживанню, з достатнім запасом на випадок стрибків напруги та майбутнього розширення. Ось короткий посібник:
- Невеликі кабіни або автофургони: інвертор потужністю від 1000 до 2000 Вт
- Середній автономний будинок: Інвертор потужністю від 3000 Вт до 5000 Вт
- Великі системи: 6000 Вт - 8000 Вт або вище, особливо для одночасного живлення декількох великих приладів
Ви повинні розрахувати загальне щоденне споживання ват-годин, врахувати пікові навантаження (наприклад, насоси або холодильники) і переконатися, що ваш автономний інвертор може впоратися як з безперервним, так і з імпульсним навантаженням.
Також переконайтеся, що ваш інвертор відповідає напрузі акумуляторної батареї (12, 24 або 48 В). Системи, що працюють на 48 В, як правило, ефективніші для великих об'єктів і дозволяють використовувати більш тонкі дроти та зменшити втрати.
5. У чому різниця між автономним та мережевим інвертором?
Основна відмінність полягає в тому, як кожен інвертор взаємодіє з електромережею:
| Особливість | Автономний інвертор | Мережевий інвертор |
| Потрібна інженерна мережа | Ні. | Так. |
| Роботи під час відключень електроенергії | ✅ Так (з батарейками) | Ні. |
| Потрібна батарея | Так. | ❌ Необов'язково |
| Можливість експорту електроенергії в мережу | Ні. | ✅ Так (за допомогою лічильника нетто) |
| Ідеальний варіант використання | Віддалені будинки, енергонезалежність | Міські сонячні будинки, економія від мережі |
Автономний інвертор призначений для повної автономії, в той час як мережевий сонячний інвертор залежить від комунальних служб для балансування попиту та пропозиції. Якщо вам потрібне резервне живлення або ви живете у віддаленому місці, автономний інвертор - кращий вибір.
6. Що краще, гібрид або автономний інвертор?
Це повністю залежить від ваших енергетичних цілей і місця розташування:
- Обирайте автономний інвертор, якщо: Ви повністю від'єднані від електромережі або хочете отримати повну енергонезалежність за допомогою акумуляторної батареї.
- Обирайте гібридний інвертор, якщо: Ви все ще підключені до електромережі, але хочете гнучко використовувати сонячну енергію, енергію від акумуляторів та енергію з мережі разом. Гібридні системи чудово підходять для зменшення рахунків за комунальні послуги, маючи при цьому певний рівень резервного живлення.
При цьому гібридні системи, як правило, коштують дорожче і складніші в установці. Якщо у вашому будинку або будиночку немає доступу до електромережі - або ви не хочете покладатися на неї - спеціальна інверторна автономна система, як правило, простіша, надійніша і спеціально створена для справжньої незалежності.